Introduction
General summary
"The organisational/activational concept of sexual differentiation of the brain arose from series of experiments begun in the 1950s showing that the central mechanisms organising sex-specific behaviours in males undergo defeminisation and masculinisation as a result of fetal testosterone secretion and action late in gestation and just after birth (...). These principles of sexual differentiation of the brain with regard to gender and sexual orientation apply to humans, as indicated by detailed brain morphological studies in the context of clinical history (...)."(Russell, John A. "Fifty Years of Advances in Neuroendocrinology." Brain and Neuroscience Advances 2 (2018): 2398212818812014.)
"There is broad evidence from across mammalian species which indicates that individual differences in prenatal exposure to sex hormonescreates individual differences in brain morphology, cognition, behavioral predispositions,and even life outcomes.They are typically studied in a sex differencesframework, but there is now enough evidence to suggest that sexual orientation differences along these parameters can also be robust and informative."
(Luoto, S. & Rantala, M. J. (in press). Female bisexuality. In T.Shackelford(Ed.), The Cambridge Handbook of Evolutionary Perspectives on Sexual Psychology. Cambridge University Press. (PrePrint))
"Animal studies on the effects of hormones have been conducted for over half a century and provide some of the clearest evidence for the role of various hormones in our bodies. In particular, manipulation of glands producing particular hormones can have startling effects on physical development as well as later behavior (e.g., [34, 40, 60, 61, 73]). Mammals have been widely studied, with castration (and subsequent reduction in the availability of gonadal hormones) a common early experiment. These experiments show that hormones are essential to the sexual differentiation of both the body and the brain (see Collaer and Hines [40] for a review). It has been recognized for a long time that castration of males during neonatal or prenatal life prevents the development of masculine genitalia, while administration of androgens to females masculinizes their genitalia [81]. Castrated males also usually show feminized neural development, cognition, and behavior; while females treated with androgen show masculinized neural development, cognition, and behavior. Similar experiments have been conducted in a wide range of mammals, comparing castrated males, normal males, normal females, and females treated with androgens on a range of sexually dimorphic features consistently demonstrating the importance of sex steroid hormones (testosterone in particular) in the development of the brain and behavior [6, 30, 61, 98, 139]. While the effects of testosterone on nonhuman mammal sexual behavior have been extensively studied, there is now increasing evidence that this and other hormones also have a substantial effect on aspects of human social and emotional
behavior."
(Auyeung, Bonnie, Michael V. Lombardo, and Simon Baron-Cohen. "Prenatal and postnatal hormone effects on the human brain and cognition." Pflügers Archiv-European Journal of Physiology 465, no. 5 (2013): 557-571.)
"High levels of prenatal testosterone exposure also impact infant cognitive, motor, and language development (Cho & Holditch-Davis, 2014)."(Cárdenas, Emilia F., Autumn Kujawa, and Kathryn L. Humphreys. "Neurobiological changes during the peripartum period: Implications for health and behavior." Social Cognitive and Affective Neuroscience (2019).)
"The field of behavioral neuroendocrinology has shown that the prenatal hormonal milieu of developing organisms bears a potentially causal relation to various adult behaviors in both humans and non-humans (Hines et al. 2004, Hines 2006, Balthazart & Adkins-Regan 2002, Balthazart 2011). Prenatal exposure to testosterone in humans influences various childhood behaviors, including the later adoption of stereotypically gendered behaviors (sometimes referred to as “sex roles”, “gender roles”, or “gender” more broadly, e.g., Ackerman 2019): For prenatal T on childhood behavior see Pasterski et al. (2005), Auyeung et al. (2009), Cohen-Bendahan et al. (2005), and Hines et al. (2016); for social learning of gender-related labels for objects as in toys that are “for girls” or “for boys” see Hines et al. (2016); for infant eye-contact Lutchmaya et al. (2002); and for lateralisation of certain cognitive functions Liu et al. (2017) and Manson (2008)."
(Hejná, M., Ackerman, L., & Wallenberg, J. C. (2020). Attention to People Like You: a proposal regarding neuroendocrine effects on linguistic variation. Journal of Biolinguistics.)
- prenatal testosterone has a significant organizing effect on the developing brain and "masculinizes" it. These changes are profound, pervasive and irreversible, and have significant effects on brain functioning and behavior
- throughout life, the effect of circulating testosterone is higher on "masculine" brains (high prenatal testosterone) than on "feminine" brains. In other words, administration of the same amount of testosterone to an adult with a masculine brain will have a more intense effect than administration of the same amount on an adult with a feminine brain
- the 2D:4D digit ratio (relative length of the 2nd or index finger compared to the 4th or ring finger) inversely correlates with levels of prenatal testosterone exposure. The lower the 2D:4D digit ratio, the higher the levels of prenatal testosterone the fetus was exposed to in the mother's womb
- the "femininity" or "masculinity" of the brain is in a certain sense independent of the chromosomal sex. While statistically speaking most biological females have a "feminine" brain (and a high 2D:4D ratio) and most biological males have a "masculine" brain (and a lower 2D:4D ratio), there are males with a "feminine" brain (and a high, "feminine" 2D:4D ratio) and females with a "masculine" brain (and a low, "masculin" 2D:4D ratio)
How testosterone secretly shapes our society (video)
A popularized but interesting documentary on the influence of testosterone on (social) behavior.
Scientific overviews and general considerations
Influence of testosterone on social behavior and status (overview)
"For human and non-human primates, testosterone is thought to play a role in advancing and maintaining status by encouraging ‘dominance behaviour’, which aims to enhance one's status compared to competitors (Mazur, 1985; Archer, 2006). While early work focused on aggression in dominance behaviour (Mazur and Booth, 1998), recent work suggests that in humans, testosterone plays a more nuanced role in status promotion, by encouraging either aggressive or prosocial behaviour depending on the context (Dreher et al., 2016; Carre and Archer, 2018). Moreover, researchers now recognise human aggression as something which can take ‘purely psychological or even economic forms, rather than being overtly violent’ (Eisenegger et al., 2011). Supporting the idea that testosterone is conducive to ‘economic aggression’, experimental work has found positive associations between testosterone and financial risk taking (Cueva et al., 2015; Nofsinger et al., 2018; Mehta et al., 2015), although null associations are also reported (Apicella et al., 2015). There is evidence that these behavioural implications could extend beyond the laboratory, potentially with relevance to longer-term socioeconomic position. A study of male executives found higher testosterone was associated with having more subordinates (Sherman et al., 2016), while other studies find that testosterone in men is associated with self-employment, a ‘riskier’ strategy than standard employment (Greene et al., 2014; Nicolaou et al., 2018), although null associations with self-employment have also been reported (van der Loos et al., 2013). Studies of male financial traders report that daily profits were predicted by morning testosterone (Coates and Herbert, 2008) and 2D:4D ratio, believed to reflect prenatal testosterone exposure (Coates et al., 2009), with authors explaining these positive associations of testosterone and profits as a function of greater risk tolerance (Coates and Gurnell, 2017). If riskier behaviour can lead to better financial outcomes, this raises the possibility of cumulative influence on long-term social position via wealth (Stanton, 2017). However, behavioural attributes which make one a successful financial trader may not be beneficial in other professions, and whether testosterone is more widely conducive to financial success is not clear. Two recent papers examined this by looking at plausible indicators of in utero testosterone exposure (2D:4D ratio, or sex of a twin) in relation to earnings in adulthood. One found that lower 2D:4D ratio, thought to correspond to high in utero testosterone, predicted greater wages for men and women. However, there was some evidence of nonlinear effects (Nye et al., 2017). The other found that male sex of the twin (corresponding to greater prenatal testosterone exposure) predicted higher earnings for men but lower earnings for women (Gielen et al., 2016)."
(Hughes, Amanda, and Meena Kumari. "Testosterone, risk, and socioeconomic position in British men: Exploring causal directionality." Social Science & Medicine (2018).)
And as almost always in science, some studies caution to not jump to conclusions, since results are sometimes mixed:
To be noted in another study:
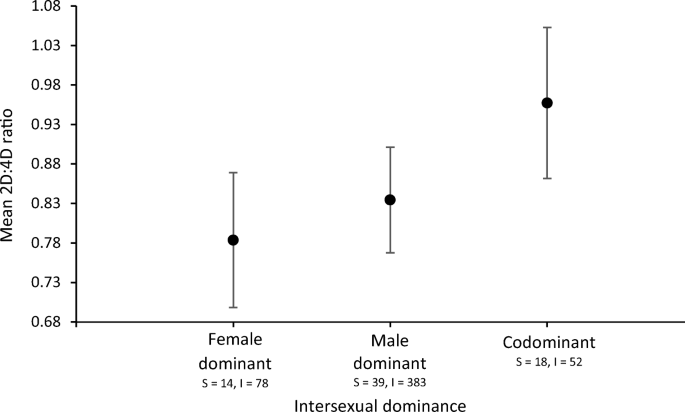
Criticism
It should be noted that the relation between 2D:4D ratio and social behavior is to some extent context-dependent (eg. dependent on the subjective well-being, current social status, etc. of the individual).And as almost always in science, some studies caution to not jump to conclusions, since results are sometimes mixed:
"Studies in hard sciences of the relationship between direct measures of prenatal exposure to testosterone and 2D:4D find mixed results, whose sign and significance seem to depend critically on whether direct measures are obtained in an early stage in utero or, instead, close to the birth. Studies in social sciences on the relationship between 2D:4D and decision-making find mixed results that may depend on the accuracy of 2D:4D measurement and, in addition, to the experimental tasks used to elicit subjects' preferences. Overall, this suggests both that additional research is awaited to reconcile existing differences across studies in the literature and that caution is used in the interpretation of results before these differences are better understood."(Alonso, Judit, Roberto Di Paolo, Giovanni Ponti, and Marcello Sartarelli. "Facts and Misconceptions about 2D: 4D, Social and Risk Preferences." Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience 12 (2018): 22.)
Digit ratio, an indicator to the world within
The 2018 study "Digit Ratio: An Indicator to the World Within" gives an overview of the relationship between various physical and psychological aspects of personality and digit ratio through a review of existing literature.
In this study, the following traits and characteristics are linked to the 2D:4D digit ratio:
- Academic success (Romano et al., 2006 - higher 2D:4D correlates with higher examination marks in men, not women)
- Athletic ability (Manning and Taylor, 2001 - low 2D:4D correlates with higher athletic ability)
- Attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (Martel et al., 2008 - low 2D:4D correlates with higher incidence of ADHD)
- Autism (de Bruin et al., 2006 - Autism/Asperger, ADHD/ODD, PDD linked to low 2D:4D ratio; anxiety disorder to high 2D:4D)
- Cooperative behaviour (Millet and Dewitte, 2006 - relation between 2D:4D ratio and social behaviour is context dependent and not linear)
- Disordered eating (Klump et al., 2006 - more eating disorders in women with higher 2D:4D ratio; Smith et al., 2010 - more eating disorders in men with higher 2D:4D ratio)
- Fertility (Manning et al., 2000 - higher reproductive success for men with low 2D:4D and women with high 2D:4D, and for couples where the woman has higher 2D:4D than the man)
- Gender-identity (Wallien et al., 2008 - women with gender identity disorder have lower 2D:4D)
- Gender-typical play (Alexander, 2006 - male infants with higher androgen levels have stronger preferences for male-typical stimuli; Burton et al., 2009 - male-typical behavior (agression, play style) in children associated with lower 2D:4D ratio)
- Pain perception (Keogh et al., 2007 - women with higher 2D:4D ratio have higher pain threshold)
- Personality (Fink et al., 2004 - weak correlations between 2D:4D ratio and 'big five' personality traits in women; Hampson et al., 2008 - lower 2D:4D ratios associated with increased aggressiveness and sensation seeking in both sexes; Loehlin et al., 2009)
- Psychological femininity and masculinity (Scarbrough and Johnston, 2005 - low 2D:4D women are less "feminine", prefer more masculinized long-term mates, and report shorter intimate relationships, less parental bonding and more menstrual irregularity)
- Schizotypal personality disorder (Walder et al., 2006 - higher 2D:4D associated with schizotypal personality disorder in men)
- Sensation seeking (Fink et al., 2006 - low 2D:4D ratio linked to sensation seeking in men)
- Sex role identity (Csatho et al., 2003 - Low 2D:4D ratio associated with more masculine sex-role identity in women)
- Sex-biased diseases (Manning and Bundred, 2000 - Possible association between 2D:4D ratio and infertility, autism, dyslexia, migraine, stammering, immune dysfunction, myocardial infarction and breast cancer; Manning et al. 2001 - low 2D:4D ratio in autism/Asperger subjects)
- Sexual orientation (Rahman and Wilson, 2003 - low 2D:4D associated with homosexuality in males and females)
- Social behaviours (Breedlove, 2010 - androgens act early in life to masculinize various human behaviors; Coates et al., 2009 - high prenatal androgens promote financial success among traders)
- Social cognition (Williams et al., 2003 - low 2D:4D related to hyperactivity and poor social cognitive function in girls, and high 2D:4D with emotional symptoms in boys)
- Spatial ability (Kempel et al., 2005 - females with low 2D:4D perform better on spatial and numerical ability tests)
- Spatial performance on visual tasks (Manning & Taylor, 2001 - higher mental rotation scores for men with lower 2D:4D)
- Sporting ability (Manning and Taylor, 2001 - low 2D:4D correlates with higher sporting ability)
- Verbal ability (Luxen & Buunk, 2005 - low 2D:4D associated with low verbal intelligence, high numerical intelligence, and low agreeableness)
(Khurana, Tanvi, Tanuja Jukariya, and Suman Singh. "Digit Ratio: An Indicator to the World Within." (2018).)
2D:4D digit ratio and prenatal androgens (overview 2015)
"There have been numerous studies done about the relationship between this 2D:4D ratio and androgen exposure during fetal development. The relative length of the fingers is established early in the gestation period, with the general ratios determined by the thirteenth week (6). Hox genes regulate the development of the digits, and different testosterone levels affect these genes (7). Free testosterone undergoes an androgen receptor-mediated mechanism to indirectly modify the Hox genes during development (8). These receptors are more prevalent in the fourth digit (9), so high levels of
testosterone would likely cause the fourth digit to be longer than the second. This causes a low 2D:4D ratio, and is just one item of many that supports the conclusion that males tend to have a lower 2D:4D ratio than females (as they typically experience higher levels of free testosterone in the womb). Therefore, digit proportions are altered by testosterone in utero.
A study following digit development of fetuses found that not only is this digit ratio determined in utero, but also, like previously suggested, males tend to have a lower 2D:4D than females (10). This continues to indicate that a low 2D:4D ratio (index finger shorter than ring finger) means a person was exposed to more androgens in utero than someone with a higher ratio. This is further confirmed by research in which amniotic fluid is studied to see fetal testosterone and estradiol levels. Then, once the children turn two, their digit ratios are measured. Results show that individuals with low 2D:4D
ratios have high fetal testosterone in relation to their fetal estradiol levels, and those with a high digit ratio have low fetal testosterone and high fetal estradiol (11). This negative association between fetal testosterone/fetal estradiol and the 2D:4D ratio further suggests that prenatal exposure to androgens affects digit length development."
6. Garn, S. M., Burdi, A. R., Babler, W. J., & Stinson, S. (1975). Early prenatal attainment of adult metacarpal-phalangeal rankings and proportions. American Journal of Physical Anthropology,
43(3), 327-332. doi:10.1002/ajpa.1330430305
7. Manning, J. T., Scutt, D., Wilson, J., & Lewis-Jones, D. I. (1998). The ratio of 2nd to 4th digit length: A predictor of sperm numbers and concentrations of testosterone, luteinizing hormone and
oestrogen. Human Reproduction (Oxford, England), 13(11), 3000-3004.
8. Quigley, C. A., De Bellis, A., Marschke, K. B., el-Awady, M. K., Wilson, E. M., & French, F. S. (1995). Androgen receptor defects: Historical, clinical, and molecular perspectives. Endocrine
Reviews, 16(3), 271-321.
9. Manning, J., Kilduff, L., & Trivers, R. (2013). Digit ratio (2D:4D) in Klinefelter's syndrome. Andrology, 1(1), 94-99.
10. Malas, M. A., Dogan, S., Evcil, E. H., & Desdicioglu, K. (2006). Fetal development of the hand, digits and digit ratio (2D:4D). Early Human Development, 82(7), 469-475. doi:10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2005.12.002
(Nick Lehan & Kayla Smith, "2D:4D Digit Ratio: Indicator of Sports and Gaming Participation in Males", Xavier Journal of Undergraduate Research, vol. 3, 2015, Complete Print edition, pp.31-45)
Low 2D:4D digit ratio linked to general masculinisation effect
"Prenatal androgen exposure can be approximated non-invasively, by measuring the second-to-fourth digit (2D:4D) ratio(46). While the early foundations of the 2D:4D approach to prenatal testosterone exposure relied heavily on correlational inference (e.g., sexually dimorphic 2D:4D ratios, cord blood measures), Zheng and Cohn(47) demonstrated the developmental and molecular pathways of the association between prenatal testosterone exposure and the 2D:4D ratio in a mouse model. Moreover, several studies have found that a direct manipulation of prenatal androgen levels, or a manipulation of the binding potential of prenatal androgens with the receptors of the embryo(s) leads to differences in adult 2D:4D ratios in the predicted directions in both mice and rats(48,49,50). However, it has remained controversial whether 2D:4D is mainly determined by prenatal testosterone, or by a balance of prenatal testosterone relative to prenatal estrogen(46), and effects as well as effect sizes in relation to other investigated traits are currently still debated.(Horn, Lisa, et al. "Social status and prenatal testosterone exposure assessed via second-to-fourth digit ratio affect 6–9-year-old children’s prosocial choices." Scientific Reports 8.1 (2018): 9198.)
(...)
The variation in 2D:4D ratios has been closely related to variation in gender-typed appearance and behaviours within each sex (for a review see(55,56)). Males with higher 2D:4D ratios have a less masculine behavioural phenotype(57) and less physical strength compared to those with lower 2D:4D(58). Females with lower 2D:4D, in turn, score higher on male-dominated dimensions, such as spatial abilities(59) and a systemizing personality(60), than same-sex individuals with a higher 2D:4D ratio. Therefore, one can argue for a general masculinisation effect of prenatal androgen exposure on multiple phenotypic levels, from brain organization to appearance and behaviours."
"[W]e'll call [the] effects [of testosterone on the human body] virility. (...) On an individual level [testosterone] influences our decisions and informs our drives to mate and to survive, and testosterone has shaped our evolution and much of our progress as a species. Yet, fueling prostate cancer is not the only black mark on testosterone's record: it is also responsible for a host of our more sinister behaviors and some of humanity's darkest moments.
(...)
Scientists have found associations between virility and violence, crime, poverty and unstable relationships. Recent experimental data shows that testosterone can negatively affect a person's capacity for compassion, generosity and empathy.
(...)
Testosterone spurs the release of dopamine, a powerful feel-good chemical. What's more, not only does this winning burst of testosterone make us feel dominant and primed for further competition, it also ensures that this competition will be even more rewarding in the future: the higher levels of testosterone following a win stimulate the production of more androgen receptors in the brain (...). (...) The spike in testosterone is (...) a cause of further testosterone-driven thoughts and actions.
(...)
[I]t is important to note that much of the influence testosterone has on us takes place well before we are born - in the fifteenth week of gestation, in fact. During this time, testosterone levels spike in both males and females (although higher in males, on average), and this surge coincides with a time of intense brain growth in the fetus. Scientists have discovered a surprising way to estimate the effect testosterone had on an individual in utero, namely by measuring the ratio of the length of the right index finger (the second digit, or 2D) to the right ring finger (4D). (...) This 2D:4D ratio is an approximate indicator of the amount of testosterone a person's brain was exposed to in the fifteenth week, know as fetal testosterone. The higher the ratio, the lower the amount of fetal testosterone exposure (...)."
(Ryan, Charles J., Md, The Virility Paradox: The Vast Influence of Testosterone on Our Bodies, Minds, and the World We Live In. BenBella Books, 2018.)
"Sexual differentiation of the brain has been conclusively demonstrated in many mammalian species. The brain seems to be inherently feminine. Masculine characteristics of the structure and function are imposed on the developing CNS (Central Nervous System) by the action of testicular hormones during a critical period. Sexual differentiation takes place through the effect of Y chromosome Testis Determining Factor (TDF) gene that leads to the development of testis and production of testosterone and its metabolites. Testosterone is a pro-hormone for dihydrotestosterone and estradiol that are responsible for sexually dimorphic characteristic of the brain."(Al-Marsoummi, Sarmad I., and Anam R. Al-Salihi, september 2015, "Sexual Differentiation of the Spinal Nucleus of Bulbo-Cavernosus Muscle (Onuf's Nucleus).")
"Testosterone is one of several chemically related “male sex hormones” collectively known as androgens. Nearly all researchers agree that testosterone is the single most important and prevalent androgen from the standpoint of helping to sexually differentiate males and females. Sexual differentiation includes nearly all parts of the body, including the brain [...]. By altering the brain both structurally and functionally, it is to be expected that cognitive and behavioral patterns will also be altered [...].(Ellis, Lee, Anthony W. Hoskin, and Malini Ratnasingam. "Testosterone, Risk Taking, and Religiosity: Evidence from Two Cultures." Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion 55.1 (2016): 153-173.)
When considering the effects that testosterone has on brain functioning (and thereby onthought processes and behavior), it is important to recognize that testosterone operates at two more or less distinct stages. [...]. The first stage begins early in gestation and continues for a few months following birth (the perinatal stage) and then surges sharply again at puberty (the postpubertal stage) [...]. Most of the effects of perinatal androgen exposure are irreversible, while the effects of exposure following puberty tend to be more transitory and dependent on how much exposure occurred perinatally [...]. If perinatal exposure is high (male-typical), postpubertal exposure usually has stronger effects than if perinatal exposure was low (female-typical) [...]."
"Androgen exposure during development also has widespread organizational effects on social behaviour. A series of classic studies found that female mice which develop between two male siblings—and thus are exposed to more androgens in utero—are more aggressive in adulthood, and more likely to compete successfully for a limited food resource [114,115]. (...) The widespread developmental effects of androgen exposure on aggression and sociality may be mediated, at least in part, by changes in the androgen sensitivity of nonapeptide systems [15,116]."
(Kelly, Aubrey M., and Maren N. Vitousek. "Dynamic modulation of sociality and aggression: an examination of plasticity within endocrine and neuroendocrine systems." Phil. Trans. R. Soc. B 372.1727 (2017): 20160243.)
(OK WP)
(Ellis, Lee, Anthony W. Hoskin, and Malini Ratnasingam. "Testosterone, Risk Taking, and Religiosity: Evidence from Two Cultures." Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion 55.1 (2016): 153-173.)
(Turban, Jack L., and Shervin Shadianloo. "TRANSGENDER AND GENDER NON-CONFORMING YOUTH." (2018).)
See also the Digit Ratio References, a list of studies related to 2D:4D digit ratio, compiled by Bernhard Fink, Research Fellow, Hanse Wissenschaftskolleg, Institute for Advanced Study in collaboration with professor John manning (Swansea University).
The difference between empathizing and systemizing has been described as
But this team of scientists is skeptical about the Ellis and Hoskin ENA (Evolutionary NeuroAndrogenic) theory. Their meta-study could not find a reliable correlation between 2D:4D digit ratio and crime:
Marina Butovskaya, Valentina Burkova, Dmitry Karelin, Bernhard Fink (2015), DOI: 10.1002/ajhb.22718)
(Mayhew, T. M., et al. "Human 2D (index) and 4D (ring) digit lengths: their variation and relationships during the menstrual cycle." Journal of anatomy 211.5 (2007): 630-638.)
(Lombardo, Michael V., et al. "Fetal programming effects of testosterone on the reward system and behavioral approach tendencies in humans." Biological psychiatry 72.10 (2012): 839-847.)
Low 2D:4D women prefer masculinized faces (high testosterone) for short- and long-term mates, don't bond well and are more promiscuous,
This study however finds no correlation between 2D:4D ratio in women and self-reported sociosexuality (the development and maintenance of interest in uncommitted sexual activity):
(Reddy RC, Amodei R, Estill CT, Stormshak F, Meaker M, Roselli CE. Effect of Testosterone on Neuronal Morphology and Neuritic Growth of Fetal Lamb Hypothalamus-Preoptic Area and Cerebral Cortex in Primary Culture. Migaud M, ed. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(6):e0129521. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0129521.)
(Martel MM, Roberts BA. Prenatal Testosterone Increases Sensitivity to Prenatal Stressors in Males with Disruptive Behavior Disorders. Neurotoxicology and teratology. 2014;44:11-17. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2014.05.001.)
(Carney, Dana R., and Malia F. Mason. "Decision making and testosterone: when the ends justify the means." Journal of Experimental Social Psychology 46.4 (2010): 668-671.)
(“instrumental” dilemmas = in which the death of one person is a means to save more people; “incidental” dilemmas = in which the death of one person is a foreseen but unintended consequence of the action aimed at saving more people)
(Lotto, Lorella, Andrea Manfrinati, and Michela Sarlo. "A new set of moral dilemmas: Norms for moral acceptability, decision times, and emotional salience." Journal of Behavioral Decision Making 27.1 (2014): 57-65.)
(the Interpersonal Reactivity Index or IRI is a self-assessment using a questionnaire the participants fill in themselves).
The study's result were:
(Blanchard, Alyson, and Minna Lyons. "An investigation into the relationship between digit length ratio (2D: 4D) and psychopathy." The British Journal of Forensic Practice 12.2 (2010): 23-31.)
(Blanchard, Alyson, and Luna C. Munoz Centifanti. "Callous-Unemotional Traits Moderate the Relation Between Prenatal Testosterone (2D: 4D) and Externalising Behaviours in Children." Child Psychiatry & Human Development (2016): 1-10.)
But: one meta-study warns for caution, although it also finds a small overall effect
In the ultimatum game giving more can have a strategic advantage for the one giving, because the receiving party has an active role (either accept or reject the offer). In the dictator game the one receiving cannot decide anything (totally passive role), so there is no advantage to the giver in giving more.
So, giving more in the ultimatum game than in the dictator game points towards low altruism: only when teher is a certain advantage for oneself, will the subject be more generous.
(Branas-Garza, Pablo. "Exposicion fetal a la testosterona, 2D: 4D y altruismo estrategico." Revista de Economia Industrial 403 (2017): 103-110.)
Males: activation increased water consumption, inhibition decreased alcohol consumption.
Females: activation increased alcohol consumption, inhibition increased water consumption.
In other words: the higher the androgen receptor activity, the higher the alcohol consumption and the lower the water consumption.
Participants were placed in various social contexts, some endorsing agression, others being neutral to it, others rejecting it. In other words, moral norms were being manipulated, and agression was measured in these different moral contexts.
The results showed that the actual behaviour of the participants was not affected by the norm manipulation, although their interpretation of it differed. In other words, changing moral norms did not affect behaviour in se, only how they reflected upon it.
Digit ratio did not seem to have an effect in this matter (the effect of norm manipulation on behaviour was not correlated with digit ratios, in other words: whether a participant had high or low digit ratio, the results remained the same, their actual behavior was not affected by social norms, and their interpretation of it was affected).
"Free riders" are those who give less than average, or not at all.
See also: women with low 2D:4D ratio have higher waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio. In other words, men with low 2D:4D may be partnered more with women of normal and high 2D:4D ratio than with low 2D:4D ratio.
(source: Second to fourth digit ratio, body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, and waist-to-chest ratio: their relationships in heterosexual men and women, B. Finka, N. Neaveb & J. T. Manning, pages 728-738, Annals of Human Biology, Volume 30, Issue 6, 2003, retrieved July 1st 2016)
and
(Cho, Keun Ja, and Sooil Kim. "Utilization of Second Digit to Fourth Digit Ratio (2D: 4D) as One of Physical Markers to Evaluate Aggression in Elementary School Students." Korean Journal of Physical Anthropology 30.4 (2017): 153-159.)
(Perceived self-efficacy is a judgment of capability to execute given types of performances. (...)
For example, perceived self-efficacy scales include items such as “I can solve most problems if I invest the necessary effort”or “I can usually handle whatever comes my way.”)
(Dalton, Patricio, and Sayantan Ghosal. "Self-confidence, overconfidence and prenatal testosterone exposure: evidence from the lab." (2014).)
Testosterone replacement therapy has been known to lower heart-rate variability:
(Poliwczak, Adam R., Maja Tylińska, and Marlena Broncel. "Effect of short-term testosterone replacement therapy on heart rate variability in men with hypoandrogen-metabolic syndrome." Pol Arch Med Wewn 123 (2013): 467-73.)
Avolition (...) is the decrease in the motivation to initiate and perform self-directed purposeful activities (...) [like] hobbies, going to work and/or school, and most notably, engaging in social activities.
Alogia (...) or poverty of speech, is a general lack of additional, unprompted content seen in normal speech.
Neurons in Onuf's nucleus are involved in the maintenance of micturition (cfr. urination) and defecatory continence, as well as muscular contraction during orgasm.
(Tambe, M. K., et al. "Influence of digit ratio (2D: 4D) on reaction time and athletic sprint performance: A short term pilot study." (2018).)
2)
Statistically, men perform better at MRT than women.
ADHD = attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder
ODD = oppositional defiant disorder
PDD = pervasive developmental disorder
NOS = not otherwise specified
(De Bruin, Esther I., et al. "Differences in finger length ratio between males with autism, pervasive developmental disorder‐not otherwise specified, ADHD, and anxiety disorders." Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 48.12 (2006): 962-965.)
But this study did not find a link between prenatal testosterone and spatial ability. It did not measure 2D:4D ratios, but looked at opposite-sex twins (in the light of the hypothesis that prenatal testosterone may transfer from a male twin to the female twin):
Mental toughness was measured using the MTQ48:
"It is well known that prenatal testosterone levels yields gender differences in brain [31]"(Yongtawee, Atcharat, and Min-Jung Woo. "The Influence of Gender, Sports Type and Training Experience on Cognitive Functions in Adolescent Athletes." Exercise Science 26.2 (2017): 159-167.)
"Compared to other well characterized critical periods, such as those for the visual system or barrel cortex, the masculinization of the brain is telescoped into a few short days and initiated prenatally."(McCarthy, Margaret M., Kevin Herold, and Sara L. Stockman. "Fast, furious and enduring: Sensitive versus critical periods in sexual differentiation of the brain." Physiology & Behavior (2017).)
"Estrogen decreases cerebral vascular tone and increases cerebral blood flow [...]. Testosterone has opposite effects, increasing cerebral artery tone. Cerebrovascular inflammation is suppressed by estrogen but increased by testosterone and progesterone. Evidence suggests that sex steroids also modulate blood-brain barrier permeability. Estrogen has important protective effects on cerebral endothelial cells by increasing mitochondrial efficiency, decreasing free radical production, promoting cell survival, and stimulating angiogenesis."(Krause, Diana N., Sue P. Duckles, and Dale A. Pelligrino. "Influence of sex steroid hormones on cerebrovascular function." Journal of applied physiology 101.4 (2006): 1252-1261.)
(Cfr. Executive function disorder (EFD). The six steps of executive function are: 1. Analyze a task, 2. Plan how to address the task, 3. Organize the steps needed to carry out the task, 4. Develop timelines for completing the task, 5. Adjust or shift the steps, if needed, to complete the task, 6. Complete the task in a timely way. It follows naturally that someone with issues with executive functioning may have problems with analyzing, planning, organizing, scheduling, and completing tasks at all — or on deadline.)
"Boys also showed a specific association between [...] higher testosterone levels [...] and lower performance on specific components of executive function (monitoring the action process and flexibly shifting between actions)."
"Taken together, these findings highlight the developmental importance of testosterone in supporting sexual differentiation of the brain and sex-specific executive function."(Nguyen, Tuong-Vi, et al. "Sex-specific associations of testosterone with prefrontal-hippocampal development and executive function." Psychoneuroendocrinology 76 (2017): 206-217.)
"Why do girls and women differ from boys and men? Gender development is typically considered to result from socialization, but sex hormones present during sensitive periods of development, particularly prenatal androgens, play an important role. Data from natural experiments, especially from females with congenital adrenal hyperplasia, show the complexity of the effects of androgens on behavior: Prenatal androgens apparently have large effects on interests and engagement in gendered activities; moderate effects on spatial abilities; and relatively small or no effects on gender identity, gender cognitions, and gendered peer involvement."(Berenbaum, Sheri A. "Beyond pink and blue: The complexity of early androgen effects on gender development." Child Development Perspectives 12.1 (2018): 58-64.)
(OK WP)
Perinatal testosterone has more impact on brain and behavior than testosterone levels later in life
(Definition of perinatal: "occurring in, concerned with, or being in the period around the time of birth", +/- from 5 months before birth to one month after.)
"[A]ndrogen levels are especially high during the third through the six months of gestation (especially for males) and then rise even more dramatically with the onset of puberty (especially for males). The postpubertal rise seems to primarily serve to fully activate the brain with respect to whatever levels of androgens were present perinatally (= five months before and one month after birth). High postpubertal levels of androgens alone do not appear to permanently affect brain functioning (and thereby on behavior)."(Ellis, Lee, and Anthony W. Hoskin. "The evolutionary neuroandrogenic theory of criminal behavior expanded." Aggression and violent behavior 24 (2015): 61-74.)
"Most of the effects of perinatal androgen exposure are irreversible, while the effects of exposure following puberty tend to be more transitory and dependent on how much exposure occurred perinatally [...]. If perinatal exposure is high (male-typical), postpubertal exposure usually has stronger effects than if perinatal exposure waslow (female-typical) [...]."
(Ellis, Lee, Anthony W. Hoskin, and Malini Ratnasingam. "Testosterone, Risk Taking, and Religiosity: Evidence from Two Cultures." Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion 55.1 (2016): 153-173.)
' "We realised that hormones act during very early life, that is to say, in utero/ovo, or during the first days of life, to irreversibly define how males and females will react to sex hormones as adults. This is what is known as the organising effects of hormones on the brain", explains the scientist. Hormones will therefore influence the structure of the brain so that it will be organised in such a way as to produce male or female sexual behaviour.'(Balthazart, Jacques. "Sexual orientation in all its aspects.", Reflexions, le site de vulgarisation de l'Université de Liège, Université de Liège - http://reflexions.ulg.ac.be/ - 06 July 2017)
Anecdotal descriptions of the effects of testosterone on brain and behavior
"In December 2015, Zahra began taking testosterone, at first swallowing pills three times a day, and then via injection. (...) “I started getting really angry from the testosterone, which is a side effect,” she says."
(Turban, Jack L., and Shervin Shadianloo. "TRANSGENDER AND GENDER NON-CONFORMING YOUTH." (2018).)
Scientific studies related to the effect of (prenatal) testosterone on brain and behavior, and correlations with the 2D:4D digit ratio
See also the Digit Ratio References, a list of studies related to 2D:4D digit ratio, compiled by Bernhard Fink, Research Fellow, Hanse Wissenschaftskolleg, Institute for Advanced Study in collaboration with professor John manning (Swansea University).
Low 2D:4D ratio linked with aggressive behavior and attention problems in boys
"Increased aggression and attention problems were both significantly associated with a lower ratio of the length of the second finger digit relative to the fourth digit ratios in boys but not girls. The effects remained significant after controlling for early adversity."(Liu, Jianghong, Jill Portnoy, and Adrian Raine. "Association between a marker for prenatal testosterone exposure and externalizing behavior problems in children." Development and psychopathology 24.03 (2012): 771-782.)
Lower 2D:4D ratio related to conduct disturbance, hyperactivity and agression in children
"Low 2D:4D (indicating higher prenatal T) was related to measures of total difficulties and poor conduct in both UK and Austrian children. In the UK sample, prosocial behaviour was positively related to 2D:4D in girls and hyperactivity and conduct correlated negatively with 2D:4D in boys. Associations were generally stronger for boys than for girls. [...] As predicted, we found that caregiver ratings of greater problems with aggression, and conduct disturbance in children were associated with lower 2D:4D ratio, in both the UK and Austria, for the total samples (boys and girls together). Furthermore, these relationships were consistent using two different behavioural measures (i.e. SDQ and CBCL/4-18)."(source: The 2nd to 4th digit ratio and developmental psychopathology in school-aged children, Fink, Manning, Williams, in Personality and Individual Differences 42(2):369-379 · January 2007, retrieved July 1st 2016)
Fetal testosterone positively correlated with systemizing
"Participants included 204 children (93 female), age 6–9 years, taking part in a long-term(Foetal testosterone and the child systemizing quotient, Bonnie Auyeung, Simon Baron-Cohen, Emma Chapman, Rebecca Knickmeyer, Kevin Taylor, and Gerald Hackett, European Journal of Endocrinology (2006) 155 S123–S130)
study on the effects of fT. [F]etal testosterone (fT) was the only significant predictor of systemizing preference when the sexes were examined together. Sex was not included in the final regression model, suggesting that fT levels play a greater role than the child’s sex in terms of differences in systemizing preference."
Fetal testosterone negatively correlated with empathizing
"The present study investigates empathizing in children, as a function of amniotic measures of fT. One hundred ninety-three mothers of children (100 males, 93 females) aged 6-8 years of age completed children's versions of the Empathy Quotient (EQ-C), and the children themselves were tested on "Reading the Mind in the Eyes" Task (Eyes-C). All mothers had had amniocentesis during the 2nd trimester of pregnancy. There was a significant negative correlation between fT and scores on both measures."(Fetal testosterone and empathy: evidence from the empathy quotient (EQ) and the "reading the mind in the eyes" test. Chapman E, Baron-Cohen S, Auyeung B, Knickmeyer R, Taylor K, Hackett G., Soc Neurosci. 2006;1(2):135-48. doi: 10.1080/17470910600992239)
"In this study, we examined whether fT was related to the tendency to interpret ambiguous visual stimuli in intentional and human terms. This test was used as a measure of mental state attribution, a component of empathy. This test was used as a measure of mental state attribution, a component of empathy. Typically, developing children were presented with a series of films featuring shapes whose movements were designed to elicit theory of mind attributions and recorded the children’s descriptions. Their narratives were analyzed for the frequency of mental and affective state terms and classified all the propositions in their narratives according to the criteria set out by Bowler and Thommen (2000). We predicted that females would use more mental and affective state terms than males. We also predicted that females would make more intentional propositions, as classified by Bowler and Thommen (2000); intentional propositions include propositions describing actions(Knickmeyer, Rebecca, et al. "Fetal testosterone and empathy." Hormones and Behavior 49.3 (2006): 282-292.)
between animate or agentive entities. We also predicted that variation in fT levels would account for the predicted sex differences. In general, our predictions were supported. Our results implicate fT in human social development. They are also compatible with the ‘empathizing–systemizing’ theory of sex differences (Baron-Cohen, 2003) since this predicts that females in the general population will score higher than males on a test of empathy. Finally, in isolating fT as related to some aspects of
empathy, the study provides further support for the hypothesis that fT is a risk factor for autism."
The more you systemize, the less you empathize
"In this article we [...] test if empathy and systemizing “compete” in the brain. We conclude that they do [...]. This suggests that females’ relatively high empathizing score compensates for their less developed systemizing score, and conversely males’ high systemizing score compensates for their less well-developed empathizing score."(EMPATHIZING AND SYSTEMIZING IN MALES, FEMALES, AND AUTISM, Nigel Goldenfeld, Simon Baron-Cohen, Sally Wheelwright, Clinical Neuropsychiatry (2005) 2, 6, 338-345)
The difference between empathizing and systemizing has been described as
"empathizing (E) strategies [...] identify, predict, and respond to mental states and systemizing (S) strategies [...] analyze a system using set rules".
(Elpers, Karrie. Relationships Between ES Theory, Theory of Mind, Ability Tilt, and College Major Preference Controlling for General Intelligence. Diss. The University of Texas at San Antonio, 2018.)
Brain types based on percentiles of male and female controls. E=empathizing, S = systemizing. AS/HFA = Asperger Syndrome/High Functioning Autism.
(source: EMPATHIZING AND SYSTEMIZING IN MALES, FEMALES, AND AUTISM, Nigel Goldenfeld, Simon Baron-Cohen, Sally Wheelwright, Clinical Neuropsychiatry (2005) 2, 6, 338-345)
(See also the fetal testosterone part of Wikipedia's article on Empathizing/Systemizing)
The S>E and S>>E brains together correspond with 53.5+6.1=59.6% of the male population, and 16.5+0=16.5% of the female population.
In a 50%-50% male-female distribution (a rather realistic model, see Wikipedia's List of Countries by Sex ratio), this corresponds with (59.6+16.5)/200=38% of the total population.
Systemizing and empathizing brains in society
| Brain type | Extreme E | E | B | S | Extreme S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brain sex | Extreme Female | Female | Balanced | Male | Extreme Male |
| Defining characteristic | S<<E | S<E | S~E | S>E | S>>E |
| Female % | 4.3 | 44.2 | 35.0 | 16.5 | 0 |
| Male % | 0 | 16.7 | 23.7 | 53.5 | 6.1 |
| AS/HFA % | 0 | 0 | 12.8 | 40.4 | 46.8 |
(source: EMPATHIZING AND SYSTEMIZING IN MALES, FEMALES, AND AUTISM, Nigel Goldenfeld, Simon Baron-Cohen, Sally Wheelwright, Clinical Neuropsychiatry (2005) 2, 6, 338-345)
(See also the fetal testosterone part of Wikipedia's article on Empathizing/Systemizing)
The S>E and S>>E brains together correspond with 53.5+6.1=59.6% of the male population, and 16.5+0=16.5% of the female population.
In a 50%-50% male-female distribution (a rather realistic model, see Wikipedia's List of Countries by Sex ratio), this corresponds with (59.6+16.5)/200=38% of the total population.
Systemizing/empathizing profiles not correlated with sex
"The absence of typical sex differences in empathizing-systemizing profiles within the autism spectrum confirms a prediction from the extreme male brain theory."(Lai, Meng-Chuan, et al. "A behavioral comparison of male and female adults with high functioning autism spectrum conditions." PloS one 6.6 (2011): e20835.)
Digit ratio correlated with empathizing-systemizing in Japanese sample
"digit ratio correlated positively with scores on EQ (empathy quotient) and negatively with scores on SQ (systemizing quotient), although correlation coefficients were very low."(Wakabayashi, Akio, and Yui Nakazawa. "On relationships between digit ratio (2D: 4D) and two fundamental cognitive drives, empathizing and systemizing, in Japanese sample." Personality and Individual Differences 49.8 (2010): 928-931.)
Low 2D:4D ratio correlates with higher numeracy, high 2D:4D with higher literacy
"The present study hypothesized that digit ratio would correlate with the relative difference between numeracy and literacy abilities. Digit ratios were calculated for 75 (mainly Caucasian) children aged between 6 and 7 attending a state funded infant school. The digit ratios were then correlated with the results from their National Standard Assessment Tests (SATs). A significant correlation was found as hypothesized. Additionally, there was a negative correlation between digit ratio and numeracy for males (indicating higher prenatal testosterone exposure related to higher numeracy SAT scores) and a positive correlation between digit ratio and literacy for females (indicating lower prenatal testosterone exposure related to higher literacy SAT scores)."(source: Brosnan, Mark J. "Digit ratio as an indicator of numeracy relative to literacy in 7‐year‐old British schoolchildren." British Journal of Psychology 99.1 (2008): 75-85.)
Controversial: Low r2D:4D linked to more criminal behavior after puberty
"Statistically significant correlations between the commission of most types of offenses and r2D:4D ratios were found for males and females even after controlling for age. It is concluded that high exposure to androgens during prenatal development contributes to most forms of offending following the onset of puberty."(Ellis, Lee, and Anthony W. Hoskin. "Criminality and the 2D: 4D Ratio Testing the Prenatal Androgen Hypothesis." International journal of offender therapy and comparative criminology 59.3 (2015): 295-312.)
But this team of scientists is skeptical about the Ellis and Hoskin ENA (Evolutionary NeuroAndrogenic) theory. Their meta-study could not find a reliable correlation between 2D:4D digit ratio and crime:
"In our two recently published meta-analyses of the literature assessing the “prenatal androgen hypothesis,” we failed to find supportive evidence in favor of the 2D:4D digit ratio—a rather crude proxy for exposure to fetal testosterone—being predictive of various forms of criminal, antisocial, and analogous behaviors (see Pratt, Turanovic, & Cullen, 2016; Turanovic, Pratt, & Piquero, 2017). (...)
[O]ur focus was centered on whether the 2D:4D digit ratio—as a proxy measure of a core theoretical concept—could be reliably linked to crime and analogous behaviors. That the digit ratio did not perform well is simply what the data revealed. (...) As social scientists, we remain open to the idea that exposure to fetal testosterone is an important developmental phenomenon that could well influence a wide array of behaviors over the life course, whether they be criminal, aggressive, risky, impulsive, and/or antisocial. This is still an important—and in our estimation, open—empirical question and one that criminologists should continue to investigate (we made this point explicitly as well in Pratt et al., 2016). We are simply skeptical that measuring fingers is going to amount to a valid and reliable way of testing ENA theory’s core propositions."
(Pratt, Travis C., Jillian J. Turanovic, Alex R. Piquero, and Francis T. Cullen. "Don’t Shoot The Messengers." (PDF))
Artists have significantly lower 2D:4D ratios
"Both male and female artists had significantly lower 2D:4D ratios (indicating high testosterone) than male and female controls."
(Crocchiola, Danae. "Art as an indicator of male fitness: does prenatal testosterone influence artistic ability?." Evolutionary Psychology 12.3 (2014): 147470491401200303.)
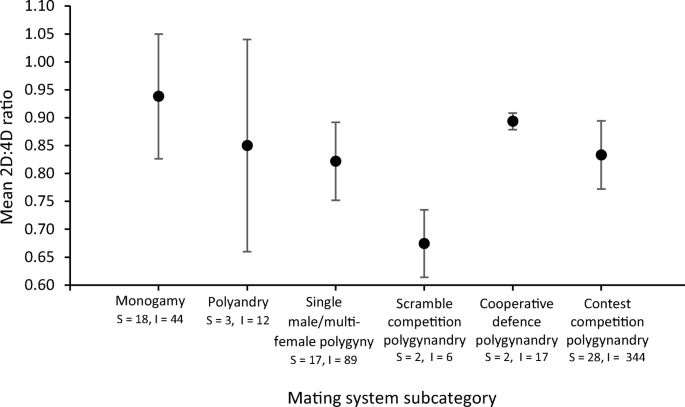
Polygamy and monogamy each correspond to a different human phenotype, marked by differences in 2D:4D ratio (low 2D:4D linked to polygamy, high 2D:4D to monogamy)
"In all comparative analyses, humans always fall on the borderline between obligate monogamy and polygamy. Here, we [...] show that this may be because there are two distinct phenotypes in both sexes. While males are more promiscuous and display higher prenatal testosterone exposure than females overall, our analyses also suggest that the within-sex variation of these variables is best described by two underlying mixture models, suggesting the presence of two phenotypes with a monogamous/promiscuous ratio that slightly favours monogamy in females and promiscuity in males. [...](Wlodarski, Rafael, John Manning, and R. I. M. Dunbar. "Stay or stray? Evidence for alternative mating strategy phenotypes in both men and women." Biology letters 11.2 (2015): 20140977.)
Modelling confirmed the existence of two phenotypes within each sex, one of low (restricted) sociosexuality [(polygamy)] and the other of high (unrestricted) sociosexuality [(monogamy)]. [...]
While the χ2 tests confirm that the male 2D : 4D data also have an underlying bimodal distribution, the female data just fail to reach statistical significance (p = 0.079). Nonetheless, modelling still supports the existence of two underlying phenotypes for both sexes [...], with low 2D : 4D males making up a larger proportion of the male distribution, and the female 2D : 4D phenotypes being more evenly distributed (figure 2).
2D:4D ratio, polygamy versus monogamy and early humans
"Recent studies have shown that the second-to-fourth digit ratio (2D : 4D), a putative biomarker for prenatal androgen effects (PAEs), covaries with intra-sexual competition and social systems across haplorrhines; non-pair-bonded polygynous taxa have significantly lower 2D : 4D ratios (high PAE) than pair-bonded monogamous species."(Nelson, Emma, et al. "Digit ratios predict polygyny in early apes, Ardipithecus, Neanderthals and early modern humans but not in Australopithecus." Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences 278.1711 (2011): 1556-1563.)
2D:4D ratio not correlated with number of children in Namibian tribe (no contraceptives used). Lower 2D:4D ratio linked to lower age for first marriage.
"The second to fourth digit ratio (2D:4D) is used as a potential marker for prenatal androgen exposure. It is associated with many behavioral and biological variables, including fertility and sexual behavior. However, direct association between 2D:4D and reproductive success—in populations where no contraceptives are used—has not been investigated. Here, we present a study conducted among the semi-nomad Himba population living in northern Namibia. 2D:4D ratios were calculated for a sample of this population (N = 99; 60 women, 39 men), and the results were correlated with age, marital status, age at first marriage, number of children, and number of marriages. As found in the majority of previous studies, males had lower 2D:4D ratios than females. The 2D:4D ratio did not correlate with number of children. Females and males with a more masculine 2D:4D were married earlier and were more likely to have a husband or wife. We suggest that mating preferences for females with masculine 2D:4D are related to masculinity of phenotypic and personality traits of such women, which are beneficial in harsh environmental conditions and/or higher facial masculinity, which influences the perceived age of an individual. At the same time, masculine (physically strong, dominant, and hardworking) males might gather resources necessary to marry their first wife earlier."(Sorokowski, Piotr, et al. "The second to fourth digit ratio and age at first marriage in semi-nomadic people from Namibia." Archives of sexual behavior 41.3 (2012): 703-710.)
High digit ratio linked to anxiety in men, not in women
"Men with a more feminine pattern of sex-linked traits and behaviors (including digit ratios) reported greater anxiety. In contrast, greater anxiety in women was associated with both female-typical and male-typical traits and behaviors, but and no significant association between digit ratio and anxiety was found."(Evardone, Milagros, and Gerianne M. Alexander. "Anxiety, sex-linked behaviors, and digit ratios (2D: 4D)." Archives of sexual behavior 38.3 (2009): 442-455.)
Higher 2D:4D ratio correlates with greater Openness personality factor
"Most interestingly, greater Openness was significantly associated with more female-typical (higher) 2D:4D ratios for the entire sample. This was significant for the male sample alone, and was found at a trend level in the female sample alone."(Burton, Leslie A., Elan Guterman, and Graham Baum. "Effect of prenatal androgen on adult personality: Greater openness with more female-typical 2D: 4D digit ratios." Current Psychology 32.2 (2013): 197-202.)
ADHD linked to more masculine (lower) 2D:4D ratio
"We examined the relationship between digit ratios and ADHD [attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder] symptoms [...] in a sample of European-descent college students (135 female, 52 male) not selected for ADHD. All digit ratios were calculated excluding the thumb. In females, the more masculine the LH 2D:4D ratio, the more the ADHD/Combined symptoms [...] and the more the ADHD/Inattentive symptoms and ADHD/Hyperactive-Impulsive symptoms. More masculine ratios also correlated between [ADHD/Combined] and RH 2D:3D, RH 2D:4D, and LH 2D:3D; and between [ADHD/Inattentive symptoms] and LH 2D:5D, and between the ADHD/Hyperactive and Impulsive symptoms and RH 3D:4D."(Stevenson, Joan C., et al. "Attention deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) symptoms and digit ratios in a college sample." American Journal of Human Biology 19.1 (2007): 41-50.)
Lower right-hand 2D:4D ratio linked to ADHD in boys
"Right-hand digit ratios showed [...] associations with ADHD diagnosis. Boys with ADHD had more masculinized digit ratios than control-group boys. More masculine right 2D:4D and 3D:4D ratios were correlated with parent- and teacher-rated inattentive and hyperactive-impulsive symptoms in boys but not in girls. Masculinized finger-length ratios were associated with hyperactive-impulsive and oppositional- defiant symptoms, but associations were largest with symptoms of inattention. It is concluded that prenatal, organizational effects of gonadal hormones may play a role in the development of ADHD and contribute to explaining sex differences in the prevalence rates of this childhood disorder."(Masculinized finger-length ratios of boys, but not girls, are associated with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder. Martel, Michelle M.; Gobrogge, Kyle L.; Breedlove, S. Marc; Nigg, Joel T. Behavioral Neuroscience, Vol 122(2), Apr 2008, 273-281)
Low right-hand 2D:4D ratio linked to aggression in African girls
"This study was conducted on children and adolescents from the three tribal cultures from Northern Tanzania: the Hadza, the Datoga and the Iraqw. [...] A significant negative correlation between the right hand 2D:4D ratio and ratings on physical aggression was found for the girls. The girls with the lowest finger index estimated themselves as more verbally aggressive, compared to girls with a medium 2D:4D ratio."(source: Marina Butovskaya, Valentina Burkova, Audax Mabulla, (2010) "Sex differences in 2D: 4D ratio, aggression and conflict resolution in African children and adolescents: a cross‐cultural study", Journal of Aggression, Conflict and Peace Research, Vol. 2 Iss: 1, pp.17 - 31)
Of two African tribes, the lower 2D:4D ratio is more agressive and dominant
"Digit ratio (2D:4D)—a putative marker of prenatal androgen activity—has been shown to correlate with self-reported physical aggression and dominance behavior, especially in male children and adolescents. This evidence is derived primarily from the study of Western samples.(source: Digit ratio (2D:4D), aggression, and dominance in the Hadza and the Datoga of Tanzania,
Digit ratios, self-reported aggression, and dominance behavior were collected from men and women in two traditional, small-scale societies, i.e., the Hadza and the Datoga of Tanzania.
We found significant differences in physical and verbal aggression, anger, and hostility between the two societies with the Datoga reporting higher scores on all four measures. Moreover, self-reported dominance in the Datoga was higher than in the Hadza. The Datoga showed lower left and right hand 2D:4D ratios than the Hadza. Men reported higher physical and verbal aggression and dominance, and had lower 2D:4D ratios than women. A significant negative association between 2D:4D and dominance was found in Hadza women."
Marina Butovskaya, Valentina Burkova, Dmitry Karelin, Bernhard Fink (2015), DOI: 10.1002/ajhb.22718)
Males with lower 2D:4D ratio are more aggressive
"We examined the relationship between trait aggression, assayed using a questionnaire, and finger length ratio in both men and women. Men with lower, more masculine, finger length ratios had higher trait physical aggression scores [...]. We found no correlation between finger length ratio and any form of aggression in females."
(source: Finger length ratio (2D:4D) correlates with physical aggression in men but not in women, Allison A. Baileya, , Peter L. Hurda, Biological Psychology, Volume 68, Issue 3, March 2005, Pages 215–222)
"Results of this study revealed that in professional soccer players, aggressive behavior, with the consequent increased risk of fouls during the game, is more likely to occur in individuals with high testosterone levels, not only in adulthood, but also during their intrauterine life."(Perciavalle, Valentina, et al. "The second-to-fourth digit ratio correlates with aggressive behavior in professional soccer players." Molecular medicine reports 7.6 (2013): 1733-1738.)
Lower 2D:4D ratio predicts higher propensity to attack without being provoked
"We tested the association between a biomarker of early sex differentiation, the second-to-fourth finger length ratio (2D:4D), and unprovoked attack during a simulated war game [...] We found that sex and lower, more male-typical, 2D:4D predicted unprovoked attack independently."
(source: Finger length ratio (2D:4D) and sex differences in aggression during a simulated war game, Matthew H. McIntyrea, Emily S. Barrettb, Rose McDermottc, Dominic D.P. Johnsond, Jonathan Cowdenc, Stephen P. Rosene, Personality and Individual Differences, Volume 42, Issue 4, March 2007, Pages 755–764)
Relation between 2D:4D ratio and social behaviour is context dependent
"In the present paper, we aim to show the context-dependency of the relation between 2D:4D and social behaviour. In two studies, we expose participants either to control or to aggression cues. Afterwards, they make a decision in a dictator game. Participants with low 2D:4D showed higher allocation levels (i.e. they were more prosocial) than participants with high 2D:4D in a neutral situation. However, this relationship inverts after exposure to an aggression cue. It turns out that in high 2D:4D people, aggression cues even increase prosocial behaviour. We call for future research which focuses on other plausible interactions between 2D:4D and context cues rather than on linear relations."
(source: The presence of aggression cues inverts the relation between digit ratio (2D:4D) and prosocial behaviour in a dictator game, Kobe Millet, Siegfried Dewitte, British Journal of Psychology, 2009, DOI: 10.1348/000712608X324359)
Boys with lower 2D:4D ratio self-rate higher physical aggressiveness
"The aim of this study was to consider digit ratio (2D:4D: a putative marker of prenatal testosterone and estrogen levels) and aggression in a sample of 1,452 children and adolescents (mean age 13.6 years) from five regions of Russia. The 2D:4D was calculated from direct measurements of the fingers, and aggression scores were obtained from completed Buss and Perry (J Pers Soc Psychol 63 (1992) 452–459) aggression questionnaires. The 2D:4D demonstrated significant sexual dimorphism, with lower 2D:4D in boys in all regions. Physical aggression scores were highest in boys, but verbal aggression, anger and hostility were highest in girls. The highest right hand 2D:4D in boys was found in the most northerly population (Central Russia Region). Our data revealed small, but highly significant negative correlations between right 2D:4D, right–left 2D:4D (DR-L) and self-ratings on physical aggression in boys, but not in girls."
(source: Sex differences in 2D:4D and aggression in children and adolescents from five regions of Russia, Marina Butovskaya, Julija Fedenok, Valentina Burkova, John Manning, American Journal of Physical Anthropology, 2013, DOI: 10.1002/ajpa.22337)
Lower 2D:4D ratio corresponds with more aggressive dominant personality
"Results showed that men had a more aggressive dominant personality when having a more masculine (lower) 2D:4D, while there was no relationship between sociable dominance and 2D:4D. Findings from this study indicate that it is important to distinguish different forms of dominance since other studies failed to find relationships between dominance and 2D:4D."
Leander van der Meij, Mercedes Almela, Abraham P. Buunk, Shelli Dubbs, Alicia Salvador, Aggressive Behavior, 2012, DOI: 10.1002/ab.21422)
In female rhesus macaques, lower 2D:4D corresponds to higher dominance rank
"Female rhesus macaques exhibit matrilineal dominance structures [...]. Here, we investigate how 2D:4D co-varies with socially inherited dominance rank in female rhesus macaques. Low 2D:4D was associated with higher-ranking females, while higher 2D:4D was associated with lower-ranking females. Similar relationships were also shown between ranked families within matrilines."
Emma Nelson , Christy L. Hoffman, Melissa S. Gerald, Susanne Shultz, Behavioral Ecology and Sociobiology, May 2010, Volume 64, Issue 6, pp 1001-1009)
Low 2D:4D ratio linked to high risk-taking
"A composite measure of risk-taking across all five domains [financial, social, recreational, ethical, and health] revealed that [...] 2D:4D [was] negatively correlated with overall risk-taking in both male sub-samples [Caucasian only, and ethnically heterogeneous). No significant correlations were found in the female sub-samples. Finally, men were more risk-seeking than women across all five contexts."
(source: Personality and Individual Differences, Volume 51, Issue 4, September 2011, Pages 412–416, Digit Ratio (2D:4D) and Individual Differences Research, Testosterone and domain-specific risk: Digit ratios (2D:4D and rel2) as predictors of recreational, financial, and social risk-taking behaviors, Eric Stenstrom, , Gad Saad, Marcelo V. Nepomuceno, Zack Mendenhall)
"Low digit ratio in men is associated with higher risk taking and higher scores in abstract reasoning ability when a combined measure of risk aversion over different tasks is used. (...) Mediation analysis shows that a substantial part of the effect of T on attitude to risk is mediated by abstract reasoning ability."(Brañas-Garza, Pablo, and Aldo Rustichini. "Organizing effects of testosterone and economic behavior: Not just risk taking." PloS one 6.12 (2011): e29842.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with more aggression when challenged
"Here we test the hypothesis that 2D:4D is robustly linked to aggression in “challenge” situations in which testosterone is increased. Participants were exposed to an aggressive video and a control video. Aggression was measured after each video and salivary free testosterone levels before and after each video. Compared to the control video, the aggressive video was associated with raised aggression responses and a marginally significant increase in testosterone. Left 2D:4D was negatively correlated with aggression after the aggressive video and the strength of the correlation was higher in those participants who showed the greatest increases in testosterone. Left 2D:4D was also negatively correlated to the difference between aggression scores in the aggressive and control conditions. The control video did not influence testosterone concentrations and there were no associations between 2D:4D and aggression. We conclude that 2D:4D moderates the impact of an aggressive stimulus on aggression, such that an increase in testosterone resulting from a “challenge” is associated with a negative correlation between 2D:4D and aggression."(source: Digit Ratio (2D:4D), Aggression, and Testosterone in Men Exposed to an Aggressive Video Stimulus, Liam P. Kilduff, Renato N. Hopp, Christian J. Cook, Blair T. Crewther, John T. Manning, Evol Psychol December 2013 vol. 11)
Low 2D:4D ratio linked to polygamy, high 2D:4D ratio to monogamy
"[P]olygynous societies reportedly have lower 2D:4D (higher PAE [Prenatal Androgen Effects]) than more monogamous populations. [...] To place 2D:4D research into a broader context, we test the relationship between digit ratios and behavior across nonhuman anthropoids; polygynous species, with higher levels of intrasexual competition, should have more pronounced markers of PAE (lower 2D:4D) than pair-bonded species. Our results accord with those found in humans: 2D:4D is lower in polygynous species and higher (lower PAE) in pair-bonded species. Old World monkeys have low, and relatively invariant 2D:4D (high PAE), which is coupled with high levels of intrasexual competition. This contrasts with higher and more variable ratios in both great apes and New World monkeys. In addition, both male and female ratios decrease with increasing levels of intrasexual competition. Human ratios are intermediate between pair-bonded and more promiscuous hominoids."(source: Finger length ratios (2D:4D) in anthropoids implicate reduced prenatal androgens in social bonding, Emma Nelson, Susanne Shultz, 2009, DOI: 10.1002/ajpa.21157)
Low 2D:4D ratio linked to preference for normative behavior
"A low second to fourth digit ratio (2D:4D) has been related to high testosterone levels and to markers of high status. In a social dilemma context status can be obtained either by acting egoistically (i.e. not contributing one's share) or by acting altruistically (i.e. contributing more than one's fair share). We therefore predicted that a low 2D:4D would be associated with high levels of egoism and altruism and low levels of common cooperativeness (i.e. contributing exactly one's fair share). We found the exact opposite: participants with a low 2D:4D were more likely to act cooperatively and less likely to act altruistically and egoistically. These findings suggest that: (1) there might be a high and a low testosterone strategy to gain status and (2) the high testosterone strategy is characterized by a preference for normative behavior."(source: Biological Psychology, Volume 71, Issue 1, January 2006, Pages 111–115, Second to fourth digit ratio and cooperative behavior, Kobe Millet, , Siegfried Dewitte)
Low 2D:4D ratio linked to alcohol dependency in males
"[W]e found that alcohol dependent patients had smaller 2D∶4D ratios compared to controls with preserved sexual dimorphism but with reduced right-left differences. The detection of alcohol dependency based on 2D∶4D ratios was most accurate using the right hand of males [...]."(source: Low Digit Ratio 2D∶4D in Alcohol Dependent Patients, Johannes Kornhuber et.al., 2011http://dx.doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0019332)
"Patients who are alcohol dependent have a significantly lower 2D:4D than controls, similar to the results of previous studies, which suggest that a higher prenatal testosterone level in the gonadal period is related to alcoholism. Furthermore, 2D:4D is a possible predictive marker of alcohol dependence."
(Han, Changwoo, et al. "The ratio of 2nd to 4th digit length in Korean alcohol-dependent patients." Clinical Psychopharmacology and Neuroscience 14.2 (2016): 148.)
Low 2D:4D ratio -> pansexualism?
"We report that (a) 2D:4D was lower in a sample of 88 homosexual men than in 88 sex- and age-matched controls recruited without regard to sexual orientation, (b) within the homosexual sample, there was a significant positive relationship between mean 2D:4D ratio and exclusive homosexuality, (c) overall, there was a decrease in 2D:4D from controls to homosexual men to bisexual men"(source: The ratio of 2nd to 4th digit length and male homosexuality, S.J Robinson, J.T Manning, Evolution and Human Behaviour, Volume 21, Issue 5, September 2000, Pages 333–345, retrieved July 1st 2016)
Lesbians who identify as "Butch" have lower 2D:4D ratio
"[L]esbians who identified themselves as “butch” had a significantly smaller 2D:4D than did those who identified themselves as “femme.” We conclude that increased early androgen exposure plays a role in only some cases of female homosexuality, and that the sexual orientation of “femme” lesbians is unlikely to have been influenced by early androgens."
(Brown, Windy M., et al. "Differences in finger length ratios between self-identified “butch” and “femme” lesbians." Archives of sexual behavior 31.1 (2002): 123-127.)
Bonobos have higher 2D:4D ratios and are less violent than chimps. The two sub-species have significantly different brains
"We observed [...] substantially higher, more human-like, 2D:4D in bonobos than chimpanzees." (Source: Bonobos have a more human-like second-to-fourth finger length ratio (2D:4D) than chimpanzees: a hypothesized indication of lower prenatal androgens, Journal of Human Evolution 56 (2009) 361–365)"Observations in the wild indicate that the males among the related common chimpanzee communities are extraordinarily hostile to males from outside the community. Parties of males 'patrol' for the neighboring males that might be traveling alone, and attack those single males, often killing them. This does not appear to be the behavior of bonobo males or females, which seem to prefer sexual contact over violent confrontation with outsiders. In fact, the Japanese scientists who have spent the most time working with wild bonobos describe the species as extraordinarily peaceful, and de Waal has documented how bonobos may often resolve conflicts with sexual contact (hence the "make love, not war" characterization for the species). Between groups, social mingling may occur, in which members of different communities have sex and groom each other, behavior which is unheard of among common chimpanzees. [...](Source: Wikipedia "Bonobo", retrieved 2015/12/31)
Recent studies show that there are significant brain differences between bonobos and chimps. The brain anatomy of bonobos has more developed and larger regions assumed to be vital for feeling empathy, sensing distress in others and feeling anxiety, which makes them less aggressive and more empathic than their close relatives. They also have a thick connection between the amygdala, an important area that can spark aggression, and the ventral anterior cingulate cortex, which helps control impulses. This thicker connection may make them better at regulating their emotional impulses and behavior."
Low 2D:4D was related to hyperactivity and poor social cognitive function in girls, and high 2D:4D with emotional symptoms in boys.
"Low 2D:4D was related to hyperactivity and poor social cognitive function in girls, and high 2D:4D with emotional symptoms in boys."(source: http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0378378203000124)
Children with autism and AS have lower 2D:4D ratios than population normative values
"We found that the 2D:4D ratios of children with autism, their siblings, fathers and mothers were lower than population normative values. Children with AS, who share the social and communicative symptoms of autism but have normal or even high IQ, had higher 2D:4D ratios than children with autism but lower ratios than population normative values."
(source: The 2nd to 4th digit ratio and autism, J T Manning PhD, S Baron-Cohen PhD, S Wheelwright MA and G Sanders PhD, Version of Record online: 2 MAR 2007, retrieved July 1st 2016)
"We found that the 2D:4D ratios of children with autism, their siblings, fathers and mothers were lower than population normative values. Children with AS, who share the social and communicative symptoms of autism but have normal or even high IQ, had higher 2D:4D ratios than children with autism but lower ratios than population normative values."(source: The 2nd to 4th digit ratio and autism, J T Manning PhD, S Baron-Cohen PhD, S Wheelwright MA and G Sanders PhD, Version of Record online: 2 MAR 2007, retrieved July 1st 2016)
Fetal testosterone attenuates socio-affective skill
"Both testosterone and oxytocin influence an individual's accuracy in inferring another's feelings and emotions. Fetal testosterone, and the second-to-forth digit ratio (2D:4D) as its proxy, plays a role in social cognitive development, often by attenuating socio-affective skill. Conversely, oxytocin generally facilitates socio-affiliative and empathic cognition and behavior. A common polymorphism in the oxytocin receptor gene, OXTR rs53576, has been repeatedly linked with psychosocial competence, including empathy, with individuals homozygous for the G allele typically characterized by enhanced socio-cognitive skills compared to A allele carriers."(source: The association between 2D:4D ratio and cognitive empathy is contingent on a common polymorphism in the oxytocin receptor gene (OXTR rs53576) (PDF Download Available). [accessed Jan 26, 2016].)
High androgen levels linked to pathological gambling, financial risk-taking, competitive sports activities, agression and criminality
"Before proceeding further, it is worth asking whether empirical evidence actually supports ENA theory's assertion that androgens alter the brain in ways that promote competitive behavior. In recent years, substantial supportive evidence has accumulated. For example, unusually high postpubertal testosterone levels were found among male pathological gamblers when compared to control males (...). Another study reported that both prenatal and postpubertal testosterone levels were statistically associated with a willingness to take financial risks (...). Also, a biomarker for prenatal exposure to testosterone (called the 2D:4D finger length ratio) was found to predict “success” among financial traders (...) as well as involvement in competitive sporting activities (...).
Regarding androgenic influences on aggression and criminality, most of the research has come from correlating so-called peripheral circulating testosterone levels (levels circulating in the blood or saliva) postpubertally. Reviews of these studies have concluded that exposure to androgens promote both aggression and criminality (...). Furthermore, studies based on the 2D:4D biomarker have implicated prenatal brain exposure to high testosterone as a predictor of aggression (...) as well as various forms of criminality (...)."
"Regarding neurochemistry, testosterone appears to affect all of the major neurotransmitter systems, including the dopaminergic system (...) and the serotoninergic system (...). Dopamine activity has been shown to enhance an individual's willingness to take risks and tolerate pain while doing so (...). In this way, dopamine activity is likely to promote the probability of many forms of criminal behavior and other forms of competition for resources (...). In the case of serotonin, numerous studies have shown it to be related to criminality, although in complex and still only partially understood ways. [...] Overall, androgens have been shown to contribute to variations in both dopamine and serotonergic neurotransmitter systems. By so doing, androgens affect the probabilities of offending and violence."(Ellis, Lee, and Anthony W. Hoskin. "The evolutionary neuroandrogenic theory of criminal behavior expanded." Aggression and violent behavior 24 (2015): 61-74.)
High androgen levels linked to relatively larger orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) and relatively smaller dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (DLPFC)
"[G]oldstein et al. (2001) did a comprehensive evaluation of the volume of 45 different brain regions from MRI scans of healthy adult subjects. There were sex differences in volume, relative to total cerebral volume, and this was especially true in PFC: females had a relatively larger volume of dorsolateral PFC whereas males had a relatively larger volume of OFC."(Kolb, Bryan, and Robbin Gibb. "Brain plasticity and behaviour in the developing brain." Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child & Adolescent Psychiatry 20.4 (2011).)
Functions of the DLPFC (smaller for high androgen exposure)
"DLPFC is known for its involvement in the executive functions, which is an umbrella term for the management of cognitive processes, including working memory, cognitive flexibility (task switching), and planning. [...] DLPFC is not required for the memory of a single item. Thus, damage to the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex does not impair recognition memory. Nevertheless, if two items must be compared from memory, the involvement of DLPFC is required. [...]
Patients with minor DLPFC damage display disinterest in their surroundings and are deprived of spontaneity in language as well as behavior. Patients may also be less alert than normal to people and events they know. Damage to this region in a person also leads to the lack of motivation to do things for themselves and/or for others.
The DLPFC is involved in both risky and moral decision making; when individuals have to make moral decisions like how to distribute limited resources, the DLPFC is activated. This region is also active when costs and benefits of alternative choices are of interest. Similarly, when options for choosing alternatives are present, the DLPFC evokes a preference towards the most equitable option and suppresses the temptation to maximize personal gain. [...]
The DLPFC may also be involved in the act of deception and lying, which is thought to inhibit normal tendency to truth telling. Research also suggests that using TMS on the DLPFC can impede a person's ability to lie or to tell the truth (right hemisphere stimulation decreases lying, left hemisphere stimulation increases lying). [...]
[T]he DLPFC may also play a role in conflict-induced behavioral adjustment, for instance when an individual decides what to do when faced with conflicting rules. [...]
[U]sing imaging studies like PET and fMRI indicate DLPFC involvement in deductive, syllogistic reasoning. Specifically, when involved in activities that require syllogistic reasoning, left DLPFC areas are especially and consistently active.
The DLPFC may also be involved in threat-induced anxiety. (Individuals with greater tonic (resting) activity in right-posterior DLPFC rate themselves as more behaviorally inhibited.)
Social areas in which the role of the DLPFC is investigated (and probably implicated) are, amongst others, social perspective taking and inferring the intentions of other people, or theory of mind; the suppression of selfish behavior, and commitment in a relationship. [...]
The dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is especially under active when a person suffers from chronic schizophrenia.
The DLPFC may contribute to depression.
Substance abuse of drugs, or substance use disorder (SUD), has links to the diminished executive functions of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex."
(source: Wikipedia, "Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex", retrieved 2016-11-04)
Consequences of deficits in dorsolateral prefrontal cortex
"Any damage to the dorsolateral prefrontal region--especially the anterior and mid sections--might impede commitment in relationships. [...] The right dorsolateral prefrontal cortex, coupled with the left temporo-parietal junction, also seems to underpin the capacity of individuals to adopt the perspective of someone else, facilitating reciprocation and cooperation--a capacity that develops during adolescence.
[The DLPFC plays a role in] the capacity of individuals to remember the association between these items. Importantly, event-related fMRI indicates the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex is involved in this process of comparing the two events. [...]
Deficits in the dorsolateral prefrontal region might underpin problem gambling. In particular, deficits in this region often manifest as undue perseveration--in which individuals do not shift their goals or states sufficiently. In addition, individuals who demonstrate problem gambling also show deficits in conditional association tasks, which are supposed to reflect functioning of the posterior-dorsolateral prefrontal region (...). Similarly, when the right dorsolateral prefrontal region is disrupted by TMS, participants are likely to gamble irresponsibly. While gambling, they choose alternatives that could return large amounts of money but are highly improbable (...). [...]
[L]imited activation of the posterior left middle-frontal gyri in this region, as indicated by PET scans, are associated with the transition to schizophrenia."
(source: SicoTests, "Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex", Dr. Simon Moss)
Funtions of the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC) (larger for higher androgen levels)
"We know very little for sure about the OFC, however, and the degree to which the functions ascribed to it [...] are truly regulated by the OFC is still being debated. [...] [A]t this point there is no consensus on what the OFC does and does not do. It seems safe to say that the OFC plays an important role in cognition, but it will take further research to determine what exactly that role is."
High androgen levels linked to ADHD, childhood conduct disorders, autism/Asperger's and status striving
"In the case of ADHD and childhood conduct disorders, substantial evidence indicates that both disorders are enhanced by exposing the brain to high levels of prenatal androgens (...). Accordingly, both conditions should be associated later involvement in delinquency and crime, which is in accordance with findings from many studies (...). The evidence that the autism/Asperger spectrum is promoted by exposing the brain to prenatal androgens is also quite strong (...). [...] Regarding Tourette syndrome, studies have links the condition to high prenatal brain exposure to androgens (...)."
"So important is testosterone to status striving that one research team declared that 'the role of testosterone in human social behavior might be best understood in terms of the search for, and maintenance of, social status' (...). One can assume that when individuals are highly motivated to achieve and maintain status, they will be very sensitive to any potential challenges; as a result, challenges can often provoke violent responses (...). Unfortunately, peers, spouses, and coworkers will be frequent victims of these violent acts."(Ellis, Lee, and Anthony W. Hoskin. "The evolutionary neuroandrogenic theory of criminal behavior expanded." Aggression and violent behavior 24 (2015): 61-74.)
Testosterone increases competitiveness and risk taking
"Research into the effects of testosterone and competitive behaviour suggests that testosterone increases competitiveness and risk taking."(source: Sex ID, Testosterone, BBC Science and nature, retrieved 27-7-2016)
"We did findevidence to support Stark’s hypothesis that testosterone was positively correlated with risk taking."(Ellis, Lee, Anthony W. Hoskin, and Malini Ratnasingam. "Testosterone, Risk Taking, and Religiosity: Evidence from Two Cultures." Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion 55.1 (2016): 153-173.)
Fetal androgen levels can be better predictor of feminine or masculine behaviours than an adult's own levels
"During the second trimester [of gestation of the fetus], androgen level is associated with gender formation. This period affects the femininization or masculinization of the fetus and can be a better predictor of feminine or masculine behaviours such as sex typed behaviour than an adult's own levels."(source: Wikipedia article on Testosteron, retrieved 21/7/2016, which refers to Swaab DF, Garcia-Falgueras A (2009). "Sexual differentiation of the human brain in relation to gender identity and sexual orientation". Functional Neurology 24 (1): 17–28. PMID 19403051)
Fetal T alters the corpus callosum
"Although there was no relationship between fetal testosterone (FT) and midsaggital corpus callosum size, increasing FT was significantly related to increasing rightward asymmetry (e.g., Right>Left) of a posterior subsection of the callosum, the isthmus, that projects mainly to parietal and superior temporal areas. This potential organizational effect of FT on rightward callosal asymmetry may [...] result in an asymmetric distribution of callosal axons. We suggest that this possible organizational effect of FT on callosal asymmetry may also play a role in shaping sexual dimorphism in functional and structural brain development, cognition, and behavior."(source: Psychoneuroendocrinology. 2010 Jan;35(1):122-32. doi: 10.1016/j.psyneuen.2009.09.009, Organizational effects of fetal testosterone on human corpus callosum size and asymmetry, Chura LR, Lombardo MV, Ashwin E, Auyeung B, Chakrabarti B, Bullmore ET, Baron-Cohen S.)
Higher fetal testosterone linked to "approach-related behaviors," such as fun-seeking and impulsivity
"Testosterone levels during early fetal development might program certain behaviors later in life, according to a new study that found high levels of the sex hormone in the womb might boost boys' impulsivity later on.(source: Fetal Testosterone May Program Boys' Behavior, By Live Science Staff | November 5, 2012, retrieved 22/07/2016)
Researchers studied a group of boys ages 8 to 11 whose fetal testosterone had been measured from amniotic fluid when their mothers were 13-20 weeks pregnant.[...] [The study result] suggests that [boys with higher levels of fetal testosterone] have a greater proclivity for "approach-related behaviors," such as fun-seeking and impulsivity. [...] For males, such behaviors are often heightened in teenage years and are found in extremes in many psychiatric conditions, such as substance abuse, autism and even psychopathy, which tend to affect more men than women. [...] 'These remarkable data provide new evidence that hormonal exposures early in life can have lasting impact on brain function and behavior.'"
Terrorism, looting and rioting may be related to high androgen levels
"Among the predictions of ENA theory are (a) that gang members, terrorists, and warriors should have highly androgenized brains, and (b) that the tactics used by all three groups should be similar (e.g., violence, confiscation, destruction). These predictions imply that members of all three groups will be predominantly males, particularly those in their second and third decades of life. While statistical data are limited, what has been reported suggests that, as with criminals generally, terrorists are indeed predominantly adolescent and young adult males (Bakker, 2006; McCauley & Segal, 1987, pp. 232–233; Pape, 2005; Silke, 2003, Thayer & Hudson, 2010)."
"Regardless of what instigates looting and rioting, ENA theory hypothesizes that the individuals involved should have brains that are highly androgenized and relatively low in learning and planning(Ellis, Lee, and Anthony W. Hoskin. "The evolutionary neuroandrogenic theory of criminal behavior expanded." Aggression and violent behavior 24 (2015): 61-74.)
capability. Therefore, they should be predominantly adolescent or young adult males with low executive functioning and low educational attainment. Supportive evidence for these expectations has been reported (Akers & Fox, 1944; Gross, 2011; Lewis et al., 2011; Sears & McConahay, 1969)."
Fetal testosterone linked to variations in grey matter volume of certain brain regions
"In human males, we show that variation in fetal testosterone (FT) predicts later local gray matter volume of specific brain regions in a direction that is congruent with sexual dimorphism observed in a large independent sample of age-matched males and females from the NIH Pediatric MRI Data Repository. Right temporo-parietal junction/posterior superior temporal sulcus (RTPJ/pSTS), planum temporale/parietal operculum (PT/PO), and posterior lateral orbitofrontal cortex (plOFC) had local gray matter volume that was both sexually dimorphic and predicted in a congruent direction by FT. That is, gray matter volume in RTPJ/pSTS was greater for males compared to females and was positively predicted by FT. Conversely, gray matter volume in PT/PO and plOFC was greater in females compared to males and was negatively predicted by FT. Subregions of both amygdala and hypothalamus were also sexually dimorphic in the direction of Male>Female, but were not predicted by FT. However, FT positively predicted gray matter volume of a non-sexually dimorphic subregion of the amygdala. These results bridge a longstanding gap between human and non-human species in showing that FT acts as an organizing mechanism for the development of regional sexual dimorphism in the human brain."(source: Fetal Testosterone Influences Sexually Dimorphic Gray Matter in the Human Brain, Michael V. Lombardo, Emma Ashwin, Bonnie Auyeung, Bhismadev Chakrabarti, Kevin Taylor, Gerald Hackett, Edward T. Bullmore, and Simon Baron-Cohen, J Neurosci. 2012 Jan 11; 32(2): 674–680., retrieved 22/7/2016)
(Gorka, Adam X., et al. "Anterior cingulate cortex gray matter volume mediates an association between 2D: 4D ratio and trait aggression in women but not men." Psychoneuroendocrinology 56 (2015): 148-156.)
"Our analyses revealed a significant positive correlation between 2D:4D ratio and gray matter volume of the dorsal anterior cingulate cortex (dACC), a brain region supporting, emotion regulation, conflict monitoring, and behavioral inhibition. [...] Our results provide novel evidence that 2D:4D ratio is associated with masculinization of dACC gray matter volume, and that this neural phenotype mediates, in part, the expression of trait aggression in women."
Fetal testosterone inversely associated with social development, language development, and empathy; and positively associated with systemizing, attention to detail, and number of autistic traits
"We [...] found that fetal testosterone is inversely associated with social development, language development, and empathy; and that fetal testosterone is positively associated with systemizing, attention to detail, and number of autistic traits."(source: University of Cambridge, Fetal steroid hormones: a longitudinal study, retrieved 22/7/2016)
Fetal Testosterone positively associated with autism, no relationship with IQ test results
"fT (fetal Testosterone) levels were positively associated with higher scores on the CAST (Childhood Autism Spectrum Test) and AQ-Child (Child Autism Spectrum Quotient). This relationship was seen within sex as well as when the sexes were combined, suggesting this is an effect of fT ratherthan of sex per se. No relationships were found between overall IQ and the predictor variables, or between IQ and CAST or AQ-Child. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that prenatal androgen exposure is related to children exhibiting more autistic traits."
(source: British Journal of Psychology (2009), 100, 1–22, Fetal testosterone and autistic traits, Bonnie Auyeung, Simon Baron-Cohen, Emma Ashwin, Rebecca Knickmeyer, Kevin Taylor, and Gerald Hackett)
Testosterone plays an important role in mammalian brain development
"Testosterone plays an important role in mammalian brain development. In neural regions with appropriate receptors testosterone, or its metabolites, influences patterns of cell death and survival, neural connectivity and neurochemical characterization. Consequently, testosterone exposure during critical periods of early development produces permanent behavioural changes. In humans, affected behaviours include childhood play behaviour, sexual orientation, core gender identity and other characteristics that show sex differences (i.e. differ on average between males and females). These influences have been demonstrated primarily in individuals who experienced marked prenatal hormone abnormalities and associated ambiguities of genital development (e.g. congenital adrenal hyperplasia). However, there is also evidence that testosterone works within the normal range to make some individuals within each sex more sex-typical than others. The size of testosterone-related influences, and perhaps even their existence, varies from one sex-typed characteristic to another. For instance: prenatal exposure to high levels of testosterone has a substantial influence on sex-typical play behaviour, including sex-typed toy preferences, whereas influences on core gender identify and sexual orientation are less dramatic. In addition: there appears to be little or no influence of prenatal testosterone on mental rotations ability, although mental rotations ability shows a marked sex difference. These findings have implications for basic understanding of the role of testosterone in normative gender development, as well as for the clinical management of individuals with disorders of sex development (formerly called intersex syndromes)."(source: Prenatal testosterone and gender-related behaviour, Melissa Hines, Department of Psychology, City University, Northampton Square, London EC1V 0HB, UK, retrieved 22/7/2016)
Elevated prenatal testosterone associated with slower social and language development, better attention to detail, autistic traits, and clinically diagnosed autism and Asperger's
"“We previously knew that elevated prenatal testosterone is associated with slower social and language development, better attention to detail, and more autistic traits. Now, for the first time, we have also shown that these steroid hormones are elevated in children clinically diagnosed with autism. Because some of these hormones are produced in much higher quantities in males than in females, this may help us explain why autism is more common in males,” [Simon Baron-Cohen of the University of Cambridge stated in a press release.] He also stated that “[t]hese new results are particularly striking because they are found across all the subgroups on the autism spectrum, for the first time uniting those with Asperger Syndrome, classic autism, or Pervasive Developmental Disorder Not-Otherwise-Specified. We now want to test if the same finding is found in females with autism.”(source: Elevated ‘Male Hormones’ During Fetal Development Linked With Autism, www.iflscience.com, retrieved 22/07/2016, referring to Molecular Psychiatry (2015) 20, 369–376; doi:10.1038/mp.2014.48; published online 3 June 2014, Elevated fetal steroidogenic activity in autism, S Baron-Cohen et al.)
Testosterone can impair emotion-recognition ability, and may link to autism
"Our findings thus reveal a neural mechanism by which testosterone can impair emotion-recognition ability, and may link to the symptomatology of ASC (Autism Spectrum Conditions), in which the same neural network is implicated."(source: Elsevier Psychoneuroendocrinology 68 (2016) 194–201, Testosterone reduces functional connectivity during the ‘Reading the Mind in the Eyes’ Test, Peter A. Bos, Dennis Hofman, Erno J. Hermans, Estrella R. Montoya, Simon Baron-Cohen, Jack van Honk, retrieved 23/7/2016)
High prenatal testosterone linked to lower social skills and more restricted interests, more systemizing and less empathizing, and angular faces
"There are supposed to be five characteristics of the male brain type: aggression, competition, self-assertion, self-confidence and self-reliance. All these are highly correlated with adult testosterone level, whether in men or women. The characteristics of the female brain type are better skills at language, sensory awareness, memory, social awareness and relationships. Male and female brain types are organized in a different way too. For instance, visual spatial perception is found in the right hemispheres in men but in the right and left hemisphere in women. Women use both hemispheres for vocabulary, men use only their left.(source: HORMONES FACTORS IN FETUS GENDER AND CHILD FUTURE DEVELOPMENT, Health Doctrine, retrieved 22/7/2016)
[...]
The researchers found that the higher the levels of prenatal testosterone in the amniotic fluid, the less eye contact the toddlers made, and the smaller their vocabulary. These toddlers were seen again when they were four years old. By this time, those children that had had the highest level of prenatal testoerone had lower social skills and more restricted interests than those who had had lower levels of testosterone in their bath of amniotic fluid.
Fetal testosterone clearly affects the brain in some way and therefore influences behavior for the rest of the baby’s life. In a nutshell, the more you have in the womb, the more of a systemizer you are; the less you have, the more of an empathizer you are. While of course baby boys produce more testosterone, baby girls also produce it, some almost to the levels of the least producing boys. Both sexes are subjected to the hormonal environment in the mother, which is yet another source of testosterone (and indeed oestrogen). In addition to the mother’s natural levels of testosterone (which vary from woman to woman), more may come from other sources.
For instance, vigorous exercise during pregnancy raises testosterone levels, although sustained exercise, such as a long run, lowers testosterone. If a woman is under a great deal of stress during pregnancy, as a result, for example, of bereavement or war, testosterone levels are increased.
[...]
More angular faces are produced by higher levels of fetal testosterone, which promotes the lateral growth of cheekbones and chin (the chiseled masculine jaw which was mentioned earlier). A rounder face, with more prominent lips and higher eyebrows, speaks of lesser levels of testosterone. Facial features are a nightmare to measure in a consistent reproducible way but John Manning, an evolutionary biologist who worked mainly at the University of Manchester, has shown that prenatal testosterone stimulates growth of the fourth finger (look at your left hand, palm up, with your thumb as No. i finger, your fourth is your ring finger). Oestrogen promotes the growth of the second finger (the index finger). A low 2D:4D ratio (fourth finger longer than the second) is a marker for high womb testosterone. A high 2D:4D ratio (second finger longer than the fourth), may be a marker for a womb environment low in testosterone."
Male facial width correlated to testosterone, aggressiveness and propensity to deceive
"Under the influence of [testosterone], men's facial width increases in relation to height (width-height ratio or WHR), independent of body size. WHR is the distance measured from cheekbone to cheekbone versus the distance between the top of the lip and midbrow. A high WHR is 1.9 or above. [...](source: Psychology Today, What's in a face, by Jena Pincott, published Nov.5 2012; retrieved 22-6-2016)
[Aggressive] men had the highest WHRs. [... T]hey also scored highest on an aggression test that measures how often a player steals points from an opponent, to no benefit for the player himself. (Women with high WHRs are perceived as more aggressive than average but aren't, presumably because the skull-shaping pubescent testosterone surge affects males only.)
Male face width is also associated with a propensity to deceive. [... M]en with high WHRs were three times likelier than their narrower-faced peers to lie to increase their financial gain in hypothetical scenarios [...]. While most men with high WHRs—60 percent—did not break the rules, this finding is still startling.
Don't dismiss your instincts, especially if your safety and well-being are at risk. Guesses about trustworthiness based on headshots tend to correlate with those individuals' self-reports and judgments by their acquaintances. In one experiment, people who were perceived as dishonest were likelier to mislead their peers than were those whose faces were thought to look honest. In studies involving the prisoner's dilemma game, participants, going by facial photos alone, could accurately identify people who were likely to deceive, and also remember the faces of prospective cheaters more than cooperators. "
Facial symmetry linked to testosterone and psychopathic behavior
"Psychopathic individuals have greater symmetry than nonpsychopathic individuals [152,153]. This finding may occur because symmetry is related to masculinity [110] and masculinity is a product of testosterone. "(source: The Relationships between Symmetry and Attractiveness and Mating Relevant Decisions and Behavior: A Review; T. Joel Wade; Department of Psychology, Bucknell University, Lewisburg, PA, 17837, USA; retrieved 22-6-2016)
152. Lalumeire, M.L.; Harris, G.T.; Rice, M.E. Psychopathy and developmental instability. Evol.Hum. Behav. 2001, 22, 75–92.153. Reilly, J.L.; Murphy, P.T.; Byrne, M.; Larkin, C.; Gill, M.; O’Callaghan, E.; Lane, A. Dermatoglyphic fluctuating asymmetry and atypical handedness in schizophrenia. Schizophr. Res. 2001, 50, 159–186.110. Scheib, J.E.; Gangestad, S.W.; Thornhill, R. Facial attractiveness, symmetry and cues of good genes. Proc. Roy. Soc. London Ser. B 1999, 266, 1913–1917.
Testosterone associated with male seeking dominance
"In the ultimatum game, one person (‘proposer’) makes an offer to a second person (‘responder’) on how to divide a sum of money. This offer is final—an ultimatum—so if the responder rejects it, there is no agreement, and neither person receives any money. Since rejections result in no money for either party, economic theories of self-interest predict that responders will accept all positive offers (Stahl 1972; Rubinstein 1982). Contrary to these predictions, the first ultimatum game experiment reported that low offers were frequently rejected (Guth et al. 1982). This deviation between behaviour and that predicted by standard theory has been replicated in myriad studies (Roth 1995), including games played for large stakes (Hoffman et al. 1996; Cameron 1999) and cross-culturally (Roth et al. 1991; Henrich et al. 2001). There is no broadly accepted explanation for these rejections, which contradict the standard definition of rationality. [...]
This study examines the relationship between ultimatum game rejections and testosterone. In a variety of species, testosterone is associated with male seeking dominance. If low ultimatum game offers are interpreted as challenges, then high-testosterone men may be more likely to reject such offers. In this experiment, men who reject low offers ($5 out of $40) have significantly higher testosterone levels than those who accept."
(source: High-testosterone men reject low ultimatum game offers, Terence C Burnham, Published 22 September 2007, DOI: 10.1098/rspb.2007.0546)
Testosterone inhibits acute fear and promotes reactive dominance
"[T]estosterone shifts reflexive as well as deliberate behaviors towards dominance and promotion of social status. Testosterone inhibits acute fear at the level of the basolateral amygdala and hypothalamus and promotes reactive dominance through upregulation of vasopressin gene expression in the central-medial amygdala. Finally, the hormone can, depending on social context and prenatal hormone exposure, promote both pro- and antisocial behaviors and decisions through its effects on prefrontal–amygdala interactions. All these effects of testosterone, however, serve to increase and maintain social status."
(source: Approach–Avoidance versus Dominance–Submissiveness: A Multilevel Neural Framework on How Testosterone Promotes Social Status, David Terburg, Jack van Honk, Emotion Review July 2013 vol. 5 no. 3 296-302)
Testosterone biases the organism toward threat approach and away from threat avoidance
"The present study [...] provides evidence for a neuroendocrine mechanism in which testosterone biases the organism toward threat approach and away from threat avoidance by modulating amygdala responses. This enhances our understanding of the processes by which testosterone primes the individual for defense of its status in social challenges. Activational effects of testosterone, such as increased vigilance and up-regulation of neural circuits mediating aggression, inhibition of fear responses, and facilitated threat approach, further contribute to adaptive responding. In competitive interactions, testosterone has been shown to promote status not only by means of overt aggression but also by more subtle dominance displays, such as increased reciprocity. [...]
Lower testosterone levels were observed in patients with social anxiety disorder, patients with generalized anxiety disorder, and patients with depression."
(source: Testosterone biases the amygdala toward social threat approach, Sina Radke et.al., Science Advances 12 Jun 2015: Vol. 1, no. 5, e1400074, DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.1400074)
Delinquent group has higher salivary testosterone levels (and equal cortisol)
"Salivary testosterone and Cortisol levels were measured in 36 U.S. college students and 29 delinquent participants of a similar age. Both groups of participants were made up of White men and women. The delinquent group, which was characterized by flamboyant dress, drug use, and violence, had significantly higher testosterone levels than the college students did, but the two groups did not differ regarding Cortisol levels. Testosterone and Cortisol were positively correlated in the women."
(source: Terry Banksa & James M. Dabbs Jr., "Salivary Testosterone and Cortisol in a Delinquent and Violent Urban Subculture", The Journal of Social Psychology, Volume 136, Issue 1, 1996)
(Lai, Meng-Chuan, et al. "Biological sex affects the neurobiology of autism." Brain 136.9 (2013): 2799-2815.)
(source: http://www.cam.ac.uk/research/news/extra-testosterone-reduces-your-empathy)High testosterone (independently of cortisol) linked to religious agression, low cortisol (independently of testosterone) linked to conventional aggression
"The researchers asked [fifty-three 14-year-old Muslim Palestinian boys, all of whom were refugees] if they agreed with two statements concerning “religiously conditioned political aggression”:(source: The biochemistry of religious aggression, February 26, 2011 by Epiphenom)
- “Religious ends justify any means” (43% agreed)
Those boys who agreed with the first statement also had higher testosterone levels (although there was no relationship with the second statement). Perhaps surprisingly, however, there was no correlation between conventional aggression and testosterone levels.
- “Harming civilians is a justifiable tool in a Muslim arsenal.” (22% agreed)
Conversely, there was no link between religious aggression and cortisol levels. Conventionally aggressive boys did, however, have low levels of cortisone.
Even stranger, there was no correlation at all between religious aggression and conventional aggression.
These results can perhaps be understood when you realise that testosterone is not really the ‘aggression’ hormone it’s often portrayed to be. In fact, testosterone seems really to be a ‘success’ or ‘social dominance’ hormone. Winners have high testosterone."
Female autists have neural 'masculinization'
"[A]typical brain areas in females with autism substantially and non-randomly [...] overlapped with areas that were sexually dimorphic in neurotypical controls, in both grey and white matter, suggesting neural ‘masculinization’."
(Lai, Meng-Chuan, et al. "Biological sex affects the neurobiology of autism." Brain 136.9 (2013): 2799-2815.)
Average testosterone levels during lifespan
Males have an average testosterone level that is 10 times as high than that of females, throughout their lifespan.
(image source: Ellis, Lee, and Anthony W. Hoskin. "The evolutionary neuroandrogenic theory of criminal behavior expanded." Aggression and violent behavior 24 (2015): 61-74.)
Administration of testosterone reduces ability to mind read in women; effect more pronounced in individuals with high prenatal testosterone
"A new study from Utrecht and Cambridge Universities has for the first time found that an administration of testosterone under the tongue in volunteers negatively affects a person’s ability to ‘mind read’, an indication of empathy.[...]
The researchers not only found that administration of testosterone leads to a significant reduction in mind reading, but that this effect is powerfully predicted by the 2D:4D digit ratio, a marker of prenatal testosterone. Those people with the most masculinized 2D:4D ratios showed the most pronounced reduction in the ability to mind read.
Jack van Honk said: 'We are excited by this finding because it suggests testosterone levels prenatally prime later testosterone effects on the mind.'"
High estrogen levels associated with poor spatial ability and depressive effect on right hemisphere
"It has been found that high oestrogen levels during the luteal phase are associated with poorer performance in tests of spatial ability (Hampson, 1990; Moody, 1997; Phillips & Silverman, 1997; McCormick & Teillon, 2001). During this phase, women also perform worse than those taking oral contraceptives (McCormick & Teillon, 2001). Functional cerebral asymmetry changes in a way consistent with the notion that oestrogen has a depressive effect on right hemisphere function (Sanders et al. 2002)."
Higher prenatal testosterone linked to increased approach behavior in later life
"[I]ncreasing FT (fetal testosterone) predicts increased behavioral approach tendencies by biasing caudate, putamen, and nucleus accumbens but not amygdala to be more responsive to positive compared with negatively valenced cues. In contrast, FT was not predictive of behavioral avoidance tendencies, either through direct or neurally mediated paths."Approach behavior is when a person moves toward a desired goal, avoidance behavior is when a person moves away from something undesired. In this study, higher levels of FT are linked to increased approach behavior (which in more extreme cases becomes pathological behavior like drug abuse and sociopathic behavior), and no effect on avoidance behavior was noted.
(Lombardo, Michael V., et al. "Fetal programming effects of testosterone on the reward system and behavioral approach tendencies in humans." Biological psychiatry 72.10 (2012): 839-847.)
High prenatal testosterone elevates probability of offending later in life
"Evolutionary neuroandrogenic (ENA) theory asserts that criminality is a crude form of competitive behavior over resources, status, and mating opportunities. Theoretically, males have been selected for resource acquisitiveness as a result of female preferences for mates who are successful at resource provisioning. ENA theory also asserts that brain exposure to both prenatal and postpubertal androgens (particularly testosterone) promotes all forms of competitiveness, including those that victimize others. [...R]esults [...] largely supported the hypothesized connection between offending and high prenatal androgen exposure, even when findings were analyzed separately by sex. Also, offending was significantly associated with r2D:4D for both males and females. Overall, this study supports the view that exposing the brain to high levels of testosterone and other androgens prenatally elevates the probability of offending later in life."
(Hoskin, Anthony W., and Lee Ellis. "Fetal testosterone and criminality: test of evolutionary neuroandrogenic theory." Criminology 53.1 (2015): 54-73.)
Evolutionary neuroandrogenic (ENA) theory surpasses general theory in predictive scope and accuracy
"General theory attributes criminal behavior primarily to low self-control, whereas evolutionary neuroandrogenic (ENA) theory envisions criminality as being a crude form of status-striving promoted by high brain exposure to androgens. [...] ENA theory's predictions of positive correlations between pain tolerance, muscularity, and offending were largely confirmed. For the 10 hypotheses tested, ENA theory surpassed general theory in predictive scope and accuracy."
(Ellis, Lee, et al. "General Theory versus ENA Theory Comparing Their Predictive Accuracy and Scope." International journal of offender therapy and comparative criminology 59.13 (2015): 1429-1458.)
Complex relationship between androgens and religiosity
"Are androgens related to religiosity? The answer is affirmative for androgen exposure linked to muscular coordination. [...R]eligiosity was significantly correlated with postpubertal androgens (for both genders and both countries [USA and Malaysia). [...] For some reason, among both males and females, high exposure to androgen regimens responsible for muscularity, strength, and athletic ability seem to promote religiosity rather than inhibiting it.
When attention is given to the inverted r2D:4D measure, nearly all of the correlations are null.
For the bone growth androgen factor, the correlations were negative and statistically significant in the Malaysian sample, while they were significant and positive for females and for the sexes combined in the U.S. sample."
(Ellis, Lee, Anthony W. Hoskin, and Malini Ratnasingam. "Testosterone, Risk Taking, and Religiosity: Evidence from Two Cultures." Journal for the Scientific Study of Religion 55.1 (2016): 153-173.)
Prenatal androgen exposure and sexual orientation, a new neurohormonal theory
(Ellis, Lee, et al. "Putative Androgen Exposure and Sexual Orientation: Cross‐Cultural Evidence Suggesting a Modified Neurohormonal Theory." The journal of sexual medicine 12.12 (2015): 2364-2377.)
"Cell A represents variations in prenatal androgen exposure and shows the typical range to which genetic males and genetic females are normally exposed. In cell B, the original version of neurohormonal theory is represented, and in cell C one finds the version we propose instead."
High prenatal testosterone leads to crude violence in adolescence, which is refined in adulthood
"Adolescent expressions of competitive/victimizing behavior are often crude, thus frequently manifesting themselves in the form of behavior that others seek to suppress. By full adulthood, most individuals with highly androgenized brains will have transitioned from crude forms to refined forms of competitive/victimizing behavior, typically as part of their normal occupational and financial activities. The theory asserts that learning ability as well as opportunities to learn forms of competition that minimally victimize others, determines how fast individuals transition from crude to refined forms of competitiveness. In the present article, ENA theory is elaborated upon and used to explain three phenomena not previously addressed by the theory: (a) the rise of the criminal justice system, (b) the criminalization of victimless offenses, and (c) gang activities and terrorism. According to the theory, all of these phenomena have similar evolutionary and neurohormonal underpinnings."(Ellis, Lee, and Anthony W. Hoskin. "The evolutionary neuroandrogenic theory of criminal behavior expanded." Aggression and violent behavior 24 (2015): 61-74.)
High testosterone is risk factor in child sex abuse
“Testosterone is involved in several of the most important risk factors for committing child sex abuse, including high sexual arousal, diminished self-control and low empathy,” says [Christoffer] Rahm [, psychiatrist and lead researcher at the Karolinska Institute in Stockholm].(source: Swedish scientists offer drug to pedophiles to stop them from sexually abusing kids, RT)
Increased testosterone causes decreased gray matter in brain's language regions, and increased fiber tract strength and functional connectivity between them
"[...] [A]nalysis showed decreased gray matter volume with increasing levels of bioavailable testosterone exclusively in Broca's and Wernicke's areas. Particularly, this may link known sex differences in language performance to the influence of testosterone on relevant brain regions. [...] [W]e further observed [what] potentially reflects a strengthening of the fiber tract particularly involved in language comprehension.[...]. Finally, [we observed] increased functional connectivity between the two brain regions with increasing testosterone levels. These findings suggest testosterone-dependent neuroplastic adaptations in adulthood within language-specific brain regions and connections. Importantly, deteriorations in gray matter volume seem to be compensated by enhancement of corresponding structural and functional connectivity."
(Hahn, Andreas, et al. "Testosterone affects language areas of the adult human brain." Human brain mapping 37.5 (2016): 1738-1748.)
High testosterone linked to polyamorous relationships
"Men who were partnered [= monogamous] had lower T [Testosterone] than all other men, and polyamorous men had higher T than single men. Polyamorous women had higher T than all other women."
(van Anders, Sari M., Lisa Dawn Hamilton, and Neil V. Watson. "Multiple partners are associated with higher testosterone in North American men and women." Hormones and Behavior 51.3 (2007): 454-459.)
Major human advances in civilization linked to decrease in testosterone
"Humans went through a major development 50,000 years ago, when the species, which first developed 150,000 years earlier, started to develop tools and art started to flourish.
Testosterone levels in humans were beginning to moderate down to modern concentrations around the same time, according to a new study. [...]
Researchers believe that lower levels of the male hormone may have led to a greater degree of understanding between people, reducing violence, allowing arts and tool making to become more advanced.
"The modern human behaviors of technological innovation, making art and rapid cultural exchange probably came at the same time that we developed a more cooperative temperament," Robert Cieri, from the University of Utah and lead author of the study, said.
Decreasing testosterone levels were noticeable through the changes to the shape of human skulls from the period. Thick eyebrow ridges receded, as heads became rounder."
(New study links lower testosterone levels to march of human civilization, Techtimes, aug. 3d 2014)
Chimps release testosterone when stressed, bonobos cortisol
"Male chimpanzees experience a large increase in testosterone levels during puberty, while concentrations among bonobos is small. When chimps become stressed, their bodies release additional testosterone, while cortisol, a hormone related to stress, floods the bloodstream of bonobos. Social interactions between chimpanzees are much more prone to violence than similar incidents between bonobos. Brow ridges are also much more pronounced in chimps than they are in the mellower species."
(New study links lower testosterone levels to march of human civilization, Techtimes, aug. 3d 2014)
High testosterone linked to antisocial behavior, inhibition of social empathy, incapacity for cooperative problem-solving
"High circulatory levels of the androgen testosterone are associated with aggression and dominance behavior, including antisocial behavior and rebellion against authority (Archer 1991; Higley et al. 1996; Mazur and Booth 1998). Testosterone has also been observed to constrain some forms of social cognition and sociality, both through prenatal developmental effects on brain organization and activationally through inhibition of social empathy in adults (Baron-Cohen, Knickmeyer, and Belmonte 2005; Pennebaker et al. 2004; van Honk et al. 2011). Androgens appear to be implicated in temperament differences between chimpanzees and bonobos and may account in part for differences in cooperative problem-solving ability between these species (Hare et al. 2007; Wobber et al. 2010). Bonobo males do not show pubertal spikes in testosterone levels (Wobber et al. 2013) and are thought to have lower prenatal and circulating testosterone levels than their chimpanzee counterparts (Mcintyre et al. 2009; Sannen et al. 2003). Also, unlike chimpanzees, bonobos do not exhibit elevated levels of testosterone in anticipation of competing for food (Wobber et al. 2010). This may be part of the mechanism that allows bonobos to share potentially monopolizable food after jointly solving instrumental cooperation problems—problems that chimpanzees understand but appear to lack the social tolerance to solve (Hare et al.
2007)."
(Cieri, Robert L., et al. "Craniofacial feminization, social tolerance, and the origins of behavioral modernity." Current Anthropology 55.4 (2014): 419-443.)
Men with low 2D:4D digit ratio invest more time and effort in courting women
One study found that "Fetal exposure to androgens, as indicated by digit ratios (2D: 4D), increases men’s agreeableness with women".
"Men were more agreeable towards women than men; this effect was significantly greater in those with smaller 2D:4D ratios. Men with smaller 2D:4D ratios were also less quarrelsome towards women than towards men."
(Moskowitz, D. S., et al. "Fetal exposure to androgens, as indicated by digit ratios (2D: 4D), increases men’s agreeableness with women." Personality and Individual Differences 75 (2015): 97-101.)
As the lead author described it herself:
“When with women, men with smaller ratios were more likely to listen attentively, smile and laugh, compromise or compliment the other person,” says Debbie Moskowitz, lead author and Professor of Psychology at McGill.However, a follow-up study found that the men with low 2D:4D ratios actually engaged more in courting behavior, rather than simply "being agreeable". In other words, they were probably agreeable in order to obtain a certain result, which is much more in accordance with other studies concerning the behavior of men with high prenatal testosterone levels.
(Can you judge a man by his fingers?, McGill University, retrieved 2016-11-28)
"In Study 1, masculinized digit ratios (low digit ratios, high prenatal testosterone) in men were associated with greater courtship-related consumption to acquire mates, and this association was stronger for men with high mating confidence. In women, feminized digit ratios (high digit ratios, low prenatal testosterone) were associated with greater courtship-related consumption to acquire mates. In Study 2, men with masculinized digit ratios engaged in greater courtship-related consumption by offering romantic gifts as a means of retaining mates. In women, feminized digit ratios were associated with greater romantic gift giving. Our findings suggest that high prenatal testosterone in men leads to greater courtshiprelated consumption, whereas low prenatal testosterone leads to greater courtship-related consumption in women."
(Nepomuceno, Marcelo Vinhal, et al. "Testosterone at your fingertips: Digit ratios (2D: 4D and rel2) as predictors of courtship-related consumption intended to acquire and retain mates." Journal of Consumer Psychology 26.2 (2016): 231-244.)
Explained in more simple terms, in this blog article:
"Recent research has found that men with lower 2D:4D ratios are nicer to women than men with higher 2D:4D ratios. According to the study’s lead author, Debbie Moskowitz, “when with women, men with smaller ratios were more likely to listen attentively, smile and laugh, compromise, or compliment the other person.” Men with higher 2D:4D ratios tend to have a more difficult time getting along with women.
A follow-up study by another group of researchers found that men with lower 2D:4D ratios make greater efforts to impress women while courting them compared to men with higher 2D:4D ratios. They’re more likely to buy things like flowers and spend more on dates. What’s more, men with low 2D:4D ratios tend to spend more time and money on their appearance than men with higher 2D:4D ratios.
These findings might seem counterintuitive: wouldn’t a more masculine, “alpha” man have trouble getting along with women, and not care about things like style and romance? And wouldn’t a more feminized man find it easier to get along with women?
A man with more T, however, may be more driven to reproduce, and is thus more motivated to learn how to woo women, while men with lower T have less of this drive, and thus care less about their success with the ladies."
(What the Length of Your Ring Finger Can Tell You About Your Masculinity, retrieved 2016-11-28)
Low 2D:4D women prefer masculinized faces (high testosterone) for short- and long-term mates, don't bond well and are more promiscuous,
high 2D:4D women prefer less masculinized faces for long-term mates, bond well, are sexually reserved
"[C]ompared with high 2D:4D females, low 2D:4D females were psychologically de-feminized (measured by the Bem Sex Role Inventory), [...], bonded poorly to their fathers (...), reported shorter intimate relationships with males, and preferred a more masculine male face around ovulation. Although all women had a preference for a masculinized STM (short-term mate) who was not significantly different from their attractive male choice, only low 2D:4D women desired similar masculine attributes in their LTMs (long-term mate).
It has been shown that women who prefer masculinized LTMs also like the odor of 4,16-androstadien-3-ol, a putative male pheromone. Furthermore, women with low 2D:4D digit ratios also score high on the Sociosexual Orientation Inventory, a measure of their willingness to engage in uncommitted sexual activity, and they might also have an impaired resistance to parasites. Taken together, these findings indicate that low 2D:4D women are more attracted to a male's secondary sexual characteristics (facial androgen markers and male pheromones), prefer such ‘good genes’ males as mates (STM, LTM, and at ovulation), but don't bond well (low paternal bonding, short relationships, and promiscuity), perhaps as a consequence of their emotional structure (de-feminized). By contrast, high 2D:4D females are stereotypically female, bond well to males, are sexually reserved, and seek less masculinized males for LTMs, or when there is a high probability of conception."(Johnston, Victor S. "Mate choice decisions: the role of facial beauty." Trends in cognitive sciences 10.1 (2006): 9-13., Part 1, Part 2)
Low 2D:4D women are less "feminine", prefer more masculinized long-term mates, and report shorter intimate relationships, less parental bonding and more menstrual irregularity
"The results indicated that(Scarbrough, Pamela S., and Victor S. Johnston. "Individual differences in women's facial preferences as a function of digit ratio and mental rotation ability." Evolution and Human Behavior 26.6 (2005): 509-526.)
(a) femininity scores [as measured by the Bem Sex-Role Inventory (BSRI)] decreased with decreasing 2D:4D,
(b) masculinity scores increased with faster MR (mental rotation),
(c) women preferred a more masculine male face for an STM (short-term mate) than for an LTM (long-term mate), and
(d) preference changes over the menstrual cycle varied systematically with 2D:4D.
When compared with women with high 2D:4D ratios, low 2D:4D women
(e) preferred a more masculine LTM (long-term mate),
(f) recalled less parental bonding,
(g) had shorter intimate relationships, and
(h) reported more menstrual irregularity."
This study however finds no correlation between 2D:4D ratio in women and self-reported sociosexuality (the development and maintenance of interest in uncommitted sexual activity):
"In sum, these data suggest that factors other than prenatal and circulating hormones explain the sex differences in self-reports of sociosexuality."
(Charles, Nora E., and Gerianne M. Alexander. "The association between 2D: 4D ratios and sociosexuality: a failure to replicate." Archives of sexual behavior 40, no. 3 (2011): 587-595.)
Prenatal testosterone increases approach behavior later in life: reduced fear, lower sensitivity to punishment, increased risk-tasking, and enhanced attention to threat
"Testosterone levels early in fetal development influence later sensitivity of brain regions related to reward processing and affect an individual's susceptibility to engage in behavior, that in extremes, are related to several neuropsychiatric conditions that asymmetrically affect one sex more than the other. [...] In adults and adolescents, heightened testosterone has been shown to reduce fear, lower sensitivity to punishment, increase risk-tasking, and enhance attention to threat. These effects interact substantially with context to affect social behavior. [...](Lombardo, Michael V., et al. "Fetal programming effects of testosterone on the reward system and behavioral approach tendencies in humans." Biological psychiatry 72.10 (2012): 839-847.)
'This study is the first to directly examine whether testosterone in fetal development predicts tendencies later in life to engage in approach-related behavior (e.g., fun-seeking, impulsivity, reward responsivity) and also how it may influence later brain development that is relevant to such behaviors,' said first author Lombardo. [...]
[I]ncreased fetal testosterone levels predicted increased behavioral approach tendencies later in life via its influence on the brain's reward system. [...]
'This work highlights how testosterone in fetal development acts as a programming mechanism for shaping sensitivity of the brain's reward system later in life and for predicting later tendency to engage in approach-related behaviors. These insights may be especially relevant to a number of neuropsychiatric conditions with skewed sex ratios and which affect approach-related behavior and the brain's reward system.'
Dr. John Krystal, Editor of Biological Psychiatry, commented, 'These remarkable data provide new evidence that hormonal exposures early in life can have lasting impact on brain function and behavior.'"
Girls exposed to high levels of androgen prenatally show increased male-typical play
"Girls exposed to high levels of androgen prenatally, because of the genetic disorder congenital adrenal hyperplasia, show increased male-typical play, suggesting similar hormonal influences on human development, at least in females. Here, we report that fetal testosterone measured from amniotic fluid relates positively to male-typical scores on a standardized questionnaire measure of sex-typical play in both boys and girls."(Auyeung, Bonnie, et al. "Fetal testosterone predicts sexually differentiated childhood behavior in girls and in boys." Psychological science 20.2 (2009): 144-148. (full text))
The lower the 2D:4D ratio (the higher prenatal testosterone), the higher the salary
"left hand 2D:4D [...] [is] negatively correlated with [...] [female] individuals’ salaries. [...] In the male subsample it is more complicated: there is a relation between [left] 2D:4D and [...] wage controlled for age, but adding level of education makes this relation no longer significant. This possibly implies that 2d:4d affects male wages mostly through education, but in the case of women there is also an effect of 2D:4D by itself."(Nye, John V., et al. "The effects of prenatal testosterone on adult wages: Evidence from russian rlms data and measured 2d: 4d digit ratios." (2014).)
Higher prenatal testosterone linked to higher wages in men, not women
"[We tested] the link between prenatal exposure to testosterone and labor market earnings. For men, the results suggest positive returns to testosterone exposure. For women, however, the results indicate that prenatal testosterone does not generate higher earnings and may even be associated with modest declines."(Gielen, Anne C., Jessica Holmes, and Caitlin Myers. "Prenatal testosterone and the earnings of men and women." Journal of Human Resources 51.1 (2016): 30-61.)
Sudden surges in testosterone levels in males may be a factor in financial disasters
"[M]ale traders, driven by an increase in testosterone due to a successful investment, [may] take exaggerated risks, which, in turn, create price bubbles."(Danny Cohen-Zada, Alex Krumer, Ze'ev Shtudiner. Psychological momentum and gender. Journal of Economic Behavior & Organization, 2017; 135: 66 DOI: 10.1016/j.jebo.2017.01.009)
In sheep, testosterone increases cell body size and outgrowth and number of branch points of neurons
"Treatment with testosterone (10 nM) for 3 days significantly (P < 0.05) increased both total neurite outgrowth (35%) and soma (cell body) size (8%) in the HPOA (hypothalamus-preoptic area) and outgrowth (21%) and number of branch points (33%) in the CTX (cerebral cortex). These findings indicate that testosterone-induced somal enlargement and neurite outgrowth in fetal lamb neurons may contribute to the development of a fully masculine sheep brain."
(Reddy RC, Amodei R, Estill CT, Stormshak F, Meaker M, Roselli CE. Effect of Testosterone on Neuronal Morphology and Neuritic Growth of Fetal Lamb Hypothalamus-Preoptic Area and Cerebral Cortex in Primary Culture. Migaud M, ed. PLoS ONE. 2015;10(6):e0129521. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0129521.)
Masculinized finger-length ratios linked to Disruptive Behavior Disorders, low conscientiousness, effortful control, high activity levels and sensation-seeking, high aggression, and slow neural development in utero
"[H]igh prenatal testosterone exposure seems to increase risk for DBD (Disruptive Behavior Disorders) symptoms particularly in males by increasing susceptibility to prenatal environmental stressors.
(...)
High levels of prenatal testosterone exposure, measured indirectly using masculinized finger-length ratios, have been associated with DBD and ADHD during childhood and adulthood, as well as associated behavioral traits including low conscientiousness/effortful control, high activity levels and sensation-seeking, and high aggression (Geschwind & Galaburda, 1985; Fink et al., 2006; Fink et al., 2007; Martel et al., 2008; McFadden et al., 2005).(...)Theory suggests that high levels of prenatal testosterone slow down neural development in utero in males compared to females [...]."
(Martel MM, Roberts BA. Prenatal Testosterone Increases Sensitivity to Prenatal Stressors in Males with Disruptive Behavior Disorders. Neurotoxicology and teratology. 2014;44:11-17. doi:10.1016/j.ntt.2014.05.001.)
Low 2D:4D ratio linked to sensation seeking in men (not women)
"Furthermore, right- and left-hand 2D:4D in males was significantly negatively associated with total sensation seeking score, and the boredom subscale. No significant associations were found for women. Since low 2D:4D is supposed to indicate exposure to higher levels of T in utero, our data suggest that there may be an organizational effect of T which influences later development of sensation seeking personality characteristics in men."
(Fink, Bernhard, et al. "Second to fourth digit ratio and sensation seeking." Personality and Individual Differences 41.7 (2006): 1253-1262.)
(Testosterone Modulates Altered Prefrontal Control of Emotional Actions in Psychopathic Offenders
Inge Volman, Anna Katinka Louise von Borries, Berend Hendrik Bulten, Robbert Jan Verkes, Ivan Toni, Karin Roelofs, eNeuro 15 January 2016, 3 (1) ENEURO.0107-15.2016; DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0107-15.2016)
Slash fiction = a genre of fan fiction that focuses on interpersonal attraction and sexual relationships between fictional characters of the same sex (such as Star Trek’s Kirk and Spock, or Sherlock’s Sherlock Holmes and John Watson). While the term was originally restricted to stories in which male media characters were involved in an explicit sexual relationship as a primary plot element (also known as "slash" or "m/m slash"), it is now used to refer to any fan story containing a pairing between same-sex characters.
(Salmon, Catherine. "The impact of prenatal testosterone on female interest in slash fiction." Evolutionary Behavioral Sciences 9.3 (2015): 161.)
Prenatal testosterone affects architecture of dendrites (neuron branches) in animals
"Treatment of castrated rats with physiological levels of testosterone significantly reduced dendritic length, volume and terminal branch number relative to the castrated rats receiving empty silastic capsules."(Danzer, Steve C., Nathaniel T. McMullen, and Naomi E. Rance. "Testosterone modulates the dendritic architecture of arcuate neuroendocrine neurons in adult male rats." Brain research 890.1 (2001): 78-85.)
"Animal models have demonstrated the prenatal testosterone can affect dendritic arborization and the number of neurons within sexually dimorphic brain regions (Cooke and Woolley, 2005; Morris et al., 2004)."(Gorka, Adam X., et al. "Anterior cingulate cortex gray matter volume mediates an association between 2D: 4D ratio and trait aggression in women but not men." Psychoneuroendocrinology 56 (2015): 148-156.)
"These findings indicate that gonadal steroids have a profound impact on the morphology of dendrites and patterns of synaptic connectivity."(Cooke, Bradley M., and Catherine S. Woolley. "Gonadal hormone modulation of dendrites in the mammalian CNS." Journal of neurobiology 64.1 (2005): 34-46.)
Significant link between male brain in women and autism
"79.6% of women with autism have a male brain, and women with a male brain are 3 times more likely to have autism"(Prof. Simon Baron-Cohen on Twitter, mentioning the study Association Between the Probability of Autism Spectrum Disorder and Normative Sex-Related Phenotypic Diversity in Brain Structure, doi:10.1001/jamapsychiatry.2016.3990)
Psychopathic offenders with highest testosterone have biggest emotional regulation problems
"[I]n people with psychopathy, this prefrontal region — necessary for controlling emotional behavior — showed a blunted response and reduced connectivity with the amygdala when they were engaged in controlling their emotional action tendencies. This cerebral pattern was strongest in psychopathic individuals with high endogenous testosterone levels.
The research results provide a neuro-hormonal explanation for emotional regulation problems in psychopathic patients. Furthermore, the results provide starting points for the treatment of psychopaths by influencing the amount of testosterone in their bodies."
(Testosterone Modulates Altered Prefrontal Control of Emotional Actions in Psychopathic Offenders
Inge Volman, Anna Katinka Louise von Borries, Berend Hendrik Bulten, Robbert Jan Verkes, Ivan Toni, Karin Roelofs, eNeuro 15 January 2016, 3 (1) ENEURO.0107-15.2016; DOI: 10.1523/ENEURO.0107-15.2016)
Eating disorders linked to low 2D:4D ratio (high prenatal testosterone)
"Findings suggest that children at high-risk for BN (bulimia nervosa) may be exposed to higher levels of testosterone in utero."(Kothari, R., Gafton, J., Treasure, J. and Micali, N. (2014), 2D:4D Ratio in children at familial high-risk for eating disorders: The role of prenatal testosterone exposure. Am. J. Hum. Biol., 26: 176–182. doi:10.1002/ajhb.22495)
Link between high prenatal testosterone, left-handedness and delinquency
"Prenatal exposure to high levels of testosterone may lead to increased probability of left-handedness. Extrapolating from arguments by Mazur & Booth leads to a prediction of increased incidence of antisocial behavior among left-handers. Six hundred ninety-four males were tested for seven indicators of delinquency in high school. Left-handers were more likely to display such behaviors, providing indirect evidence for the hypothesized behavioral effects of testosterone."(Coren, Stanley. "Prenatal testosterone exposure, left-handedness, and high school delinquency." Behavioral and Brain Sciences 21.03 (1998): 369-370.)
Female slash fiction readers have lower 2D:4D ratios (higher prenatal testosterone)
"Female slash readers had significantly lower 2D:4D ratios than females who were not readers of slash fiction, indicating higher prenatal testosterone exposure, thereby supporting the hypothesis that prenatal testosterone exposure may influence individual differences in preferences for erotic literature."
Slash fiction = a genre of fan fiction that focuses on interpersonal attraction and sexual relationships between fictional characters of the same sex (such as Star Trek’s Kirk and Spock, or Sherlock’s Sherlock Holmes and John Watson). While the term was originally restricted to stories in which male media characters were involved in an explicit sexual relationship as a primary plot element (also known as "slash" or "m/m slash"), it is now used to refer to any fan story containing a pairing between same-sex characters.
(Salmon, Catherine. "The impact of prenatal testosterone on female interest in slash fiction." Evolutionary Behavioral Sciences 9.3 (2015): 161.)
Lower 2D:4D ratio linked to greater likelihood of self-employment
"The results indicated males with a lower 2D:4D ratio in their left hand, or higher prenatal testosterone exposure, have a significantly greater likelihood of self-employment. This was also found to be marginally significant for females."
“Higher levels of testosterone can not only enhance an individual’s willingness to take risks but also diminish the likelihood that they feel fear with regards to risky situations, when coupled together it is possible that individuals with higher levels of testosterone could be prone to engage in entrepreneurial activities and self-employment.”(Forget about going into business, girls - we just don't have what it takes, Cambridge news, Jenny Chapman, 27 apr 2017, mentioning the study by Nicolaou, Nicos, Pankaj C. Patel, and Marcus T. Wolfe. "Testosterone and Tendency to Engage in Self-Employment." Management Science (2017).)
Testosterone decreases cognitive reflection
"The researchers found that men given doses of testosterone performed more poorly on a test designed to measure cognitive reflection than a group given a placebo.(Testosterone Makes Men Less Likely to Question Their Impulses, Neuroscience News, Apr. 28, 2017)
(...)
“What we found was the testosterone group was quicker to make snap judgments on brain teasers where your initial guess is usually wrong,” says Caltech’s Colin Camerer, the Robert Kirby Professor of Behavioral Economics and T&C Chen Center for Social and Decision Neuroscience Leadership Chair. “The testosterone is either inhibiting the process of mentally checking your work or increasing the intuitive feeling that ‘I’m definitely right.'”
(...)
Participants were not limited on time while taking the test and were offered $1 for each correct answer and an additional $2 if they answered all the questions correctly.
The results show that the group that received testosterone scored significantly lower than the group that received the placebo, on average answering 20 percent fewer questions correctly. The testosterone group also “gave incorrect answers more quickly, and correct answers more slowly than the placebo group,” the authors write. The same effect was not seen in the results of the basic math tests administered to both groups. The results “demonstrate a clear and robust causal effect of [testosterone] on human cognition and decision-making,” they conclude.
(...)
Camerer says (...) "Do [men in take testosterone replacement therapy] become too mentally bold and thinking they know things they don’t?”
High salivary testosterone linked to utilitarian morality
"Studies involving human and nonhuman animals indicate that high basal testosterone is associated with decreased aversion to risk and an increased threshold for conflict, fear, stress, and threat. We tested the role of testosterone in moral decision making. We predicted and found that individuals high in (basal salivary) testosterone are more likely to make utilitarian decisions—specifically when doing so involves acts of aggression and social cost.
(...)
Looking specifically at the testosterone levels of the individuals who endorsed pushing versus not pushing the man in the footbridge dilemma, those willing to push (...) were significantly higher on basal testosterone than those unwilling to push the man (...).
(...)
Consistent with our hypothesis, intransigent utilitarians had significantly higher basal testosterone levels than those who no longer endorsed utilitarian outcomes when achieved through action which violated a strong moral norm. In other words, high-testosterone individuals appear willing to endorse a tough and costly decision, provided it promotes the greater good.
(...)
The implication of these results extends beyond ethics and moral reasoning and illuminates how high-testosterone individuals reason and behave generally. A heightened focus on outcomes and disregard for the cost of pursuit may help explain why individuals high in testosterone have more success on Wall Street and in other contexts (Coates & Herbert, 2008) where success requires insensitivity to some of the more immediate consequences of one’s actions."
(Carney, Dana R., and Malia F. Mason. "Decision making and testosterone: when the ends justify the means." Journal of Experimental Social Psychology 46.4 (2010): 668-671.)
T administration changes moral behavior
"T administration was associated with increased utilitarian behavior within incidental moral dilemmas, but with decreased utilitarian decision-making in instrumental dilemmas, although neither trend was statistically-significant."(Arnocky, Steven, et al. "The Effects of Exogenous Testosterone on Men’s Moral Decision-Making." Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology (2016): 1-13.)
(“instrumental” dilemmas = in which the death of one person is a means to save more people; “incidental” dilemmas = in which the death of one person is a foreseen but unintended consequence of the action aimed at saving more people)
(Lotto, Lorella, Andrea Manfrinati, and Michela Sarlo. "A new set of moral dilemmas: Norms for moral acceptability, decision times, and emotional salience." Journal of Behavioral Decision Making 27.1 (2014): 57-65.)
Testosterone increases sensitivity to immediate reward
"The researchers think that sensitivity to immediate rewards is associated with the effects of testosterone on certain reward-related regions of the brain, such as the striatum. Chronological age cannot explain this sensitivity."(Adolescent Impatience Increases As Testosterone Rises, Neuroscience News, may 15th 2017)
High testosterone correlates with low empathy in men and women. Men with high testosterone and low cortisol self-report high empathy, but this is not corroborated by measurements
"In the present study, we investigated the association between basal testosterone, basal cortisol, and empathy in a large population of MBA students. Empathy was assessed with a short version of the Davis’s Interpersonal Reactivity Index and with the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test (RMET)."(the Interpersonal Reactivity Index or IRI is a self-assessment using a questionnaire the participants fill in themselves).
The study's result were:
- taking into account only the RMET, high testosterone correlated with low empathy, in men and in women. This was independent of cortisol levels.
- taking into account the self-assessment using the IRI, there was the following difference: in men (not women) with high testosterone, those with high cortisol self-reported high empathy. The RMET however did not corroborate this self-reported high empathy. "The effect was limited to self-reported empathy as no association was found with the RMET."
(Zilioli, Samuele, et al. "Testosterone, cortisol and empathy: evidence for the dual-hormone hypothesis." Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology 1.4 (2015): 421-433.)
2D:4D digit ratio correlation to measures of aggressive and violent behavior is weak but statistically significant
"Our results reveal that the overall mean effect size of the 2D:4D digit ratio to measures of aggressive and violent behavior is weak but statistically significant (mean r = 0.036, p < 0.05). Moderator analyses confirm that these weak effects are generally consistent (and often non-significant) across a variety of methodological conditions (e.g., different outcome measures, different kinds of samples). We conclude with a call for caution against placing emphasis on the 2D:4D digit ratio as a reliable risk factor for aggressive and violent behavior."(Turanovic, Jillian J., Travis C. Pratt, and Alex R. Piquero. "Exposure to fetal testosterone, aggression, and violent behavior: A meta-analysis of the 2D: 4D digit ratio." Aggression and violent behavior 33 (2017): 51-61.)
Self-reports give opposite effects concerning 2D:4D digit ratio, empathy and psychopathy, compared to Reading the Mind in the Eyes test
Using a a quasi‐experimental method consisting of questionnaires and digit measurements, female participants with high 2D:4D ratios self-reported higher on psychopathy, and males with high 2D:4D ratios self-reported higher on callous affect (low empathy)."Within the male cohort, Callous affect and right hand 2D: 4D ratio significantly positively correlated (r = 0.41, p = 0.03). This indicates that, overall, a feminised digit ratio scored higher on the callous affect subscale for males. In the female sample, psychopathy and right hand 2D:4D ratio were significantly positively correlated (r = 0.45, p = 0.04). This also shows that females who had more feminised digit ratios scored higher for psychopathy.This study found no negative correlation between digit ratios and RMET scores.
(...)
Significant correlations were found for right hand 2D: 4D and psychopathy for females, and callous affect for males. This means that, instead of a more masculinised digit ratio being associated with psychopathy (as measured using the SRP-II), it is in fact a higher, more feminised digit ratio. The regression analysis confirms these results, showing that a larger right hand 2D: 4D digit ratio and gender are statistical correlates of psychopathy in the model produced."
(Blanchard, Alyson, and Minna Lyons. "An investigation into the relationship between digit length ratio (2D: 4D) and psychopathy." The British Journal of Forensic Practice 12.2 (2010): 23-31.)
Low left 2D:4D digit ratio predicts psychopathy in women
"Low LH2D:4D predicted primary and secondary psychopathy in women."(Blanchard, Alyson, Minna Lyons, and Luna Centifanti. "Baby was a black sheep: Digit ratio (2D: 4D), maternal bonding and primary and secondary psychopathy." Personality and Individual Differences 99 (2016): 67-71.)
High prenatal testosterone related to psychopathy in children and worse externalising behavior
"Interestingly, our findings corroborate what prior studies revealed. Namely, that high PT is related to hyperactivity, ADHD symptoms, conduct problems and poor social cognitive functioning in children from 3 to 7 years of age [36, 37]. We extend these findings to include children who exhibit traits and behaviours associated with child psychopathy."
"children exposed to higher levels of PT (prenatal testosterone) expressed more EB (externalising behaviours) if they were high in CU (callous-unemotional) traits. Conversely, children exposed to lower levels of PT but were high in CU traits expressed less EB."In other words, the externalising behavior (violence, agression, ...) of psychopathic children is worse with higher prenatal testosterone.
(Blanchard, Alyson, and Luna C. Munoz Centifanti. "Callous-Unemotional Traits Moderate the Relation Between Prenatal Testosterone (2D: 4D) and Externalising Behaviours in Children." Child Psychiatry & Human Development (2016): 1-10.)
High R2D:4D in females (in absolute figures, and compared to L2D:4D) associated with agression in females when provoked
"High aggression scores were associated with high directional asymmetry of 2D:4D (left hand 2D:4D minus right hand 2D:4D) and masculinized (low) right hand 2D:4D, only in females and under high provocation. Directional asymmetry of 2D:4D was positively correlated with T in males (...). Taken together, these data confirm the predominantly right-sided influence of androgens on digit length and suggest that digit length ratios may be associated with female reactive aggression when sufficient provocation is present."
(Benderlioglu, Zeynep, and Randy J. Nelson. "Digit length ratios predict reactive aggression in women, but not in men." Hormones and behavior 46.5 (2004): 558-564.)
A review on the relationship between testosterone and life-course persistent antisocial behavior
"Life-course persistent antisocial behavior is 10 to 14 times more prevalent in males and it has been suggested that testosterone levels could account for this gender bias. Preliminary studies with measures of fetal testosterone find inconsistent associations with antisocial behavior, especially studies that use the 2D:4D ratio as a proxy for fetal testosterone. However, circulating testosterone consistently shows positive associations with antisocial behaviors throughout childhood, adolescence, and adulthood, particularly in males. It is suggested that high fetal/circulating testosterone interactively influence the maturation and functionality of mesolimbic dopaminergic circuitry, right orbitofrontal cortex, and cortico-subcortical connectivity, resulting in a strong reward motivation, low social sensitivity, and dampened regulation of strong motivational/emotional processes. The link between these testosterone induced endophenotypes and actual display of antisocial behavior is strongly modulated by different social (e.g., social rejection, low SES) and genetic (e.g., MAOA, 5HTT) risk factors that can disturb socio-, psycho-, and biological development and interact with testosterone in shaping behavior. When these additional risk factors are present, the testosterone induced endophenotypes may increase the risk for a chronic antisocial lifestyle. However, behavioral endophenotypes induced by testosterone can also predispose towards socially adaptive traits such as a strong achievement motivation, leadership, fair bargaining behaviors, and social assertiveness. These adaptive traits are more likely to emerge when the high testosterone individual has positive social experiences that promote prosocial behaviors such as strong and secure attachments with his caregivers, affiliation with prosocial peers, and sufficient socioeconomic resources."(Yildirim, Bariş O., and Jan JL Derksen. "A review on the relationship between testosterone and life-course persistent antisocial behavior." Psychiatry research 200.2 (2012): 984-1010.)
2D:4D ratio positively correlated with external locus of control in females (not males)
"Significant positive correlations were observed between LoCQ scores in females and right hand 2D:4D and D(R–L), though no such relationships emerged in males (...).(Richards, Gareth, Steve Stewart-Williams, and Phil Reed. "Associations between digit ratio (2D: 4D) and locus of control." Personality and Individual Differences 83 (2015): 102-105.)
(...)
Locus of control refers to the extent to which an individual believes they can control events affecting them, and is conceptualised as either internal, whereby a person feels that they are in control of their life, or external, by which a person feels that their decisions are controlled by external forces (Rotter, 1966). Locus of control shows marked sexual dimorphism, with females, on average, demonstrating a more external locus of control than males; an effect that has been demonstrated to be stable across cultures (McGinnies, Nordholm, Ward, & Bhanthumnavin, 1974). Locus of control is also known to be associated with a diverse range of behaviours and outcomes, such as stress and depression, (Benassi, Sweeney, & Dufour, 1988), religious belief (Kahoe, 1974), and job satisfaction and performance (Judge & Bono, 2001), suggesting that it is an important and far-reaching dimension of an individual’s personality."
Male heroin abusers have significantly lower 2D:4D digit ratios
"We examined the 2D:4D digit ratios in male heroin abusers.(Cicek, Ismet Esra, et al. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D), impulsiveness and aggression in male heroin addicts: A prospective controlled study." Personality and Individual Differences 117 (2017): 1-5.)
The patients' digit ratios were significantly lower than controls.
The patients had significantly higher scores of impulsiveness, aggression and ADHD.
Prenatal high testosterone exposure might have a role in the etiology of heroin addiction."
The higher the difference between the left- and right-hand 2D:4D digit ratio, the lower the capability of mentalizing
"In the current work, we test whether the difference between the digit ratios of the left and right hands may function as a better predictor of mentalizing than digit ratio alone. (...) [W]e demonstrate that a) 2D:4D is quadratically related to asymmetry, b) asymmetry is negatively associated with mentalizing, and c) the relationship between asymmetry and mentalizing cannot be explained by the relationship between asymmetry and short-term memory."(Christian, Colton B., and Azim F. Shariff. "Asymmetry and empathy: Higher asymmetry is associated with lower levels of mentalizing." Early Human Development 111 (2017): 6-15.)
(Wikipedia, Mentalization, accessed 2017-05-23)
"In psychology, mentalization is the ability to understand the mental state, of oneself or others, that underlies overt behaviour."
Low 2D:4D digit ratio correlates to high surfing ability (study on men only)
"It appears that in line with other sports that low right 2D:4D (high prenatal testosterone and low prenatal estrogen) correlates to high surfing ability in men."(Kilduff, Liam P., Christian J. Cook, and John T. Manning. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and performance in male surfers." The Journal of Strength & Conditioning Research 25.11 (2011): 3175-3180.)
Low 2D:4D ratio significant predictor of criminal offense in men
"44 male offenders and 46 nonoffenders completed the Eysenck Impulsivity Questionnaire, and had their 2D∶4D ratio measured. Offenders exhibited smaller right hand digit ratio measurements compared to non-offenders, but higher impulsivity scores. Both impulsivity and 2D∶4D ratio measurements significantly predicted criminality (offenders vs. nonoffenders). Controlling for education level, the 2D∶4D ratio measurements had remained a significant predictor of criminality, while impulsivity scores no longer predicted criminality significantly."(Hanoch, Yaniv, Michaela Gummerum, and Jonathan Rolison. "Second-to-Fourth Digit Ratio and impulsivity: a comparison between offenders and nonoffenders." PloS one 7.10 (2012): e47140.)
But: one meta-study warns for caution, although it also finds a small overall effect
"(...) one important proposition has gained increasing attention: that the 2D:4D finger digit ratio—a purported physical biomarker for exposure to fetal testosterone—is related to criminal, aggressive, and risky/impulsive behavior. Strong claims in the literature have been made for this link even though the findings seem to be inconsistent. To establish the empirical status of this relationship, we subjected this body of work to a meta-analysis. Our multilevel analyses of 660 effect size estimates drawn from 47 studies (14,244 individual cases) indicate a small overall effect size (mean r = .047). Moderator analyses indicate that this effect is rather “general” across methodological specifications—findings that are at odds with theoretical propositions that specify the importance of exposure to fetal testosterone in predicting criminal and analogous behavior later in life. We conclude with a call for exercising caution over embracing the findings from one or two studies and instead highlight the importance of systematically organizing the full body of literature on a topic before making decisions about what does, and what does not, predict criminal and analogous behavior."(Pratt, Travis C., Jillian J. Turanovic, and Francis T. Cullen. "REVISITING THE CRIMINOLOGICAL CONSEQUENCES OF EXPOSURE TO FETAL TESTOSTERONE: A META‐ANALYSIS OF THE 2D: 4D DIGIT RATIO." Criminology 54.4 (2016): 587-620.)
In rats, higher prenatal testosterone causes more anxiety in female offspring
"The results of our research suggest that prenatal testosterone exposure increases anxiety-like behavior in female offspring."(Rasic-Markovic, Aleksandra, et al. "Prenatal testosterone exposure increases anxiety-like behavior in female rats." (2017).)
Female-to-Male transsexuals may have been exposed to higher prenatal testosterone
"In conclusion, this first meta-analysis of 2D:4D associations with TGI (TransGender Identity) finds that any such effects are small at best. The literature is not contradictory; rather, study findings fluctuate according to expected sampling variability. The currently available cumulative empirical evidence is insufficient to decide whether such effects are sexually asymmetric (i.e., present for MtF, but not FtM)."
(Voracek, Martin, et al. "META-ANALYSIS SHOWS ASSOCIATIONS OF DIGIT RATIO (2D: 4D) AND TRANSGENDER IDENTITY ARE SMALL AT BEST." Endocrine Practice (2018).)
Lower left-hand 2D:4D ratio predicts risky financial behavior in Columbian population
"People with higher prenatal T exposure (lower left-hand 2D:4D, rel2 ratios) tend to choose more risky lotteries, although the effect is weak and better captured in binary-choice than in ordered-logit models. Results are statistically significant for the left hand but not for the right hand."(Chicaiza-Becerra, Liliana Alejandra, and Mario Garcia-Molina. "Prenatal testosterone predicts financial risk taking: Evidence from Latin America." Personality and Individual Differences 116 (2017): 32-37.)
Higher wages not correlated with biological sex (male versus female), but with high prenatal testosterone
"We combine unique data from the Russian Longitudinal Monitoring Survey with measured markers (2D:4D ratios) for testosterone exposure and find that lower digit ratios (higher T) correlate with higher wages for women and for men, when controlling for age, education and occupation. There is also some evidence of a potential non-linear, inverse U-effect of digit ratios on wages but this is sensitive to choice of specification."(Nye, John VC, et al. "The effects of prenatal testosterone on wages: Evidence from Russia." Economics & Human Biology 24 (2017): 43-60.)
Low 2D:4D linked to physical agression and contact sport
"Sports people have lower 2D:4D and higher physical aggression than non-sport people.
Contact sport athletes have significantly lower 2D:4D than non-contact sports people.
Findings could be replicated in different sports and contexts."
"Results showed individuals involved in sport exhibited significantly greater levels of both prenatal testosterone (lower 2D:4D) and physical aggression compared with their non-sporting counterparts. Athletes from contact sports (rugby and football) were found to have significantly lower 2D:4D and significantly higher levels of physical aggression compared to athletes from non-contact sports (basketball, golf, weight-training, badminton). Additional findings, regarding longevity, showed those exposed to higher levels of prenatal testosterone (low 2D:4D) had been involved in sport for more years compared to those with high 2D:4D, adjusting for age."(Reed, Scott, Jennifer Meggs, and John T. Manning. "Examining the effect of prenatal testosterone and aggression on sporting choice and sporting longevity." Personality and Individual Differences 116 (2017): 11-15.)
Firms run by high prenatal testosterone entrepreneurs have lower profitability, because of their "empire building preferences"
"Entrepreneurs with lower ratio manage larger firms, manage larger firms when acquire control and experience faster average growth. Firms run by high prenatal testosterone entrepreneurs have lower profitability as measured by return on assets and return on sales."
"We offer evidence that this is because the same biological factor that enhances entrepreneurial skills also induces empire building preferences, which leads high-testosterone entrepreneurs to target a firm size that exceeds the profit mpaximizing value."(Guiso, Luigi, and Aldo Rustichini. "Understanding the size and profitability of firms: The role of a biological factor." (2011)., HTML abstract, full PDF)
Low 2D:4D digit ratio correlates with psychopathic personality, fearlessness and impulsive non-conformity
"The present study investigated the relationship between adult 2D:4D ratios and psychopathic personality amongst a community and undergraduate sample in Philadelphia (n=89). Initial findings from the first phase of data collection indicate that 2D:4D was negatively correlated with psychopathic personality, as well as with fearlessness and impulsive non-conformity subscales of psychopathic personality. Additionally, amongst a high social adversity group, low 2D:4D ratios were related to the cold-heartedness psychopathy subscale."(Portnoy, Jill., Raine, Adrian., Seigerman, Matthew. and Gao, Yu. "The Relationship between Prenatal Testosterone and Adult Psychopathic Personality" Paper presented at the annual meeting of the ASC Annual Meeting, Washington Hilton, Washington, DC, <Not Available>. 2014-11-25)
Low reactivity to cortisol linked to higher aggression in males, but only if they had low 2D:4D
"In males, low cortisol reactivity was associated with higher levels of aggression and rule-breaking behavior, but only among subjects with low 2D:4D (i.e., high prenatal testosterone)."(Portnoy, Jill, et al. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) moderates the relationship between cortisol reactivity and self-reported externalizing behavior in young adolescent males." Biological psychology 112 (2015): 94-106.)
Low 2D:4D ratio correlates with strategic gameplay (in dictator and ultimatum games)
"Using a sample of 629 students we show that low 2D:4D (higher exposure) subjects are more likely to play strategically, that is passing more money in the Dictator than in the Ultimatum game."Both the ultimatum and dictator game revolve around dividing a sum of money between the giver and the receiver. In the ultimatum game the giver proposes a certain division of the sum, and the receiver either accepts or rejects the offer. In the dictator game the giver decides (and may decide to keep everything for himself) and the receiver has nothing to say about it.
In the ultimatum game giving more can have a strategic advantage for the one giving, because the receiving party has an active role (either accept or reject the offer). In the dictator game the one receiving cannot decide anything (totally passive role), so there is no advantage to the giver in giving more.
So, giving more in the ultimatum game than in the dictator game points towards low altruism: only when teher is a certain advantage for oneself, will the subject be more generous.
(Branas-Garza, Pablo. "Exposicion fetal a la testosterona, 2D: 4D y altruismo estrategico." Revista de Economia Industrial 403 (2017): 103-110.)
2D:4D correlates with social behavior
"[I]ndividuals with low 2D:4D become more central in their social environment. Interestingly, low 2D:4D males are more likely to exhibit high betweenness centrality (they connect separated parts of the social structure), while low 2D:4D females are more likely to exhibit high in-degree centrality (more people name them as friends). These gender-specific differences are reinforced by transitivity (the likelihood that one's friends are also friends with one another): neighbors of low 2D:4D men tend not to know each other; the contrary is observed for low 2D:4D women. Our results suggest that biological predispositions influence the organization of human societies and that exposure to prenatal androgens influences different status seeking behaviors in men and women."(Kovářík, Jaromír, et al. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and social integration: an effect of prenatal sex hormones." Network Science (2016).)
Low 2D:4D ratio linked to poor firm performance and commitment to strategic goals
"Our most interesting findings conclude that lower 2D:4D ratios (higher levels of testosterone) is negatively associated with both firm performance and commitment to strategic goals."(Trahms, Cheryl A., Joseph E. Coombs, and Murray Barrick. "Does biology matter? How prenatal testosterone, entrepreneur risk propensity, and entrepreneur risk perceptions influence venture performance." Frontiers of Entrepreneurship Research 30.5 (2010): 4.)
Cortisol and testosterone interact to regulate dominance: only in low-cortisol individuals does high testosterone correlate with high dominance
"In the domains of leadership (Study 1, mixed-sex sample) and competition (Study 2, male-only sample), testosterone was positively related to dominance, but only in individuals with low cortisol. In individuals with high cortisol, the relation between testosterone and dominance was blocked (Study 1) or reversed (Study 2). Study 2 further showed that these hormonal effects on dominance were especially likely to occur after social threat (social defeat). The present studies provide the first empirical support for the claim that the neuroendocrine reproductive (HPG) and stress (HPA) axes interact to regulate dominance. Because dominance is related to gaining and maintaining high status positions in social hierarchies, the findings suggest that only when cortisol is low should higher testosterone encourage higher status. When cortisol is high, higher testosterone may actually decrease dominance and in turn motivate lower status."(Mehta, Pranjal H., and Robert A. Josephs. "Testosterone and cortisol jointly regulate dominance: Evidence for a dual-hormone hypothesis." Hormones and behavior 58.5 (2010): 898-906.)
High prenatal testosterone correlates with tendency to become entrepreneur (risk-taking)
"This study examines the relationship between prenatal testosterone exposure (PTE) and selection into entrepreneurship. We argue that the relationship between PTE and entrepreneurial intent is positive and mediated by general and domain-specific risk-taking related to financial investment and professional career. Using the second-to-fourth digit ratio (2D:4D) as noninvasive retrospective marker for PTE, we identify two-step mediation effects of PTE on entrepreneurial intent through both general and domain-specific risk-taking. To account for possible socialization-based effects, we control for gender and parental self-employment. Applying ordinary least squares (OLS) regression analyses and structural equation models, we provide empirical evidence for a biological association between 2D:4D and entrepreneurial intent."(Bönte, Werner, Vivien D. Procher, and Diemo Urbig. "Biology and selection into entrepreneurship—The relevance of prenatal testosterone exposure." Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice 40.5 (2016): 1121-1148.)
High circulating testosterone increases financial risk-taking (systematic review of existing studies)
"The results obtained show a relationship between circulating testosterone and financial risk-taking. As regards prenatal exposure, research on this topic is still in its infancy, since the few articles found widely differ in methodologies and results."(Goel, Nirupa, and Tracy L. Bale. "Organizational and activational effects of testosterone on masculinization of female physiological and behavioral stress responses." Endocrinology 149.12 (2008): 6399-6405.)
In quail, higher testosterone (and mesotocin) levels may cause higher agression
"Taken together, our findings suggest that higher testosterone and mesotocin levels in the hypothalamus may be responsible for higher aggression in the NIES-Brn quail strain."(Maekawa, Fumihiko, et al. "Strain differences in intermale aggression and possible factors regulating increased aggression in Japanese quail." General and Comparative Endocrinology (2017).)
Higher prenatal androgen activity is a risk factor for higher alcohol consumption
Experiment with inhibition and activation of prenatal androgen receptors in mice, and adult alcohol and water consumption.Males: activation increased water consumption, inhibition decreased alcohol consumption.
Females: activation increased alcohol consumption, inhibition increased water consumption.
In other words: the higher the androgen receptor activity, the higher the alcohol consumption and the lower the water consumption.
"These findings demonstrate that prenatal androgen activity is a risk factor for the establishment of alcohol consumption in adults by its organizational effects."(Huber, Sabine E., et al. "Prenatal androgen receptor activation determines adult alcohol and water drinking in a sex‐specific way." Addiction Biology (2017).)
Higher prenatal testosterone may be implicated in female homosexuality
"Homosexual women’s life history strategies are masculinized, deviating from typical female optima. This shift is likely mediated by higher prenatal testosterone exposure and("Female homosexuality (butch/femme/bisexual), A testosterone-mediated life history strategy?", Powerpoint Presentation, University of Auckland, Severi Luoto, Markus J. Rantala, Indrikis Krams, 2017)
masculinizing genes, a finding also supported by nonhuman animal studies."
Low left 2D:4D linked to higher aggression when challenged
"The relative lengths of the 2(nd) and 4(th) digits (2D:4D) is a negative biomarker for prenatal testosterone, and low 2D:4D may be associated with aggression. However, the evidence for a 2D:4D-aggression association is mixed. Here we test the hypothesis that 2D:4D is robustly linked to aggression in "challenge" situations in which testosterone is increased. Participants were exposed to an aggressive video and a control video. Aggression was measured after each video and salivary free testosterone levels before and after each video. Compared to the control video, the aggressive video was associated with raised aggression responses and a marginally significant increase in testosterone. Left 2D:4D was negatively correlated with aggression after the aggressive video and the strength of the correlation was higher in those participants who showed the greatest increases in testosterone. Left 2D:4D was also negatively correlated to the difference between aggression scores in the aggressive and control conditions. The control video did not influence testosterone concentrations and there were no associations between 2D:4D and aggression. We conclude that 2D:4D moderates the impact of an aggressive stimulus on aggression, such that an increase in testosterone resulting from a "challenge" is associated with a negative correlation between 2D:4D and aggression."(Kilduff, Liam P., et al. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D), aggression, and testosterone in men exposed to an aggressive video stimulus." Evolutionary psychology 11.5 (2013): 147470491301100502.)
Low 2D:4D associated with higher incidence of boxers fractures due to aggression
"[... O]ur results showed that those presenting with a boxers fracture due to an aggression related injury had a statistically significant smaller 2D:4D ratio when compared to the normal population.(Joyce, C. W., et al. "Second to fourth digit ratio confirms aggressive tendencies in patients with boxers fractures." Injury 44.11 (2013): 1636-1639.)
CONCLUSION:
Boxers fractures are injuries that typically occur from an aggressive act. It is well documented that a low 2D:4D ratio is reflective of an increased prenatal exposure to androgens, particularly testosterone. We have shown that boxers fractures are associated with a smaller 2D:4D ratio than the normal population, thus suggesting that persons exposed to high levels of prenatal androgens are more likely to exhibit aggressive tendencies in adulthood. Our results suggest that smaller digit ratios may predict a predisposition to acts of aggression, and as such result in an increased likelihood of sustaining an injury such as a boxers fracture. This relationship seems to be present independently of gender."
Low 2D:4D ratio linked to low self-control in preschoolers
"We replicate the Stanford marshmallow experiment with a sample of 141 preschoolers and find a correlation between lack of self-control and 2D:4D digit ratio. Children with low 2D:4D digit ratio are less likely to delay gratification."(Da Silva, Sergio, Bruno Moreira, and Newton Da Costa Jr. "2D: 4D digit ratio predicts delay of gratification in preschoolers." PloS one 9.12 (2014): e114394.)
Low 2D:4D linked to internet addiction
"For men, 2D:4D ratios on the right hand were inversely correlated with Internet addiction severity even after controlling for individual differences in impulsivity. These findings suggest that high prenatal testosterone levels may contribute to the occurrence of PPIU (Problematic and pathological Internet use) among men."(Canan, Fatih, et al. "The relationship between second-to-fourth digit (2D: 4D) ratios and problematic and pathological Internet use among Turkish university students." Journal of Behavioral Addictions 6.1 (2016): 30-41.)
Higher 2D:4D ratio linked to longer and more frequent eye contact in toddlers
"Results indicated that larger 2D:4D ratios (indicative of lower androgen levels) significantly predicted longer duration and more frequency of eye contact, while postnatal testosterone levels were unrelated to eye contact. These novel findings suggest prenatal androgens may influence the emergence of social development."(Saenz, Janet, and Gerianne M. Alexander. "Digit ratios (2D: 4D), postnatal testosterone and eye contact in toddlers." Biological psychology 94.1 (2013): 106-108.)
Actual testosterone levels correlate with love style in men, no correlation found with 2D:4D ratio
"There are six love styles which are primary including Eros (passionate romantic love), Ludus (playful) and Storge (friendly) and secondary love consisting of Mania (obsessive), Pragma (practical realistic) and Agape (altruistic). Our results pointed out that low testosterone concetractions are associated with higher score for Eros, Ludus, Pragma, Mania love style. No significant association was proved for other tested parameters of androgenicity (2D:4D, sensitivity of androgen receptor) and love style after correction was applied."(Babková, Durdiaková J., et al. "How do we love? Romantic love style in men is related to lower testosterone levels." Physiological research (2017).)
Lower prenatal testosterone associated with decreased sexual function in aging men
"Lower prenatal T (i.e. higher digit-ratio) and higher CTr [=cortisol to testosterone ratio] (increased C and lower T) seem to be associated with decreased sexual function [in aging men]."(Lacker, Tim, Andreas Walther, and Ulrike Ehlert. "How prenatal testosterone exposure influences sexual function in aging men. Findings from the Men's Health 40+ study." Psychoneuroendocrinology 83 (2017): 38.)
Norm manipulation does not alter actual behavior
In this study, aggression was measured by the decision to reject an unfair offer in the ultimatum game (UG).Participants were placed in various social contexts, some endorsing agression, others being neutral to it, others rejecting it. In other words, moral norms were being manipulated, and agression was measured in these different moral contexts.
The results showed that the actual behaviour of the participants was not affected by the norm manipulation, although their interpretation of it differed. In other words, changing moral norms did not affect behaviour in se, only how they reflected upon it.
Digit ratio did not seem to have an effect in this matter (the effect of norm manipulation on behaviour was not correlated with digit ratios, in other words: whether a participant had high or low digit ratio, the results remained the same, their actual behavior was not affected by social norms, and their interpretation of it was affected).
"It was hypothesized that lower 2D:4D would predict increased aggression when aggressive behavior was endorsed by group members for gaining/maintaining status. Conversely, lower 2D:4D would predict decreased aggression when aggressive behavior was proscribed by group members for gaining/maintaining status. Based on the Male Warrior Hypothesis, although it was hypothesized that outgroup membership would predict aggressive behavior, it was also hypothesized that this effect would be maximal among those with lower 2D:4D, particularly when an aggression-for-status norm was endorsed.(Isbell, Jason. "STATUS RELEVANT SOCIAL CONTEXT, GROUP MEMBERSHIP, AND FINGER LENGTH RATIO (2D: 4D) AS PREDICTORS OF ONLINE SOCIOECONOMIC BEHAVIOR." (2017).)
The data did not support the primary hypotheses. The digit ratio did not predict any DV [=dependent variable]. The norm manipulation did not affect UG [ultimatum game] decisions and there was a methodological issue with the group manipulation. The norm manipulation did affect secondary DVs, however. There were significant differences between the pro-, neutral, and anti-aggression groups regarding participants’ endorsement of a fictional character’s aggressive behavior to gain status. Those in the pro-aggression group endorsed it the most and those in the anti-aggression group endorsed it the least. Despite no effect of the norm manipulation on the decision in the UG, there was an effect of the manipulation on participants’ confessed intent, with those in the pro-aggression condition rating their decision to reject as “aggressive” more so than those in the anti-aggression condition. The norm manipulation also influenced meta-perceptions of how participants thought their teammates viewed them based on their decision in the UG. Exploratory analyses modeled these effects.
[...]
"Group norms pertaining to status did affect the extent to which individuals publicly endorsed aggressive behavior. Group norms affected participants’ metacognition about how their group members would allocate them status based on their behavior. Group norms affected the extent to which individuals interpreted their behavior as an act of aggression after the fact, and despite these norms not affecting their actual behavior."
Effects of castration on male monkeys: social hierarchy becomes less linear, and they become less agressive
"We found that castrated males exhibited a social hierarchy, but not a linear hierarchy, as was the case in intact males. Castrated males were less aggressive than intact males, probably because fT [=testosterone] concentrations were lower in the castrated males. Age was positively correlated with fGC [=glucocorticoids, eg. cortisol] levels, while fT concentrations were lower in old males than younger adult males. Fecal T levels correlated with both rank and atmospheric temperature. In intact males, both fGC and fT levels were elevated during the mating season. We found a negative correlation between fGC levels and the amount of grooming received. Our findings indicate that castration had a minimal impact on sociality, with season, temperature, and rank all influencing male sex steroid levels in intact males. Our study indicates that castration can be adopted as a population control mechanism without drastically altering the social relationships of males."(Takeshita, Rafaela SC, et al. "Effect of castration on social behavior and hormones in male Japanese macaques (Macaca fuscata)." Physiology & Behavior (2017).)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with more sexual jealousy
"We examined the relationship between second-to-fourth digit ratio (2D:4D), a correlate of prenatal testosterone exposure, and distress at sexual versus emotional infidelity in hypothetical scenarios of relationship threat. As predicted, a significant negative association was found between 2D:4D and greater distress at sexual infidelity for the whole sample (N = 179, females = 101)."(Martínez-León, Nancy Consuelo, et al. "A systematic review of romantic jealousy in relationships." Terapia Psicológica 35.2 (2017): 195-204.)
Male jealousy is more sexual, female jealousy more emotional. 2D:4D ratio is not correlated to overall level of jealousy
"As predicted, female participants reported that emotional jealousy was more distressing,(Corzine, Kayla. "Sex differences in multiple dimensions of jealousy.")
while male participants reported that sexual jealousy was more distressing. [...] Participants also had their second and fourth digits measured on both hands to obtain a 2D:4D ratio. This ratio was used to see if there was a correlation between testosterone levels and jealousy. There was no significant difference found between digit length and jealousy."
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with more sexual jealousy
"We examined the relationship between second-to-fourth digit ratio (2D:4D), a correlate of prenatal testosterone exposure, and distress at sexual versus emotional infidelity in hypothetical scenarios of relationship threat. As predicted, a significant negative association was found between 2D:4D and greater distress at sexual infidelity for the whole sample (N = 179, females = 101)."(Fussell, Nicola J., Angela C. Rowe, and Justin H. Park. "Masculinised brain and romantic jealousy: Examining the association between digit ratio (2D: 4D) and between-and within-sex differences." Personality and Individual Differences 51, no. 2 (2011): 107-111.)
In schizophrenic patients, age of onset of schizophrenia is negatively correlated with 2D:4D ratio
"A total of 214 schizophrenia patients participated in this study. [...] [T]here was a statistically significant negative correlation between 2D : 4D and the age of onset of schizophrenia in male."("The Association of the 2nd to 4th Digit Ratio with the Age of Onset and Metabolic Factors in Korean Patients with Schizophrenia", Hong Rae Kim et al., Korean J Biol Psychiatry 2017;24(3):142-148)
Children with low 2D:4D ratio are more likely to give less in public goods game
In the public goods game, participants secretly choose how many of their private tokens to put into a public pot. The tokens in this pot are multiplied by a factor and this "public good" payoff is evenly divided among players. Each subject also keeps the tokens they do not contribute."Free riders" are those who give less than average, or not at all.
"We play a public goods game with Ugandan children born during a conflict characterised by high civilian victimisation. Children whose caregivers suffer from post-traumatic stress disorder are more likely to free-ride in the game. Genetic and environmental factors alone do not explain the relationship, but children’s 2D:4D digit ratio – a marker of fetal hormone exposure associated with epigenetic effects of maternal distress – does."(Cecchi, Francesco, and Jan Duchoslav. "The Effect of Prenatal Stress on Cooperation: Evidence from Violent Conflict in Uganda." European Economic Review (2017).)
Low 2D:4D ratio in female basket players correlates with more blocks, rebounds and field-goals
"2D:4D was a substantial negative correlate of blocks, rebounds, and field-goal percentage; meaning, females with lower 2D:4Ds were generally better defensively as they recorded more blocks and rebounds, and were more efficient scorers, irrespective of their age and body size. Mean 2D:4D differed by position in the starting lineup, as females with lower 2D:4Ds were more likely to be in the starting lineup."(Dyer, Makailah, et al. "Relationships between the second to fourth digit ratio (2D: 4D) and game‐related statistics in semi‐professional female basketball players." American Journal of Human Biology (2017).)
Low 2D:4D ratio correlates with higher Internet Usage and Gaming Disorder
"It appeared that more female hands (right side; characterized by higher digit ratio of the index to the ring finger, i.e. >1, meaning lower prenatal testosterone) were associated with lower IGD [Internet Gaming Disorder] (rho = -.170, p = .013, N = 211). This effect was driven by the female subsample and the facet of loss of control over Internet Gaming (rho = -.198, p = .020, N = 137). Aside from this a negative association appeared between the facet of loss of control of generalized IUD and the right digit ratio in males underlining earlier work."(Müller, Marko, et al. "The 2D: 4D marker and different forms of Internet Use Disorder." Frontiers in Psychiatry 8 (2017): 213.)
"Subjects included 653 middle-school students from Chuncheon, Korea who completed measures assessing Internet addiction, mood, temperament, and social interactions. Finger digit (2D:4D) ratios were also assessed. (...) In boys, IAT [Internet Addiction Test] correlated inversely with the 2D:4D digit ratio"(Kim, Yoon-Jung, Daeyoung Roh, Sang-Kyu Lee, Fatih Canan, and Marc N. Potenza. "Factors Statistically Predicting At-Risk/Problematic Internet Use in a Sample of Young Adolescent Boys and Girls in South Korea." Frontiers in Psychiatry 9 (2018): 351.)
Low 2D:4D ratio correlates with more status seeking
"Individuals with lower 2D:4D (i.e., more masculine) had more positive attitudes for high-status goods on an Implicit Association Task".According to the status theory of testosterone, status seeking can be done by agression toward threat but also by generosity:
"The status theory of testosterone predicts that, while in social contexts where status is threatened by perceived provocation (e.g., unfair offers in the UG), this motivation may lead to increased aggression (rejection behavior); in the other case, non-aggressive behavior such as generosity, will be more appropriate for increasing social status (Eisenegger et al., 2011)."(Wu, Yin, et al. "The Effect of Testosterone Administration and Digit Ratio (2D: 4D) on Implicit Preference for Status Goods in Healthy Males." Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience 11 (2017): 193.)
Testosterone administration increases feelings of power and infallibility
Women who were administered testosterone had more illusion of control, and predicted more positive outcomes of their actions."Sense of agency (SoA) refers to feelings of being in control of one’s actions. Evidence suggests that SoA might contribute towards higher-order feelings of personal control – a key attribute of powerful individuals. Whether testosterone, a steroid hormone linked to power in dominance hierarchies, also influences the SoA is not yet established. In a repeated-measures design, 26 females participated in a double-blind, placebo-controlled trial to test the effects of 0.5 mg testosterone on SoA, using an implicit measure based upon perceived shifts in time between a voluntary action and its outcome. Illusions of control, as operationalized by optimism in affective forecasting, were also assessed. Testosterone increased action binding but there was no significant effect on tone binding. Affective forecasting was found to be significantly more positive on testosterone. SoA and optimistic expectations are basic manifestations of power which may contribute to feelings of infallibility often associated with dominance and testosterone."(van der Westhuizen, Donné, et al. "Testosterone facilitates the sense of agency." Consciousness and Cognition 56 (2017): 58-67.)
Regions with low 2D:4D digit ratio have lower emancipation of women
"Exploiting variation across communities in indices correlated with women emancipation, we show that in regions where women are less emancipated the average 2D4D Digit Ratio [of men (?)] is lower than that of men compared to regions with higher indices, (...)."(Guiso, Luigi, and Aldo Rustichini. "What drives women out of management? The joint role of testosterone and culture." European Economic Review (2017).)
Organizing effect of testosterone on male brain happens during short critical prenatal period; females remain sensitive longer and also postnatally
"The sexual differentiation of the brain is a unique critical period in that it is initiated by endogenous production of a critical signaling molecule in only one sex, testosterone in fetal males. Females, by contrast, do not produce testosterone but are highly responsive to it and remain sensitive to its masculinizing effects well past the close of the critical period in males. Compared to other well characterized critical periods, such as those for the visual system or barrel cortex, the masculinization of the brain is telescoped into a few short days and initiated prenatally. The slightly longer and postnatal sensitive period in females provides a valuable tool for understanding this challenging but fundamental developmental process."(McCarthy, Margaret M., Kevin Herold, and Sara L. Stockman. "Fast, furious and enduring: Sensitive versus critical periods in sexual differentiation of the brain." Physiology & Behavior (2017).)
Low 2D:4D ratio correlates with higher incidence of Developmental Language Disorder
"A group of 29 boys affected by DLD and a group of 76 boys with typical language abilities participated (age range = 5;6–11;0 years). (...) Significant group differences indicated lower 2D:4D digit ratios in the group with DLD (Developmental Language Disorder)."(Redmond, Sean M., and Andrea C. Ash. "Associations Between the 2D: 4D Proxy Biomarker for Prenatal Hormone Exposures and Symptoms of Developmental Language Disorder." Journal of Speech, Language, and Hearing Research: 1-11.)
Fight bite injuries more prevalent among males with lower 2D:4D ratio
"We have demonstrated that male patients who sustained fight bite injuries have a lower 2D:4D ratio then the general population, thereby suggesting that exposure to prenatal androgens can lead to aggressive tendencies in adulthood. This suggests that lower ratios may predict a predisposition to acts of aggression, and as such result in an increased likelihood of sustaining an injury such as a fight bite."(Joyce, Cormac W., et al. "Fight Bite Injuries: Aggressive Tendencies Associated with Smaller Second to Fourth Digit Ratio." The Journal of Hand Surgery (Asian-Pacific Volume) 22.04 (2017): 452-456.)
Low 2D:4D digit ratio linked to high degree of tomboyism
Tomboyism: "A tomboy is a girl who exhibits characteristics or behaviors considered typical of a boy, including wearing masculine clothing and engaging in games and activities that are physical in nature and are considered in many cultures to be unfeminine or the domain of boys." (Wikipedia)"The results of the current study indicate that lower 2D:4D ratios are associated with increasing tomboy scores and that tomboyism is associated with higher scores on the testosterone component of Fisher's temperament model as well as a marginal negative association with the estrogen/oxytocin factor. This lends support to Fisher's model as well as documenting the relationship between 2D:4D and tomboyism in a non-clinical population."(Salmon, Catherine A., and Jessica A. Hehman. "Second to fourth digit ratio (2D: 4D), tomboyism, and temperament." Personality and Individual Differences 123 (2018): 131-134.)
"We show in a sample of 44 women that a woman's right hand 2D:4D ratio is a significant predictor of whether they will be labeled as a “tomboy”, with a decrease in 2D:4D ratio corresponding to an increase in the probability of being called “tomboy”."(Atkinson, Beth M., Tom V. Smulders, and Joel C. Wallenberg. "An endocrine basis for tomboy identity: The second-to-fourth digit ratio (2D: 4D) in “tomboys”." Psychoneuroendocrinology 79 (2017): 9-12.)
(Prenatal) testosterone weakens empathy
"[...], we expatiated the factors related to endocrine system that may influence individuals’ empathy and their related behaviors. Whereas oxytocin facilitates the response of empathy, testerone weakens it. In addition, fetal testosterone would influence the development of individual empathy."(YANG, Ye, et al. "Empathy: The genetics-environment-endocrine-brain mechanism." Chinese Science Bulletin (2017).)
Steroidogenic activity is elevated in fetal development of those who later receive diagnoses on the autism spectrum
"We find that amniotic fluid steroid hormones are elevated in those who later received diagnoses on the autism spectrum. Rather than the abnormality being restricted to a specific steroid hormone, a latent steroidogenic factor is elevated, which includes all hormones in the Δ4 pathway, as well as cortisol. (...) The source of elevated steroidogenic activity in the fetal development of autism was not tested in the current study, and more research will be needed to understand how different sources such as the fetus, mother, placenta or other environmental factors might contribute to such elevations.(Baron-Cohen, Simon, et al. "Elevated fetal steroidogenic activity in autism." Molecular psychiatry 20.3 (2015): 369-376.)
(...)
In conclusion, we report the first direct evidence that steroidogenic activity is elevated in fetal development of those who later receive diagnoses on the autism spectrum. These results raise new questions for understanding a wide array of other observations about the early development of autism, through their interactions with early fetal steroidogenic abnormalities and provide initial support for the importance of fetal steroid hormones as important epigenetic fetal programming mechanisms for autism."
Prenatal testosterone exposure influences sexual orientation and sex-typed interests in childhood
"The evidence supports a role for prenatal testosterone exposure in the development of sex-typed interests in childhood, as well as in sexual orientation in later life, at least for some individuals. It appears, however, that other factors, in addition to hormones, play an important role in determining sexual orientation. These factors have not been well-characterized, but possibilities include direct genetic effects, and effects of maternal factors during pregnancy. Although a role for hormones during early development has been established, it also appears that there may be multiple pathways to a given sexual orientation outcome and some of these pathways may not involve hormones.(Hines, Melissa. "Prenatal endocrine influences on sexual orientation and on sexually differentiated childhood behavior." Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology 32.2 (2011): 170-182.)
Research highlights: Prenatal exposure to androgenic hormones influences human sexual orientation. Androgen dose predicts the likelihood of non-heterosexual orientation. (...)"
Elevated prenatal tesosterone related to increased male-typical juvenile play behavior, alterations in sexual orientation and gender identity, and increased agression
"Individuals exposed to atypical concentrations of testosterone or other androgenic hormones prenatally, for example, because of genetic conditions or because their mothers were prescribed hormones during pregnancy, have been consistently found to show increased male-typical juvenile play behavior, alterations in sexual orientation and gender identity (the sense of self as male or female), and increased tendencies to engage in physically aggressive behavior."(Hines, Melissa, Mihaela Constantinescu, and Debra Spencer. "Early androgen exposure and human gender development." Biology of sex differences 6.1 (2015): 3.)
"2D:4D and sex-typed play behavior as assessed by parents were negatively correlated in a sample of 83 pre-school boys but not in a sample of 93 girls. This finding lends some support to the ideas that early testosterone has a masculinising effect upon sex-typed play behavior in humans and that 2D:4D is a valuable tool for studying effects of early testosterone on human behavior."(Hönekopp, Johannes, and Christine Thierfelder. "Relationships between digit ratio (2D: 4D) and sex-typed play behavior in pre-school children." Personality and Individual Differences 47, no. 7 (2009): 706-710.)
Men with low 2D:4D ratio are partnered more with women with narrow waists and large breasts
"Men with more masculine 2D:4D were coupled with women with significantly lower waist-to-hip ratios. They were also four times more often partnered with women who had both relatively narrow waists and large breasts."(Kuna, Berenika, and Andrzej Galbarczyk. "Men with more masculine digit ratios are partnered with more attractive women." Personality and Individual Differences 124 (2018): 8-11.)
See also: women with low 2D:4D ratio have higher waist circumference and waist-to-hip ratio. In other words, men with low 2D:4D may be partnered more with women of normal and high 2D:4D ratio than with low 2D:4D ratio.
"Significant negative correlations were found between female’s left and right hand 2D:4D, waist and hip circumference, and WCR (waist-to-chest-ratio). (...) Generally, the relationships were stronger for females than for males."In other words: in females, low 2D:4D ratio goes together with high waist and hip circumference and high waist-to-chest ratio.
(source: Second to fourth digit ratio, body mass index, waist-to-hip ratio, and waist-to-chest ratio: their relationships in heterosexual men and women, B. Finka, N. Neaveb & J. T. Manning, pages 728-738, Annals of Human Biology, Volume 30, Issue 6, 2003, retrieved July 1st 2016)
and
"[M]others with high waist to hip ratios (...) have been shown to have low 2D:4D ratios (...)."(Liu, Jianghong, Jill Portnoy, and Adrian Raine. "Association between a marker for prenatal testosterone exposure and externalizing behavior problems in children." Development and psychopathology 24.03 (2012): 771-782.)
The more "abnormal" the 2D:4D digit ratio (either high or low instead of medium), the less altruistic the behavior
"We analyze the association between altruism in adults and the exposure to prenatal sex hormones, using the second-to-fourth digit ratio. We find an inverted U-shaped relation for left and right hands, which is very consistent for men and less systematic for women. Subjects with both high and low digit ratios give less than individuals with intermediate digit ratios. We repeat the exercise with the same subjects seven months later and find a similar association, even though subjects' behavior differs the second time they play the game. We then construct proxies of the median digit ratio in the population (using more than 1000 different subjects), show that subjects' altruism decreases with the distance of their ratio to these proxies. These results provide direct evidence that prenatal events contribute to the variation of altruistic behavior and that the exposure to fetal hormones is one of the relevant biological factors. In addition, the findings suggest that there might be an optimal level of exposure to these hormones from social perspective."(Branas-Garza, Pablo, Jaromír Kovářík, and Levent Neyse. "Second-to-fourth digit ratio has a non-monotonic impact on altruism." PloS one 8.4 (2013): e60419.)
Prenatal and pubertal testosterone interact in complex ways with respect to brain lateralization
"For boys, we found a significant interaction effect between prenatal and pubertal testosterone on lateralization of Mental Rotation and Chimeric Faces. In the boys with low prenatal testosterone levels, pubertal testosterone was positively related to the strength of lateralization in the right hemisphere, while in the boys with high prenatal testosterone levels, pubertal testosterone was negatively related to the strength of lateralization. For Word Generation, pubertal testosterone was negatively related to the strength of lateralization in the left hemisphere in boys. For girls, we did not find any significant effects, possibly because their pubertal testosterone levels were in many cases below quantification limit. To conclude, prenatal and pubertal testosterone affect lateralization in a task-specific way. Our findings cannot be explained by simple models of prenatal testosterone affecting brain lateralization in a similar way for all tasks."(Beking, T., et al. "Prenatal and pubertal testosterone affect brain lateralization." Psychoneuroendocrinology (2017).)
Lower 2D:4D ratio correlates with greater decrease in effort when payment changes from fixed to "per piece"
When people are paid according to their performance (eg. for every piece they produce) instead of a fixed payment (eg. a monthly wage independent of performance), they level of effort changes. In this study, a correlation with 2D:4D ratio was found."When the piece rate is replaced with fixed payment, men and participants with lower 2D:4D show a greater decrease in effort than the rest. We do not observe any impact of gender or 2D:4D on effort adjustment behavior when fixed payment is replaced with a piece rate."(Friedl, Andreas, Levent Neyse, and Ulrich Schmidt. "Payment Scheme Changes and Effort Adjustment: The Role of 2D: 4D Digit Ratio." Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Economics (2017).
Sex-differences in gray matter asymmetry in the brain
"Males show a significantly stronger rightward asymmetry than females within the cerebellum, specifically in lobules VII, VIII, and IX. This finding agrees closely with prior research suggesting sex differences in sensorimotor, cognitive and emotional function, which are all moderated by the respective cerebellar sections."(Kurth, Florian, Paul M. Thompson, and Eileen Luders. "Investigating the Differential Contributions of Sex and Brain Size to Gray Matter Asymmetry." Cortex (2017).)
Sex differences in brain partly due to fetal testosterone (limbic system), partly to sex chromosomes (motricity related parts)
"Utilizing the inherent differences in sex and X-chromosome dosage among XXY males, XY males, and XX females, comparative voxel-based morphometry was conducted using sex hormones and sex chromosomes as covariates. Sex differences in the cerebellar and precentral gray matter volumes (GMV) were found to be related to X-chromosome dosage, whereas sex differences in the amygdala, the parahippocamus, and the occipital cortex were linked to testosterone levels. An increased number of sex chromosomes was associated with reduced GMV in the amygdala, caudate, and the temporal and insular cortices, with increased parietal GMV and reduced frontotemporal white matter volume. No selective, testosterone independent, effect of the Y-chromosome was detected. Based on these observations, it was hypothesized that programming of the motor cortex and parts of cerebellum is mediated by processes linked to X-escapee genes, which do not have Y-chromosome homologs, and that programming of certain limbic structures involves testosterone and X-chromosome escapee genes with Y-homologs."(E. Lentini, M. Kasahara, S. Arver, I. Savic; Sex Differences in the Human Brain and the Impact of Sex Chromosomes and Sex Hormones, Cerebral Cortex, Volume 23, Issue 10, 1 October 2013, Pages 2322–2336)
High prenatal testosterone decreases Theory of Mind (Reading the Mind in the Eyes performance) in women
Women with increased exposure to prenatal testosterone score significantly lower on the Reading the Mind in the Eyes test than control women and women with androgen insensitivity, and equal to control men."ToM (Theory of Mind) performance was examined using the RMET (Reading the Mind in the Eyes) in(Khorashad, Behzad S., et al. "Prenatal Testosterone and Theory of Mind Development: Findings from Disorders of Sex Development." Psychoneuroendocrinology (2017).)
- female-assigned-at-birth individuals with increased prenatal testosterone exposure (Congenital Adrenal Hyperplasia (CAH) and 5-alpha Reductase type-2 Deficiency (5α-RD-2)),
- female-assigned-at-birth individuals with testosterone insensitivity (Complete Androgen Insensitivity Syndrome (CAIS)),
[...] Women with CAH scored significantly lower on RMET than control women and CAIS individuals.
- and age-matched unaffected male and female relatives.
CAIS individuals scored significantly higher than control men and participants with 5α-RD. Statistically, CAIS individuals' performance on RMET was similar to control women's, women with CAH did not differ significantly from control men and 5α-RD-2 individuals scored significantly lower than control men.
These results, which are in line with previous theories, illustrate that performance on the RMET, as an index of ToM, may be influenced by variations in prenatal androgens levels."
High facial Width to Height ratio correlates (weakly) with greater status defense, low R2D:4D with prosocial (cooperative) behavior in the ultimatum game. 2D:4D ratio and facial Width to Height ratio may be overestimated as markers of agression and competition in socio-economic context
"By applying structural equation modelling we estimated the latent level association of 2D:4D and WHR with negative reciprocity, assertiveness and prosociality in both sexes. Results revealed no robust association between any of the trait measures and hormonal markers. The measures of 2D:4D and WHR were not related with each other. Multigroup models based on sex suggested invariance of factor loadings allowing to compare hormone-behavior relationships of females and males. Only when collapsing across sex greater WHR was weakly associated with assertiveness, suggesting that individuals with wider faces tend to express greater status defense. Only the right hand 2D:4D was weakly associated with prosocial behavior, indicating that individuals with lower prenatal testosterone exposure are more cooperative. Rejection behavior in UG was not related with 2D:4D nor WHR in any of the models. There were also no curvilinear associations between 2D:4D and prosociality as theorized in the literature. Our results suggest that previous studies over-estimated the role of static markers of testosterone in accounting for aggression and competition behavior."(Kaltwasser, Laura, et al. "No robust association between static markers of testosterone and facets of socio-economic decision making." Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience 11 (2017): 250.)
Meta review: increased (prenatal and postnatal) testosterone associated with alcohol use in males, increased estrogen associated with alcohol use in females
"Existing evidence supports the association of increased testosterone level and increased risk for alcohol use and AUD in males but results are inconclusive in females. In contrast, the evidence supports the association of increased estrogen level and increased alcohol use in females, with mixed findings reported in males."(Erol, Almila, et al. "Sex hormones in alcohol consumption: a systematic review of evidence." Addiction Biology (2017).)
ADHD boys have higher 2D:4D ratio than normal, ADHD girls lower
"ADHD boys had a more feminized 2D:4D left hand ratio than the controls. [...] [T]he more masculine 2D:4D right hand ratio was observed in ADHD girls."(Buru, Ece, et al. "Evaluation of the hand anthropometric measurement in ADHD children and the possible clinical significance of the 2D: 4D ratio." Eastern Journal Of Medicine 22.4: 137-142.)
Testosterone supplements increase spatial working memory and long-term memory of castrated rats, dependent on dose
"Testosterone replacement restored spatial working memory in castrated male rats.(Wagner, Benjamin A., et al. "Effects of testosterone dose on spatial memory among castrated adult male rats." Psychoneuroendocrinology (2017).)
Testosterone replacement had no effect on reference memory in castrated male rats.
Testosterone replacement improved long-term memory in castrated male rats.
[...]
Testosterone replacement restored spatial memory among castrated male rats [...], but there was a complex dose-response relationship; therefore, the therapeutic value of testosterone is likely sensitive to dose."
Testosterone increases financial risk-taking
"This systematic review undertook to evaluate the influence of circulating testosterone (activational effects) and the pre-natal exposure to this (organisational effects) as regards risk-taking decisions in financial behaviour. An evaluation was also made on the research work to date on this subject. The bibliographic database analysed was obtained from different databases specialised in the field of psychology and neuroscience. The results obtained show a relationship between circulating testosterone and financial risk-taking. As regards prenatal exposure, research on this topic is still in its infancy, since the few articles found widely differ in methodologies and results."(Siurana, David, Marien Gadea, and Raúl Espert. "Organizational and activational effects of testosterone on risk-taking in economical behavior: A systematic review." Suma Psicológica 24.2 (2017): 142-152.)
Subjects with low 2D:4D ratio are less generous
"We examine whether social preferences are partially determined by biological factors. We do this by investigating whether digit ratios (2D:4D) (...) are correlated with choices in ultimatum, trust, public good and dictator games. (...) Subjects with lower 2D:4D are less generous in all games."(Buser, Thomas. "Digit ratios, the menstrual cycle and social preferences." Games and Economic Behavior 76.2 (2012): 457-470.)
Higher prenatal testosterone correlates with lower empathy, higher post-natal testosterone correlates with higher number of sexual partners
"In this study, we examine the influence of prenatal and postnatal testosterone on the NSP (Number of Sexual Partners) and on the empathic abilities which affect sociosexual strategies in student heterosexual men (n=23, aged 24.00±1.46). A questionnaire was used for stating the total NSP; the 2nd and 4th finger was measured using a vernier caliper, while the circulating testosterone was measured with enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). The empathizing quotient (EQ) was determined using a special empathy test (Baron-Cohen and Wheelwright 2004). (...) Our results suggest that prenatal testosterone influences the empathic abilities [tendency for negative correlation between prenatal testosterone levels and EQ (Empathizing Quotient)], whereas postnatal testosterone influences the NSP."(Skalná, Zuzana, et al. "VPLYV MIERY PRENATÁLNEJ EXPOZÍCIE TESTOSTERÓNU A JEHO POSTNATÁLNEJ KONCENTRÁCIE NA POČET SEXUÁLNYCH PARTNERIEK A SCHOPNOSŤ EMPATIZÁCIE U MUŽOV ZO SLOVENSKA." SLOVENSKÁ ANTROPOLÓGIA: 42.)
Testosterone changes expression of genes related to autism
"RNA-sequencing revealed that treatment with dihydroxytestosterone (DHT) leads to subtle but significant changes in the expression of about two hundred genes (...). (...) DHT-DEGs (Differentially Expressed Genes) appear enriched in genes involved in ASD (Autism Spectrum Disorder) (...), associated with ASD (...), or differentially expressed in patients with ASD (...)."(Quartier, Angélique, et al. "Genes and pathways regulated by androgens in human neural cells, potential candidates for the male excess in autism spectrum disorders." Biological Psychiatry (2018).)
High basal testosterone correlates with intrasexual competitiveness among men and agressive mate-retention behavior
"Results showed that higher basal testosterone predicted more self-reported mate retention effort. This relationship was mediated by intrasexual competitiveness, such that high T men reported more intrasexual competitiveness, which when included in the model predicted mate retention, and reduced the initial T – mate retention relationship to statistical non-significance. When examined separately, this mediation effect applied specifically to cost-inflicting [that renders defection from the relationship risky or dangerous for the partner], rather than benefit-provisioning [that makes the relationship more beneficial for the partner], mate retention behavior."(Arnocky, Steven, et al. "Intrasexual competition mediates the relationship between men's testosterone and mate retention behavior." Physiology & Behavior (2018).)
Low left 2D:4D digit ratio correlates with higher agression, hostility and anger in adolescent males
"The aim of this study is to provide basic data to prevent adolescent crime or violence by analyzing aggression according to second digit to fourth digit ratio (2D : 4D). (...) This study was done on 187 elementary school students (98 males, 89 females). (...)
This study showed that the 2D : 4D of males was significantly lower than female, and the aggression score of males was significantly higher than female. Especially, there was significantly differences between 0.900 or less than 0.900 digit ratio group and 1.000 or more than 1.000 digit ratio group only left hand of males. [More agression for lower digit ratios.]
The results of this study suggest that left digit ratio of males in elementary school students are able to be used as one of physical markers to evaluate aggression."
 |
| Fig. 1. Aggression differences according to left digit ratio level group in male. There was significantly aggression differences between 0.900 or less than 0.900 digit ratio group and 1.000 or more than 1.000 digit ratio group only left hand of males. |
(Cho, Keun Ja, and Sooil Kim. "Utilization of Second Digit to Fourth Digit Ratio (2D: 4D) as One of Physical Markers to Evaluate Aggression in Elementary School Students." Korean Journal of Physical Anthropology 30.4 (2017): 153-159.)
Men with high 2D:4D ratio (low prenatal testosterone) are overconfident on math-like task
"(...) [W]e found that [overconfidence and right-hand 2D:4D digit ratio] were significatively positive correlated, suggesting that high overconfidence was associated with low prenatal testosterone exposure (...). After controlling for possible confounding variables, like previous experience with the task, risk attitude index and self-efficacy, the association between prenatal testosterone exposure and overconfidence became even stronger. (...). Again, we found this effect only in men. Also, as expected, we found that the higher the degree of previous expertise with the task and the higher the self-efficacy, the lower the overconfidence."
(Perceived self-efficacy is a judgment of capability to execute given types of performances. (...)
For example, perceived self-efficacy scales include items such as “I can solve most problems if I invest the necessary effort”or “I can usually handle whatever comes my way.”)
(Dalton, Patricio, and Sayantan Ghosal. "Self-confidence, overconfidence and prenatal testosterone exposure: evidence from the lab." (2014).)
High prenatal testosterone dampens connectivity in "social" brain networks in men
"Here we find that variation in fetal testosterone (FT) exerts sex-specific effects on later adolescent functional connectivity between social brain default mode network (DMN) subsystems. Increased FT is associated with dampening of functional connectivity between DMN subsystems in adolescent males, but has no effect in females. (...) This work highlights sexspecific prenatal androgen influence on social brain DMN circuitry and autism-related mechanisms and suggests that such influence may impact early neurodevelopmental processes (e.g., neurogenesis, cell differentiation) and later developing synaptic processes."(Lombardo, Michael V., et al. "Sex-specific impact of prenatal androgens on intrinsic functional connectivity between social brain default mode subsystems." bioRxiv (2018): 253310.)
Men with higher testosterone levels also have higher intrasexual competition scores and lower left 2D:4D
"It was found a positive correlation between testosterone levels and intrasexual competition scores, and a negative correlation between testosterone levels and left 2D:4D. Finally, we did not find a significant association between digit ratios 2D:4D and intrasexual competition scores. Our study shows that men with higher testosterone levels also have higher intrasexual competition scores and lower values of left digit ratio 2D:4D. Further studies will have to take into account fluctuations in testosterone over the time to observe if the relation between competitiveness scores and digit ratios 2D:4D becomes significant."(Borráz-León, Javier I., et al. "Testosterone and intrasexual competition in men: is there any relation with digit ratio (2D: 4D)?." acta ethologica (2018): 1-4.)
In men, visuospatial performance declines with increasing 2D:4D ratio, in women opposite effect
"Men performed slightly better on the MRT (Mental Rotation Task). Scores declined with increases in (right-hand) 2D:4D ratios in men. An opposite pattern was seen in women."(Samanta, Bijli Nandaand Prajna Paramita. "Visuospatial task performance is not correlated with 2D: 4D ratio in medical students." (2017).)
Higher heart-rate variability, better face expression recognition, parasympathetic activity and low testosterone levels may be linked
"Higher heart-rate variability (the variation in the time between each heart beat) -- an index of parasympathetic nervous system activity -- is positively associated with facial expression recognition accuracy."(Bar-Ilan University. "Certain smiles aren't all they're cracked up to be: 'Dominance' smiles, which signal disapproval, have an adverse effect on the human body's central stress response system, researchers find." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 1 March 2018)
Testosterone replacement therapy has been known to lower heart-rate variability:
"A 9‑week testosterone supplementation therapy improves HRV parameters."
(Poliwczak, Adam R., Maja Tylińska, and Marlena Broncel. "Effect of short-term testosterone replacement therapy on heart rate variability in men with hypoandrogen-metabolic syndrome." Pol Arch Med Wewn 123 (2013): 467-73.)
More conduct disorder among children with low 2D:4D ratio
"The second-to-forth digit length ratio (2D:4D) is considered to be a biomarker for intrauterine androgen levels. It is associated with adult and child mental health problems, primarily with behavioral symptoms and predominantly in males. (...) [W]e examined whether 2D:4D was associated with conduct disorder (CD) symptoms in 138 primary-school aged children (...). The regression analyses revealed that 2D:4D ratios were associated with behavioral symptoms in boys (...), but not in girls (...). In conclusion, prenatal brain hyperandrogenization - operationalized by the 2D:4D biomarker - could result in behavioral symptoms in boys at early school age, reflecting one predictor for early onset CD. Our data support the use of 2D:4D as a marker of prenatal androgen exposure."(Eichler, Anna, et al. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and behavioral symptoms in primary-school aged boys." Early Human Development 119 (2018): 1-7.)
More frequent and more severe binge drinking among adults with low 2D:4D ratio
"[B]inge drinkers showed lower 2D:4D (...) and reported later pubertal onset (...) than non-binge drinkers. These findings consistently suggest excess prenatal androgen exposure in adult binge drinkers. Moreover, 2D:4D was negatively associated with severity (...) and frequency of binge drinking episodes (...)."(Lenz, Bernd, et al. "Low digit ratio (2D: 4D) and late pubertal onset indicate prenatal hyperandrogenziation in alcohol binge drinking." Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry (2018).)
Males: more avolition (listlessness) with high 2D:4D, more anxiety with low 2D:4D. Females: more depression with high 2D:4D, more alogia (incapable to hold a conversation) with low 2D:4D
"In male patients, the 2D:4D ratio was positively associated with avolition and inversely associated with anxiety. In female patients, it was inversely associated with alogia, and tended to be positively associated with depression.(Paipa, Nataly, et al. "Second-to-fourth digit length ratio is associated with negative and affective symptoms in schizophrenia patients." Schizophrenia Research (2018).)
(...)
[P]renatal sex hormone concentration seems to be associated with predisposition to anxiety in male patients, and to depression in female patients."
Avolition (...) is the decrease in the motivation to initiate and perform self-directed purposeful activities (...) [like] hobbies, going to work and/or school, and most notably, engaging in social activities.
Alogia (...) or poverty of speech, is a general lack of additional, unprompted content seen in normal speech.
Depression in men is associated with more feminine finger length ratios
"Variation in the influence of prenatal androgens is thought to be reflected in an individual’s finger length ratio (2D:4D). Many recent studies have examined the relationship between adult finger length ratio and traits thought to be affected by prenatal androgens. For example, Martin, Manning, and Dowrick (1999) have suggested that increased risk of clinical depression is a cost of high organizational testosterone in men. They presented data demonstrating a non-significant trend (p = 0.24) towards higher depression in men with more masculine finger length ratios. Given that women commonly show higher rates of depression than men, we suggest that depression should be associated with lower, rather than higher organizational testosterone. We tested a sample three times larger than that used by Martin et al. (1999) and found that men with more feminine finger ratios scored higher on a test for depression measured as a personality trait (p = 0.04). This result is consistent with the hypothesis that a portion of the variation in depression is due to the organizational effects of sex hormones in men."(Bailey, Allison A., and Peter L. Hurd. "Depression in men is associated with more feminine finger length ratios." Personality and Individual Differences 39, no. 4 (2005): 829-836.)
In male rhesus macaques, prenetal androgen treatment causes bigger cell size of certain neurons, which may explain behavioral differences
"Onuf's nucleus is a column of motoneurons in the sacral spinal cord that innervates the striated perineal muscles. This cell group is larger in males [meaning: more cells] than in females of many species, due to androgens acting during a sensitive perinatal period. (...) Prenatal testosterone treatment of males did not alter Onuf's nucleus motoneuron number, but did increase the size of both Onuf's and Pes9 motoneurons. Thus, prenatal androgen manipulations cause cellular-level changes in the primate CNS, which may underlie previously observed effects of these manipulations on behavior."(Forger, N. G., et al. "Effects of sex and prenatal androgen manipulations on Onuf's nucleus of rhesus macaques." Hormones and behavior (2018).)
Neurons in Onuf's nucleus are involved in the maintenance of micturition (cfr. urination) and defecatory continence, as well as muscular contraction during orgasm.
No correlation between 2D:4D ratio and religiosity (except in a subgroup of females)
"Here, we initially examined 2D:4D in relation to self-reported religious affiliation and questionnaire measures of general religiosity, spirituality, religious fundamentalism, and religious commitment in male (N = 106) and female (N = 105) university students (Study 1). Although no significant correlations were observed between 2D:4D and the questionnaire measures, females who affiliated with organised religions had higher right and left hand digit ratios compared to agnostic or atheist females. Study 2 attempted to replicate these findings in an adult general population sample (N = 172 males, N = 257 females), but did not observe significant effects in either sex. Overall, these findings suggest that high 2D:4D may be relatively-specifically associated with increased religious affiliation in young, highly-educated, females."(Richards, Gareth, et al. "2D: 4D digit ratio and religiosity in university student and general population samples.")
Students in Health have higher 2D:4D ratios than students in Economics and Engineering, indepent of gender; no correlation between 2D:4D and mental rotation test
"The population considered for this study was the set of all students enrolled in Campus 2 of the Polytechnic Institute of Leiria (totaling about 5,200), of which a sample of 252 subjects (127 men and 125 women) was chosen, with an average of 22.9 years (standard deviation of 6,366), obtained in a simple randomized way. All the participants were digitalized in both hands using a scanner (...)(Paixão, Jorge Manuel Duarte. 2D: 4D e rotação mental: estudo de um biomarcador putativo dos efeitos pré-natais dos esteroides sexuais no desempenho numa prova de rotação mental numa população estudantil. Diss. Universidade de Coimbra, 2018.)
[T]here are statistically significant differences between the education areas and the right/left hand ratio, with the students in the Health area presenting, on average, a higher ratio, followed by students in the area of Economics and Engineering (...). That is, the engineering students present an average 2D:4D of the right/left hands lower when compared to the rest; ascertaining whether these statistically significant differences persist in the analyzes within the sex variable, in both the female participants group and the male participants group, there was no statistically significant difference.
(...)
[T]here were no statistically significant differences between the lowest and the highest 2D:4D relative to the performance in the mental rotation test"
High testosterone may correlate with faster physical reflexes
1) Under stress, males sprinters react quicker than female sprinters
See table below. Casual RT = reaction time in rest situation, where the reaction time for males and females is about equal. RT 1 = reaction time just before the subjects (who were all sprinters) had to sprint, so under stress. Under stress, the reaction time for males drops a lot more than for females.(Tambe, M. K., et al. "Influence of digit ratio (2D: 4D) on reaction time and athletic sprint performance: A short term pilot study." (2018).)
2)
"Significant associations between cognitive performances and testosterone decline were documented: visuomotor slowing, slowed reaction times in some attentional domains including working memory and impaired hit rate in a vigilance test, impaired delayed recall and recognition speed of letters, but improvement in object recall."(Salminen, Eeva K., et al. "Associations between serum testosterone fall and cognitive function in prostate cancer patients." Clinical Cancer Research 10.22 (2004): 7575-7582.)
"Our results suggest that prenatal androgens (...) promote more rapid visuomotor scanning and physical reflexes."(Coates, John M., Mark Gurnell, and Aldo Rustichini. "Second-to-fourth digit ratio predicts success among high-frequency financial traders." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 106.2 (2009): 623-628.)
Low 2D:4D digit ratio in male suicide victims
"Here, we studied the second-to-fourth-finger length ratio (2D:4D), a proxy for prenatal androgen exposure, in 46 suicide corpses and 25 non-suicide corpses. We report significantly lower 2D:4D in male suicide corpses than non-suicide corpses (p = .030, partial η 2 = .147). There was no significant association between 2D:4D and the suicide method. Our findings indicate increased risk of suicide following higher prenatal androgen exposure in males."(Lenz, Bernd, et al. "Low digit ratio (2D: 4D) in male suicide victims." Journal of neural transmission 123.12 (2016): 1499-1503.)
In children with Specific Language Impairment, a higher r2D:4D ratio correlates with more linguistic problems
"Children with SLI showed significantly higher values of 2 D:4 D ratio of the right hand, and a negative correlation between this ratio and their linguistic competence. (...) A higher value of the biological 2 D:4 D ration (lower intrauterine exposure to testosterone) seems to be associated with language difficulties in boys with SLI, but not with their behavioural difficulties. Their behavioural difficulties seem to be a consequence of their linguistic difficulties and their level of cognition."(Font-Jordà, Antònia, et al. "Uso del índice digital D2: D4 como indicador biológico del trastorno específico del lenguaje." Anales de Pediatría. Elsevier Doyma, 2018.)
High 2D:4D ratio correlates with higher generosity, trust and reciprocity, but only in subjects who experience low subjective well-being
"[G]enerosity, bargaining and trust-related behaviors are correlated neither linearly nor non-linearly with 2D:4D, and this holds for both males and females and left- and right-hands. At the first sight, these results support the evidence that prenatal exposure to sexual hormones do not systematically predict social attitudes in humans.(Brañas-Garza, Pablo, et al. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) predicts pro-social behavior in economic games only for unsatisfied individuals." (2018).)
This null result notwithstanding, once we take subjective wellbeing into account, we document positive associations of 2D:4D with generosity in the Dictator Game (for both males and females) and trust and reciprocity in the Trust Game (only for males) among subjects reporting low wellbeing. In sharp contrast, this relationship disappears and may slightly reverse for individuals with relatively high wellbeing ratings."
No significant relationship between 2D:4D ratio and cognitive abilities in 19-year old students in India
"The mean 2D:4D ratio of the study population was 0.97 ± 0.034. The mean 2D:4D ratio of males (0.97 ± 0.32) was not significantly different from that of females (0.98 ± 0.035). There was no significant correlation between higher secondary scores and the 2D:4D ratio. Significant relationships with 2D:4D ratios and domains of cognition tested (free and placement recall, category fluency, and working memory) were not observed. Existing literature also revealed many inconsistencies within the pattern of associations between 2D:4D digit ratio and cognitive abilities."(Selvaraj, Ramaneshwar, Muthu Prathibha, and Vijayanand Dharmalingam. "2D: 4D ratio and its association with examination scores and cognitive abilities in adolescent students-A cross-sectional study." National Journal of Physiology, Pharmacy and Pharmacology 8.1 (2018): 62-67.)
2D:4D ratio correlates (inversely) with performance on mental rotation task, independent of biological gender
"Both men and women showed a significant negative correlation between left and right digit finger ratio and MRT (mental rotation task) scores, such that individuals with smaller digit ratios (relatively longer ring finger than index finger) performed better than individuals with larger digit ratios."(Peters, Michael, John T. Manning, and Stian Reimers. "The effects of sex, sexual orientation, and digit ratio (2D: 4D) on mental rotation performance." Archives of Sexual Behavior 36.2 (2007): 251-260.)
Statistically, men perform better at MRT than women.
Power corrupts people, but only if they have high levels of testosterone
"Taken together, these results suggest that people with high (but not low) testosterone [measured from saliva sample the day before the test] may be inclined to misuse their power because having power over others makes them feel entitled to special treatment. This work identifies testosterone as a characteristic that contributes to the development of the socially-toxic component of narcissism (Exploitative/Entitlement).(Mead, Nicole L., et al. "Power Increases the Socially Toxic Component of Narcissism Among Individuals with High Baseline Testosterone.")
(...)
Leaders with high testosterone were prone to use their position of power to improve their own outcomes at the expense of others (Bendahan, Zehnder, Pralong, & Antonakis, 2015). (...) Testosterone is positively associated with dominant behavior that is intended to achieve or maintain high social rank (Archer, 2009; Mazur & Booth, 1998). Those highly motivated to dominate others strive to retain their positions of power, even at the expense of group interests (Maner & Mead, 2010)."
2D:4D digit ratio positively correlated with examination marks in male students
"2D:4D of right hand positively predicted examination marks of males from two three-year degree courses (TYDCs). Marks of females did not covary with 2D:4D. (...) If testosterone affects 2D:4D and intellectual performance, our results suggest that testosterone levels are under stabilizing selection because of effects on performance traits documented in previous studies and antagonistic effects on intellectual performance (present study)."(Romano, Maria, Barbara Leoni, and Nicola Saino. "Examination marks of male university students positively correlate with finger length ratios (2D: 4D)." Biological Psychology 71.2 (2006): 175-182.)
Autism/Asperger, ADHD/ODD, PDD linked to low 2D:4D ratio; anxiety disorder to high 2D:4D
"Children with autism have a relatively shorter index finger (2D) compared with their ring finger (4D). (...) Males with autism/Asperger syndrome (p<0.05) and ADHD/ODD (p<0.05) had significantly lower (though not significantly; p=0.52) ratios than males with an anxiety disorder, and males with autism/Asperger syndrome had lower ratios than those in the comparison group. These results indicated that higher fetal testosterone levels may play a role, not only in the origin of autism, but also in the aetiology of PDD-NOS and of ADHD/ODD. Males with anxiety disorders might have been exposed to lower prenatal testosterone levels."
ADHD = attention-deficit-hyperactivity disorder
ODD = oppositional defiant disorder
PDD = pervasive developmental disorder
NOS = not otherwise specified
(De Bruin, Esther I., et al. "Differences in finger length ratio between males with autism, pervasive developmental disorder‐not otherwise specified, ADHD, and anxiety disorders." Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 48.12 (2006): 962-965.)
High 2D:4D associated with increased eating disorder symptoms
"RESULTS:(Klump, Kelly L., et al. "Preliminary evidence that gonadal hormones organize and activate disordered eating." Psychological medicine 36.4 (2006): 539-546.)
Positive associations were found between disordered eating and both finger-length ratios and circulating estradiol levels [in women].
CONCLUSIONS:
Findings suggest that lower levels of prenatal testosterone exposure and higher adult levels of estradiol are associated with increased eating disorder symptoms."
"RESULTS:(Smith, April R., Sean E. Hawkeswood, and Thomas E. Joiner. "The measure of a man: Associations between digit ratio and disordered eating in males." International Journal of Eating Disorders 43.6 (2010): 543-548.)
There were significant correlations between 2D:4D ratio and disordered eating and drive for leanness [in men], indicating that greater prenatal testosterone exposure was associated with less disordered eating and increased drive for muscularity."
Higher reproductive success for men with low 2D:4D and women with high 2D:4D
"Significant negative associations were found between 2D:4D in men and reproductive success in the English and Spanish samples and significant positive relationships between 2D:4D in women and reproductive success in the English, German, and Hungarian samples. The English sample also showed that married women had higher 2D:4D ratios than unmarried women, suggesting male choice for a correlate of high ratio in women, and that a female 2D:4D ratio greater than male 2D:4D predicted high reproductive success within couples. Comparison of 2D:4D ratios of 62 father:child pairs gave a significant positive relationship. This suggested that genes inherited from the father had some influence on the formation of the 2D:4D ratio. Waist:hip ratio in a sample of English and Jamaican women was negatively related to 2D:4D."(Manning, John T., et al. "The 2nd: 4th digit ratio, sexual dimorphism, population differences, and reproductive success: evidence for sexually antagonistic genes?." Evolution and Human Behavior 21.3 (2000): 163-183.)
Women with gender identity disorder have lower 2D:4D
"In the sample of adult men with [Gender Identity Disorder] GID (both homosexual and non-homosexual) and children with GID, we found no evidence of an altered 2D:4D ratio relative to same-sex controls. However, women with GID had a significantly more masculinized ratio compared to the control women."(Wallien, Madeleine SC, et al. "2D: 4D finger-length ratios in children and adults with gender identity disorder." Hormones and Behavior 54.3 (2008): 450-454.)
Male infants with higher androgen levels have stronger preferences for male-typical stimuli
"As a first test of the relationship between hormones and behavior in early infancy we measured digit ratios and salivary hormone levels in forty-one male and female infants (3-4 months of age) who watched a video depicting stimuli differentially preferred by older males and females (toys, groups). An eye-tracker measured visual fixations and looking times. In female infants, hormones were unrelated to visual preferences. In male infants, higher androgen levels predicted stronger preferences for male-typical stimuli. These data provide the first evidence for a role for hormones in emerging sex-linked behavior in early development."(Alexander, Gerianne M., Teresa Wilcox, and Mary Elizabeth Farmer. "Hormone–behavior associations in early infancy." Hormones and Behavior 56.5 (2009): 498-502.)
Male-typical behavior (agression, play style) in children associated with lower 2D:4D ratio
"Gender differences in aggression and in the finger length ratios were found, in the directions reported in the literature. Correlations between greater current report of aggression and play style more typical of boys during childhood were found in both the male and female samples. This relationship between current level of aggression and gender-typical childhood play across time was notable. Gender-typical finger length ratios were associated with gender-typical patterns of play for several indices. The current findings provide support for the idea that physical aggression, childhood play style, and finger length ratios may reflect prenatal androgenic influence."(Burton, Leslie A., et al. "Aggression, gender-typical childhood play, and a prenatal hormonal index." Social Behavior and Personality: an international journal 37.1 (2009): 105-115.)
Women with higher 2D:4D ratio have higher pain threshold
"As expected, females had greater symmetry between the second and fourth digits, and also reported lower pain tolerance levels. Although some significant relationships were found between digit ratio/digit length and cold pressor pain reports they were relatively inconsistent. Furthermore, the main finding, that pain thresholds were positively related to digit ratio in women but not men, is somewhat inconsistent with predictions."(Keogh, Edmund, Charlotte Mounce, and Mark Brosnan. "Can a sexually dimorphic index of prenatal hormonal exposure be used to examine cold pressor pain perception in men and women?." European Journal of Pain 11.2 (2007): 231-236.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with increased aggressiveness and sensation seeking in both sexes
"The 2D:4D ratio was a significant predictor of scores on three of the four aggression subscales, total aggression, thrill and adventure seeking, and total sensation-seeking, in the sample as a whole and in women. In men, correlations with 2D:4D were significant only for total sensation-seeking and verbal aggression. In both sexes, lower 2D:4D ratios were associated with increased aggressiveness and sensation seeking."(Hampson, Elizabeth, Connie L. Ellis, and Christine M. Tenk. "On the relation between 2D: 4D and sex-dimorphic personality traits." Archives of sexual behavior 37.1 (2008): 133.)
Association between high 2D:4D ratio and schizotypal personality disorder in males
"More ‘feminized’ 2D:4D phenotype has been demonstrated in schizophrenia versus same-sex controls. This study examined 2D:4D in adolescents with schizotypal personality disorder (SPD). Among normal controls, right 2D:4D was significantly greater (more feminized) in females than males. We replicated laterality effects; significant sex differences only on right. There were no significant sex differences among SPDs. Diagnostic group differences were restricted to White/Caucasian males with greater right 2D:4D in SPDs."(Walder, Deborah J., et al. "Sex differences in digit ratio (2D: 4D) are disrupted in adolescents with schizotypal personality disorder: Altered prenatal gonadal hormone levels as a risk factor." Schizophrenia research 86.1 (2006): 118-122.)
High 2D:4D ratio associated with schizophrenia
"Schizophrenic men and women showed a more "feminine" phenotype of the index and ring fingers in both hands than same-sex controls. This finding implies that low fetal androgen/estrogen ratio may have a predisposing role in the development of schizophrenia and points toward involvement of endocrine factors in the disturbed hemispheric lateralization attributed to the illness."(Arató, Mihaly, Ede Frecska, Cindy Beck, Mary An, and Huba Kiss. "Digit length pattern in schizophrenia suggests disturbed prenatal hemispheric lateralization." Progress in Neuro-Psychopharmacology and Biological Psychiatry 28, no. 1 (2004): 191-194.)
"In this study, we examined a retrospective marker of prenatal testosterone release — 2D:4D finger length ratio (2D:4D), the relative length of 2nd to 4th digit, in 64 Asian patients with schizophrenia and 64 sex-matched controls. No significant difference in mean finger lengths was present, however 2D:4D ratio was significantly different between patients and controls. The effect was primarily seen in males consistent with a ‘less masculinised’ pattern and hypotheses suggesting that schizophrenia may be associated with an abnormality in prenatal circulating testosterone."(Collinson, Simon Lowes, Matthew Lim, Jia Hui Chaw, Swapna Verma, Kang Sim, Attilio Rapisarda, and Siow Ann Chong. "Increased ratio of 2nd to 4th digit (2D: 4D) in schizophrenia." Psychiatry research 176, no. 1 (2010): 8-12.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with more masculine sex-role identity in women
"It was found that the lower 2D:4D ratios associated significantly with higher, masculinized bias scores in BSRI [Bem Sex Role Inventory] indicating that 2D:4D ratio predicts the female or male self-reported sex-role identity in females."(Csathó, Árpád, et al. "Sex role identity related to the ratio of second to fourth digit length in women." Biological psychology 62.2 (2003): 147-156.)
Possible association between 2D:4D ratio and infertility, autism, dyslexia, migraine, stammering, immune dysfunction, myocardial infarction and breast cancer
"Prenatal levels of testosterone and oestrogen have been implicated in infertility, autism, dyslexia, migraine, stammering, immune dysfunction, myocardial infarction and breast cancer. We suggest that 2D:4D ratio is predictive of these diseases and may be used in diagnosis, prognosis and in early life-style interventions which may delay the onset of disease or facilitate its early detection."(Manning, J. T., and P. E. Bundred. "The ratio of 2nd to 4th digit length: a new predictor of disease predisposition?." Medical hypotheses 54.5 (2000): 855-857.)
Low 2D:4D ratio in autism/Asperger subjects
"We found that the 2D:4D ratios of children with autism, their siblings, fathers and mothers were lower than population normative values. Children with AS, who share the social and communicative symptoms of autism but have normal or even high IQ, had higher 2D:4D ratios than children with autism but lower ratios than population normative values. There were positive associations between 2D:4D ratios of children with autism and the ratios of their relatives. Children with autism had lower than expected 2D:4D ratios and children with AS higher ratios than expected in relation to their fathers' 2D:4D ratio. It was concluded that 2D:4D ratio may be a possible marker for autism which could implicate prenatal testosterone in its aetiology."(Manning, John T., et al. "The 2nd to 4th digit ratio and autism." Developmental medicine and child neurology 43.3 (2001): 160-164.)
Low 2D:4D associated with homosexuality in males and females
"Homosexual males and females showed significantly lower 2D:4D ratios in comparison to heterosexuals (...). The evidence may suggest that homosexual males and females have been exposed to non-disruptive, but elevated levels of androgens in utero."(Rahman, Qazi, and Glenn D. Wilson. "Sexual orientation and the 2nd to 4th finger length ratio: evidence for organising effects of sex hormones or developmental instability?." Psychoneuroendocrinology 28.3 (2003): 288-303.)
Androgens act early in life to masculinize various human behaviors
"Using 2D:4D as a correlate, researchers have found evidence that prenatal androgens affect many sexually differentiated human behaviors, including sexual orientation in women (but not in men), attention deficit disorder, autism, eating disorders, aggression, and risk-taking. In each case, lower 2D:4D, indicative of greater prenatal androgen stimulation, is associated with behavior more commonly displayed by males than females. The correlation between 2D:4D and prenatal androgen stimulation is too imperfect to accurately predict the phenotype of a particular individual, even in terms of sex. However, digit ratio is the best available retrospective marker of average differences in prenatal androgen stimulation between groups of people, and/or correlations of prenatal androgen stimulation with particular behaviors and characteristics within a group. Thus digit ratios offer a valid test of the organizational hypothesis that androgens act early in life to masculinize various human behaviors."(Breedlove, S. Marc. "Minireview: organizational hypothesis: instances of the fingerpost." Endocrinology 151.9 (2010): 4116-4122.)
Low 2D:4D related to hyperactivity and poor social cognitive function in girls, and high 2D:4D with emotional symptoms in boys
"Low 2D:4D was related to hyperactivity and poor social cognitive function in girls, and high 2D:4D with emotional symptoms in boys.(Williams, Justin HG, K. D. Greenhalgh, and John T. Manning. "Second to fourth finger ratio and possible precursors of developmental psychopathology in preschool children." Early human development 72.1 (2003): 57-65.)
CONCLUSIONS:
We suggest that during early brain development androgens increase the probability of hyperactivity and poor social cognition in girls. Early oestrogens increase the probability of emotional problems in boys."
Females with low 2D:4D perform better on spatial and numerical ability tests
"Subjects completed several subtests of intelligence batteries for verbal, numerical and spatial abilities. Levels of T [actual testosterone in saliva] were not related to any of the cognitive functions. The 2D:4D was lower in males as compared to females. Males outperform females on spatial ability. Moreover, females with low 2D:4D performed better on cognitive tests measuring spatial as well as numerical ability as compared to females with high 2D:4D."(Kempel, P., et al. "Second-to-fourth digit length, testosterone and spatial ability." Intelligence 33.3 (2005): 215-230.)
But this study did not find a link between prenatal testosterone and spatial ability. It did not measure 2D:4D ratios, but looked at opposite-sex twins (in the light of the hypothesis that prenatal testosterone may transfer from a male twin to the female twin):
"Contrary to the previous studies, our results gave no indication that prenatally transferred testosterone, from a male to a female twin, influences sex differences in spatial ability."(Toivainen, Teemu, Giulia Pannini, Kostas A. Papageorgiou, Margherita Malanchini, Kaili Rimfeld, Nicholas Shakeshaft, and Yulia Kovas. "Prenatal testosterone does not explain sex differences in spatial ability." Scientific Reports 8, no. 1 (2018): 13653.)
Low 2D:4D associated with low verbal intelligence, high numerical intelligence, and low agreeableness
"We found a relation between right-hand 2D:4D and Verbal and Numerical Intelligence as well as Agreeableness (R2’s around .22), in a typical masculine pattern (low 2D:4D, low verbal intelligence, high numerical intelligence, and low agreeableness). We conclude 2D:4D is a valuable tool in the study of the determinants of individual differences."(Luxen, Marc F., and Bram P. Buunk. "Second-to-fourth digit ratio related to verbal and numerical intelligence and the Big Five." Personality and Individual Differences 39.5 (2005): 959-966.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with higher numerical competencies in boys, not girls
"We studied relations between 2D:4D and competencies in the domains of counting, number knowledge, and visual-number representation in 73 children aged 6–11 years. Significant negative correlations between numerical performance in all of these areas and right and left hand 2D:4D ratios were found for boys but not girls. To the extent that 2D:4D ratios reflects prenatal exposure to T, the implications are (i) high prenatal T may be associated with better performance on some basic numerical measures for boys, and (ii) prenatal exposure to T may affect boys and girls differently with respect to some numerical competencies."(Fink, Bernhard, Helen Brookes, Nick Neave, John T. Manning, and David C. Geary. "Second to fourth digit ratio and numerical competence in children." Brain and Cognition 61, no. 2 (2006): 211-218.)
Higher prenatal testosterone levels are associated with reduced social skills but superior attention to detail in infants
"Cambridge scientists were the first to discover that a part of the brain called the amygdala is under-active when people with autism and Asperger Syndrome are trying to decode emotional facial expressions. (...)(The autistic brain, Cambridge Neuroscience, retrieved 29/4/2018)
Because autism and Asperger Syndrome affect boys far more often than girls, Cambridge neuroscientists have been driving research into foetal testosterone in order to examine its effects on brain development and postnatal behaviour. Cambridge has analysed the effects of prenatal testosterone levels, produced by the foetus and measured via amniocentesis during the first trimester of pregnancy, on autistic behaviour. Foetal testosterone shapes brain development to alter an individual’s cognitive profile by binding to androgen receptors in the brain, the amygdala being one region that is rich in such receptors. Strikingly, Cambridge researchers have shown that higher prenatal testosterone levels are associated with reduced social skills but superior attention to detail in infants."
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with neurodevelopmental disorders
"[F]or both males and females (...), the [2D:4D digit] ratio decreased with the presence of any NDD [NeuroDevelopmental Disorder] diagnosis. (...)(Myers, Lynnea, et al. "2D: 4D Ratio in Neurodevelopmental Disorders: A Twin Study." (2018).)
An association was found between the 2D:4D ratio and the presence of any NDD and ADHD diagnoses in males in the between-pairs model and any NDD in females in the
within-pairs model. For males, the finding of a significant relationship between the ratio and any NDD or ADHD diagnosis in the between-pairs model may suggest the influence of genetic factors in the development of the ratio, resulting in a lower 2D:4D ratio for those males with a NDD in general or an ADHD diagnosis in particular."
Correlation between testosterone and risk-taking
"We conducted a systematic literature search and independent meta-analyses to assess the link between endogenous testosterone, estradiol, and cortisol levels and risk-taking related constructs (i.e., risk-taking propensity, impulsivity, sensation seeking, novelty seeking). We found small correlations between risk-taking constructs and testosterone (...) as well as estradiol (...), but not cortisol (...). Overall, these results suggest a biological foundation for individual differences in risk taking."(Kurath, Jennifer, and Rui Mata. "Individual differences in risk taking and endogeneous levels of testosterone, estradiol, and cortisol: A systematic literature search and three independent meta-analyses." Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews (2018).)
Women's perceptions of male attractiveness do not vary according to their salivary hormone levels
"[W]e conducted the largest-ever longitudinal study of the hormonal correlates of women’s preferences for facial masculinity (N = 584)Analyses showed no compelling evidence that preferences for facial masculinity were related to changes in women’s salivary steroid hormone levels. Furthermore, both within-subjects and between-subjects comparisons showed no evidence that oral contraceptive use decreased masculinity preferences. However, women generally preferred masculinized over feminized versions of men’s faces, particularly when assessing men’s attractiveness for short-term, rather than long-term, relationships."(Jones, Benedict C., et al. "No compelling evidence that preferences for facial masculinity track changes in women's hormonal status." bioRxiv (2017): 136549.)
Female athletes with lower 2D:4D ratio are mentally "tougher"
"The key results included that those competing at the highest levels of competition had lower 2D:4D, higher levels of mental toughness and a stronger identification with both masculine and feminine traits. These findings suggest that 2D:4D could provide a marker for sporting potential and mental toughness in female sport participants."(Meggs, Jenny. "The organizational effect of prenatal testosterone upon gender role identity and mental toughness in female athletes." Women in Sport and Physical Activity (2018).)
Mental toughness was measured using the MTQ48:
Increase in testosterone may lead to lower levels of important gene, possibly linked to autism
"Neuroscientists have been interested in RORA [retinoic acid-related orphan nuclear receptor alpha] for decades. (...) The gene encodes a transcription factor, a protein that turns other genes on and off. (...)(Study uncovers molecular targets of autism-linked RORA gene, Virginia Hughes, Spectrum News, 6 june 2013)
The new study analyzed the genome of cultured human neurons and found that RORA binds to 2,544 unique genes. Just because RORA binds to a gene doesn’t mean it will influence its expression, however. (...)
RORA didn’t catch the attention of autism researchers until 2010, when Hu’s team published a study on the characteristic chemical changes to DNA in people with autism, the so-called ‘epigenetic’ signature. She showed that identical twins who are discordant for autism — meaning that one twin has the disorder and the other does not — carry different levels of methylation in their DNA. RORA turned out to be one of the genes that is methylated differently in the twin with autism than in the twin without.
In later experiments, Hu’s group showed that cultured neurons exposed to estrogen produce more RORA4. Conversely, they dial down RORA production when exposed to testosterone. (...)
An increase in testosterone could lead to lower levels of RORA."
Higher testosterone correlates with less religious ties in men
"[M]en with higher levels of the sex hormones testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in their bodies had weaker religious ties"(Springer. "Older men with higher levels of sex hormones could be less religious, study suggests: Amount of testosterone and dehydroepiandrosterone (DHEA) in a man's body may influence how religious he is." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 30 May 2018. )
Higher (prenatal) testosterone increases risk of suicide completion
"We present multiple lines of direct and indirect evidence showing that both an increased prenatal androgen load (with subsequent permanent neuroadaptations) and increased adult androgen activity are involved in suicide completion. We also review data arguing that modifiable maternal behavioral traits during pregnancy contribute to the offspring’s prenatal androgen load and increase the risk for suicide completion later in life.(Lenz, Bernd, et al. "The androgen model of suicide completion." Progress in Neurobiology (2018).)
We conclude that in utero androgen exposure and adult androgen levels facilitate suicide completion in an additive manner."
Lower 2D:4D digit ratio linked to higher participation in competitive sports and games for males
"The difference between male and female 2D:4D digit ratios was statistically significant, as was the difference between the digit ratios of males who play sports versus those who do not. Males that(Nick Lehan & Kayla Smith, "2D:4D Digit Ratio: Indicator of Sports and Gaming Participation in Males", Xavier Journal of Undergraduate Research, vol. 3, 2015, Complete Print edition, pp.31-45)
competitively game had statistically significant different ratios than males that do not competitively game. Those who major in the social and natural sciences tend to have lower digit ratios than those who major in the humanities. Though the 2D:4D digit ratio was not found to be an indicator of competitiveness as a trait as expected, according to the Revised Competitiveness Index, it does seem to be a marker for participation in some competitive activities for males."
Children with high 2D:4D ratio act more prosocially
"We found that [6-to-9-year old school-]children behaved prosocially, and that their prosocial tendencies were negatively correlated with prenatal androgen exposure; i.e., children with high 2D:4D ratios (reflecting low prenatal androgen exposure) acted more prosocially than children with low 2D:4D ratios."
Prosocial behaviour is defined here as “voluntary behavior intended to benefit another”.
(Horn, Lisa, Niklas A. Hungerländer, Sonja Windhager, Thomas Bugnyar, and Jorg JM Massen. "Social status and prenatal testosterone exposure assessed via second-to-fourth digit ratio affect 6–9-year-old children’s prosocial choices." Scientific Reports 8, no. 1 (2018): 9198.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with general violent behavior in young adult males
"Recent meta-analyses on the relationship between prenatal testosterone—measured by the 2D:4D digit ratio—and aggression and analogous traits have reported an overall weak association. Fewer studies, however, have focused specifically on violent behavior. Yet, many of these studies have relied on small samples of incarcerated men and limited their focus to intimate partner violence. Less is known about whether the link between the 2D:4D ratio and violence holds for non-incarcerated populations, for females as well as males, and for general measures of violence. To address these issues, original data were collected on a sample of young adults to estimate the association between the 2D:4D ratio and self-reported violence. The study yielded two important findings. First, the 2D:4D ratio was associated with a majority of the individual violent behaviors examined, as well as multi-item measures of violence, in both bivariate and multivariate models. Second, the 2D:4D ratio was associated with violent behavior among separate samples of men and women, though associations were frequently non-statistically significant for females."(Hoskin, Anthony W., and Ryan Charles Meldrum. "The association between fetal testosterone and violent behavior: Additional evidence using the 2D: 4D digit ratio." Personality and Individual Differences 134 (2018): 293-297.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with less close same-sex friends
" (...) male-typed (i.e., low 2D:4D) men had fewer close same-sex friends and larger numbers of general cross-sex friends than female-typed men did. Similarly, female-typed (i.e., high 2D:4D) women showed larger numbers of close same-sex friends than male-typed women did. In summary, the relations between 2D:4D and friendship ties provide further support for the claim that social behavior is affected by prenatal hormone stimulation at least to some extent."(Altmann, Tobias, and Marcus Roth. "2D: 4D digit ratio and its relations to cross-sex and same-sex friendship choices." Personality and Individual Differences 134 (2018): 278-282.)
Low circulating testosterone associated with eating disorders in males
- "Early testosterone exposure reduces eating pathology in males relative to females. (...)
- Lower circulating testosterone is associated with higher eating pathology in males."
(Culbert, Kristen M., Cheryl L. Sisk, and Kelly L. Klump. "Sex steroid hormones and differential risk for eating pathology: a review of genetic and phenotypic effects across development." Current Opinion in Behavioral Sciences 23 (2018): 124-130.)
Boosting actual testosterone levels causes men to be more interested in higher-status goods
"New findings from the largest study of its kind, led by Gideon Nave, an assistant marketing professor at the University of Pennsylvania's Wharton School, underscore a biological factor at play in the choice of products conveying status: testosterone. Giving men a single dose of testosterone increased their preference for higher-status goods.(University of Pennsylvania. "Boosting testosterone makes men prefer higher-status products." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 3 July 2018. )
The study supports previous research that connects transient increases in testosterone levels to a rise in behaviors aimed at boosting social rank."
Prenatal testosterone associated with criminality (Evolutionary neuroandrogenic (ENA) theory)
"Evolutionary neuroandrogenic (ENA) theory asserts that the main underlying forces behind human criminality is evolutionary (in ultimate terms) and neuroandrogenic (in proximate terms). Neuroandrogenic factors primarily refer to the influence of sex hormones on brain functioning, especially both prenatal and post-pubertal testosterone. We recently reported evidence that supports the theory. Using a rather crude measure of prenatal testosterone exposure (known as the 2D:4D digit ratio), our two studies indicated that even within each sex, prenatal testosterone was significantly correlated with various forms of self-reported offending as theoretically predicted. Since these two studies were published, two meta-analyses have appeared that ostensibly provide little evidence that 2D:4D is actually predictive of criminality and associated behavior. However, we believe that both of these meta-analyses have deficiencies in terms of methodology and theory interpretation that can account for why some of their conclusions are subject to question. The present commentary identifies the deficiencies and shows how the meta-analytic findings most pertinent to criminality actually support the hypothesis that prenatal testosterone is a significant contributor to variations in criminal behavior."(Ellis, Lee, and Anthony W. Hoskin. "Status of the prenatal androgen hypothesis after two meta-analyses reported little support: A commentary." Aggression and Violent Behavior (2018).)
Color preference in women associated with digit ratio
"The analysis revealed that the preferred color was shifted to more reddish color within blue-purple spectrum in females with high (female-typical) than low (male-typical) digit ratio. There was no association between salivary testosterone concentration and color preference either in females or males. This pattern of results indicates the possibility that organizational effect of androgen influences individual differences in color preference, giving support to the contention that biological predispositions underlie aesthetic tastes."(Doi, Hirokazu, and Kazuyuki Shinohara. "2nd to 4th digit ratio (2D: 4D) but not salivary testosterone concentration is associated with the overall pattern of color preference in females." Personality and Individual Differences 135 (2018): 45-50.)
Non-straight twins have lower 2D:4D digit ratio than their straight (heterosexual) co-twins
"For 18 female twin pairs, non-straight (bisexual or lesbian) twins had significantly lower, or more masculinized, 2D:4D ratios than their straight co-twins, but only in the left hand. For 14 male pairs, non-straight twins had, contrary to our prediction, more masculinized finger length ratios than straight co-twins, but this difference was not significant."(Watts, Tuesday M., Luke Holmes, Jamie Raines, Sheina Orbell, and Gerulf Rieger. "Finger Length Ratios of Identical Twins with Discordant Sexual Orientations." Archives of Sexual Behavior (2018): 1-10.)
Correlations between 2D:4D ratio and sex-different play behavior in infant girls, and prenatal testosterone levels and self-control in infant boys
"In the present studies testosterone, estradiol, and estriol were measured in amniotic fluid and 2D:4D ratios were measured for both hands at four occasions (age: five, nine, 20, and 40 months), to investigate the relationship between behavioral sex differences and prenatal sex hormones.(Körner, Lisa Martina. "Geschlechterunterschiede im Spielverhalten und der Selbstkontrolle bei 40 Monate alten Kindern und der Zusammenhang mit pränatalen Sexualhormonen.", Dissertation, Heinrich Heine Universität Dusseldorf, 2018)
In study A, sex-specific play behavior, which typically shows large sex differences, was measured at the age of 40 months for 51 girls and 42 boys. (...) The results show a large sex difference in play behavior and in 2D:4D (...). In addition, the sex difference in 2D:4D remained stable over infancy and early childhood, which supports the assumption, that 2D:4D development is mainly determined by early prenatal testosterone exposure. Most importantly, girls with a smaller 2D:4D showed more male-typical play behavior at the age of 40 months while this correlation was absent in boys. Moreover, there was neither a correlation between play behavior and sex hormone levels from the amniocentesis samples, nor between amniotic fluid testosterone levels and 2D:4D ratios.
However, boys’ and girls’ play behavior was influenced by their older siblings. In boys and girls, the number of older brothers was predictive of more male-typical play behavior, as was the number of older sisters for feminine-typical play behavior. Additionally in girls, the sex and number of the older siblings, as well as the 2D:4D were independent predictors of the sex-specific play behavior.
In study B, self-control was assessed with a delay of gratification task and the Attention Problems/Overactive scale of the Preschool and Kindergarten Behavior Scales II for 60 girls and 63 boys at the age of 40 months. (...) Study B showed that girls waited longer for a delayed reward than boys. Boys tended to show more attention problems/ overactive behavior than girls as described by their parents. This behavior was associated with a shorter waiting time for the boys in the delay of gratification task. Noteworthy, higher amniotic fluid testosterone levels were associated with shorter waiting times and more attention problems/overactive behavior in boys (for girls, prenatal testosterone levels in the amniotic fluid were too low to be measured or quantified). There were no correlations with 2D:4D ratios.
Both studies provide strong evidence that sex differences in play behavior and self-control in 40-month-old children are influenced by organizing effects of prenatal testosterone. Several sensitive prenatal periods for the organizing influences of sex hormones on developing brain structures are discussed, as an explanation for the divergent results for 2D:4D and testosterone levels from amniotic fluid in relation to different behaviors in childhood.
(...)
While the determination of the testosterone level in the amniotic fluid has the distinct advantage that it is a more direct measuring method, it has the disadvantage that it is a one-time measurement (...). This leads to the fact that intraindividual fluctuations in the testosterone level in the course of pregnancy but also in the daily schedule cannot be determined. The amniocentesis usually takes place during a period in which the greatest gender differences in testosterone levels are measurable, but it is impossible to determine the intraindividual peak of the respective fetus by multiple measurements. Thus the measured level does not necessarily reflect the value that influences the involved brain structures underlying the behavior studied."
High left 2D:4D associated with primary psychopathy in males
"(...) males with lower levels of prenatal testosterone exposure, as measured by the left hand 2D:4D, scored higher on the subscale measuring primary psychopathy. Neither the right hand 2D:4D nor the left hand 2D:4D were significant predictors of secondary psychopathy. In the female subsample, digit ratios did not correlate with either primary or secondary psychopathy."(Marchegiani, Vanessa, Fabio Zampieri, Mila Della Barbera, and Alfonso Troisi. "Gender differences in the interrelations between digit ratio, psychopathic traits and life history strategies." Personality and Individual Differences 135 (2018): 108-112.)
Low 2D:4D digit ratio associated with sensation seeking, disinhibition and drug behavior in males
"This study examined multiple 2D:4D relationships. Men who were found to have a more masculinized (ie. lower) digit ratio had significantly higher rates of overall sensation seeking, boredom susceptibility, disinhibition, experience seeking, and lifetime drug behaviors. We found no significant relationships between 2D:4D ratio and behaviors in females. Similarly, we found no relationship between digit ratio and sensation seeking, impulsive, or risky personality traits either. Digit ratio had no relationship with sexual orientation, nor on number of older brothers. Overall, our findings suggest that there is a significant relationship between a masculinized digit ratio and certain sensation seeking and risk taking behaviors in men."(Hobson, Hanna Elizabeth. "Digit Ratio as a Predictor of Risk Taking and Sensation Seeking Personality Traits and Behaviors.", Thesis, Eastern Illinois University, 2018)
Administration of testosterone impairs socio-cognitive abilities in men, only if they have low 2D:4D ratio and/or low levels of interpersonal/affective psychopathy
"Recent evidence suggests that testosterone is negatively correlated with empathic processes in both men and women. Also, administration of testosterone to young women impairs socio-cognitive performance as assessed using the “Reading the Mind in the Eyes Task”, especially among those exposed to elevated testosterone concentrations prenatally. However, the extent to which testosterone plays a similar causal role in socio-cognitive abilities in men is currently unknown. Here, using a crossover, double-blind, placebo-controlled, within-subject design, we investigated the extent to which a single administration of testosterone to healthy young men (N = 30) would impair socio-cognitive abilities assessed using the “Reading the Mind in the Eyes Task” (RMET). Also, we investigated whether individual differences in 2D:4D ratio and psychopathic traits would moderate the effect of testosterone on task performance. Results indicated that testosterone administration on its own did not impair RMET performance. However, variability in both 2D:4D ratio and psychopathic traits moderated the effect of testosterone on task performance. Specifically, testosterone impaired RMET performance among individuals with relatively low (i.e., masculinized) 2D:4D ratio and among individuals scoring relatively low on the interpersonal/affective facet (i.e., Factor 1) of psychopathy."(Carré, Justin M., Triana L. Ortiz, Brandy Labine, Benjamin JP Moreau, Essi Viding, Craig S. Neumann, and Bernard Goldfarb. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and psychopathic traits moderate the effect of exogenous testosterone on socio-cognitive processes in men." Psychoneuroendocrinology 62 (2015): 319-326.)
2D:4D ratio does not correlate with risk-taking and economic behavior in a sample of low-income African-Americans
"Several studies present evidence of correlations between prenatal testosterone exposure measured with the 2D:4D ratio and behaviors such as pro-social behavior, risk and patient attitudes, and self-employment. Individuals exposed prenatally to higher levels of testosterone have lower levels of risk aversion, higher levels of patience and invest more in others, and in themselves, therefore have higher individual financial wellbeing. We test these hypotheses with a sample of 115 African-Americans who live in a low-income urban area in the U.S. The 2D:4D ratio in our sample of males and females does not have a consistent and robust correlation with risk, patient attitudes, pro-social behavior and self-employment in contrast to previous studies."(Candelo, Natalia, and Catherine Eckel. "The 2D: 4D Ratio Does Not Always Correlate with Economic Behavior: A Field Experiment with African-Americans." Economics & Human Biology (2018).)
Low 2D:4D ratio and high impulsivity associated with heroin abuse
"In this study, we found that patients with heroin use disorder had lower 2D:4D ratios on the right hand than those of non-drug abusing controls. This finding lends support to previous studies, which indicate that alcohol misuse may be related to more masculinized (lower) 2D:4D ratios (...). (...) We have contributed to the existing literature by showing that a diagnosis of heroin use disorder was associated with lower 2D:4D ratios (i.e., elevated in utero testosterone levels). (...)(HARCP, Vol. 20 • No. N3 • June 2018, "The Second to Fourth Digit (2d:4d) Ratios in Patients with Heroin Use Disorder", Canan F., Sogucak S., Karaca S., Tegin C., Gecici O., and Kuloglu M.)
However, our logistic regression analysis suggested that 2D:4D ratios did not predict heroin use disorder in males, whereas attentional and non-planning impulsiveness were, indeed, found to be significant predictors. This authorizes us to put forward the hypothesis that the association between low 2D:4D ratios and heroin use disorder is not independent when impulsivity is taken into consideration. (...)
Our study is consistent with the notion that fetal testosterone exposure, as assessed indirectly by 2D:4D ratios, is associated with substance use disorder among males."
Women with PCOS (associated with elevated prenatal testosterone) and their children at higher risk for autism
"Elevated levels of prenatal testosterone may increase the risk for autism spectrum conditions (autism). Given that polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) is also associated with elevated prenatal testosterone and its precursor sex steroids, a hypothesis from the prenatal sex steroid theory is that women with PCOS should have elevated autistic traits and a higher rate of autism among their children. (...) [W]e found increased prevalence of PCOS in women with autism (...) and elevated rates of autism in women with PCOS (...). [W]e found the odds of having a child with autism were significantly increased, even after adjustment for maternal psychiatric diagnoses, obstetric complications, and maternal metabolic conditions (...). These studies provide further evidence that women with PCOS and their children have a greater risk of autism."(Cherskov, Adriana, Alexa Pohl, Carrie Allison, Heping Zhang, Rupert A. Payne, and Simon Baron-Cohen. "Polycystic ovary syndrome and autism: A test of the prenatal sex steroid theory." Translational Psychiatry 8, no. 1 (2018): 136.)
Testosterone administration may make men a tiny bit more honest (but effect is inignificant)
"We find evidence for self-serving lying in both treatment and control groups and a statistically insignificant negative effect (...) indicating more honest behavior (i.e., lower reports) following testosterone administration. Although insignificant, the direction was the same as in the Wibral et al. study, and the meta-analytic effect of the two studies demonstrates lower reporting (i.e., more honesty) following testosterone (vs. placebo) administration (...)"(Henderson, Austin, Garrett Thoelen, Amos Nadler, Jorge Barraza, and Gideon Nave. "Testing the influence of testosterone administration on men’s honesty in a large laboratory experiment." Scientific Reports 8, no. 1 (2018): 11556.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with less risk-averse behavior
"The results of the experiment (...) corroborate the hypothesis that, for volunteers with lower 2D:4D ratios, they bet more after a gain and also after a loss. This result is in agreement with the suggestion of the literature of (HME) and the biological marker, that is, volunteers with greater exposure to the hormone testosterone invest more, considering that they are less risk-averse. Regarding the robustness analysis the results indicated that the 2D: 4D biological marker was a significant predictor for the difference in behavior between men and women."(Teixeira, Anderson M., Benjamin M. Tabak, and Daniel O. Cajueiro. "THE HOUSE-MONEY EFFECT, ESCALATION OF COMMITMENT AND TESTOSTERONE (2D: 4D RATIO): AN EXPERIMENTAL APPROACH.")
Increased prenatal testosterone associated with reduced social brain functioning in males (but not females)
"we find that increasing prenatal testosterone in humans is associated with later reduction of functional connectivity between social brain default mode (DMN) subsystems in adolescent males, but has no effect in females. (...) Androgens have male-specific prenatal influence over social brain circuitry in humans (...)."(Lombardo, Michael V., Bonnie Auyeung, Tiziano Pramparo, Angélique Quartier, Jérémie Courraud, Rosemary J. Holt, Jack Waldman et al. "Sex-specific impact of prenatal androgens on social brain default mode subsystems." Molecular Psychiatry (2018): 1.)
Lower 2D:4D digit ratio (and higher facial symmetry) associated with higher levels of narcissism in males and females
"A group of 119 healthy college students ([48 males and] 71 females) answered the short dark triad questionnaire. Photographs were used to determine their degree of facial fluctuating asymmetry (FA) and the digit ratios (2D:4D) on both hands were directly measured. The data revealed that narcissism was predicted by lower left-hand 2D:4D and lower facial fluctuating asymmetry (FA).(Borráz-León, Javier I., Markus J. Rantala, and Ana Lilia Cerda-Molina. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and facial fluctuating asymmetry as predictors of the dark triad of personality." Personality and Individual Differences 137 (2019): 50-55.)
(...) We found that Machiavellianism and psychopathy were not related to facial FA or 2D:4D. (...)"
Higher levels of prenatal androgens associated with more masculine play behavior in preschool children
"These findings support the role of androgens in the development of sex-typical childhood play behavior, with those being exposed to higher levels of fetal functional androgens expressing more masculine behavior at preschool ages."(Khorashad, Behzad S., Ghasem M. Roshan, Alistair G. Reid, Zahra Aghili, Maliheh Dadgar Moghadam, Behnaz Khazai, Mehran Hiradfar et al. "Childhood Sex-Typed Behavior and Gender Change in Individuals with 46, XY and 46, XX Disorders of Sex Development: An Iranian Multicenter Study." Archives of Sexual Behavior (2018): 1-12.)
Feminist activist sample has more masculinized 2D:4D digit ratio and are more dominant than males of the same country
"We measured the 2D:4D digit ratios (collected from both hands) and a personality trait known as dominance (measured with the Directiveness scale) in a sample of women attending a feminist conference. The sample exhibited significantly more masculine 2D:4D and higher dominance ratings than comparison samples representative of women in general, and these variables were furthermore positively correlated for both hands. (...)(Madison, Guy, Ulrika Aasa, John Wallert, and Michael A. Woodley. "Feminist activist women are masculinized in terms of digit-ratio and social dominance: a possible explanation for the feminist paradox." Frontiers in psychology 5 (2014): 1011.)
Comparisons between the study sample and the male comparison samples showed that the feminist activists have a more masculinized 2D:4D ratio than males from the same country."
Low 2D:4D associated with autism in Saudi boys
"This case–control study was conducted with 60 male children with 31 individuals having classic-onset autism and 29 individuals serving as age-matched, healthy controls. (...) The results showed that the 2D:4D was significantly lower in boys with autism compared to the controls."(Al-Zaid, Felwah S., AbdelFattah A. Alhader, and Laila Y. Al-Ayadhi. "The second to fourth digit ratio (2D: 4D) in Saudi boys with autism: A potential screening tool." Early human development 91, no. 7 (2015): 413-415.)
Low 2D:4D in Guatemalan women associated with more patience in financial choices
"Inter-temporal trade-offs are ubiquitous in human decision making. We study the relationship between preferences over such trade-offs and the ratio of the second digit to that of the forth (2D:4D), a marker for pre-natal exposure to sex hormones. Specifically, we study whether 2D:4D affects discounting. Our sample consists of 419 female participants of a Guatemalan conditional cash transfer program who take part in an experiment. Their choices in the convex time budget (CTB) experimental task allow us to make inferences regarding their patience (discounting), while controlling for present-biasedness and preference for smoothing consumption (utility curvature). We find that women with lower digit ratios tend to be more patient."To be noted, the mean 2D:4D ratios were extremely low: these Guatemalan women had significantly more masculinized digit ratios than the general male populations in eg. Europe, India and USA.
"The digit ratios for our sample are lower than those typically found in the literature. For the right hand, mean 2D:4D is 0.9322 (with a standard deviation of 0.0315); for the left hand the mean is 0.9337 (with a standard deviation of 0.0321)".(Aycinena, Diego, and Lucas Rentschler. "Discounting and digit ratio: Low 2D: 4D predicts patience for a sample of females." Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience 11 (2018): 257.)
Association between some autistic traits and low 2D:4D ratio in males, but only in the lowest 10% of 2D:4D ratios
"In other words, there was no association between 2D:4D ratios and autistic traits [when taking the whole sample in consideration]. (...) Individuals who had the lowest 10 % of right 2D:4D ratios (i.e., the most male-biased ratio) were significantly more likely to have SCDC [Social Communication Disorders Checklist] scores over the “probably autistic” threshold (higher than cut-off) (...). Those in the lowest 10 % of right 2D:4D ratios were significantly more likely to make more mistakes in recognizing emotions for sad facial expressions on the DANVA [Diagnostic Analysis of Nonverbal Accuracy] (...) and facial expressions of low intensity (all expressions) (...). Individuals with the lowest 10 % of right 2D:4D ratios were also more likely to misattribute facial expressions (of whatever type) as angry (...). These odds ratios held only for males after stratifying by gender."
(Barona, Manuela, Radha Kothari, David Skuse, and Nadia Micali. "Social communication and emotion difficulties and second to fourth digit ratio in a large community-based sample." Molecular autism 6, no. 1 (2015): 68.)
Low 2D:4D ratio in women associated with more masculine handwriting style
"women’s right hand digit ratio correlated with relative sexuality of handwriting, but there was no corresponding relationship for the males. These findings suggest that prenatal hormonal influences can affect later female handwriting performance and might even affect developmental inter-hemispheric differences, but do not appear to impact on males."
(Beech, John R., and Isla C. Mackintosh. "Do differences in sex hormones affect handwriting style? Evidence from digit ratio and sex role identity as determinants of the sex of handwriting." Personality and individual differences 39, no. 2 (2005): 459-468.)
No association between 2D:4D digit ratio and dyslexia
"This study examined 2D : 4D digit ratio (a marker of fetal testosterone exposure) in dyslexic and normal reading children. No group differences in 2D : 4D were observed. Digit ratio did not show the postulated relation with reading, spelling, phonological ability, speech perception, auditory processing and visual processing. These findings challenge the validity of theories that allocate a prominent role to fetal testosterone exposure in the aetiology of dyslexia and its sensory impairments."(Boets, Bart, Bert De Smedt, Jan Wouters, Katrien Lemay, and Pol Ghesquière. "No relation between 2D: 4D fetal testosterone marker and dyslexia." Neuroreport 18, no. 14 (2007): 1487-1491.)
Low 2D:4D ratio in men makes them more attractive to women (but only as short-term mates, and especially to masculinized women)
"Results also indicated that a low (more masculine) 2D:4D ratio in the right hand was related to men’s attractiveness. This relationship occurred controlling for body size and personality/sex roles, along with relevant demographics. The findings suggest that women may be partially attracted to men because of their relative level of prenatal androgen exposure; and that features of physical attractiveness in men are, at least partly, androgen-based markers of fitness detectable by women."(Bogaert, Anthony F., Catherine C. Fawcett, and Luanne K. Jamieson. "Attractiveness, body size, masculine sex roles and 2D: 4D ratios in men." Personality and Individual Differences 47, no. 4 (2009): 273-278.)
To be noted in another study:
"Although all women had a preference for a masculinized STM (short-term mate) who was not significantly different from their attractive male choice, only low 2D:4D women desired similar masculine attributes in their LTMs (long-term mate).
(...) Low 2D:4D women are more attracted to a male's secondary sexual characteristics (facial androgen markers and male pheromones), prefer such ‘good genes’ males as mates (STM, LTM, and at ovulation), but don't bond well (low paternal bonding, short relationships, and promiscuity), perhaps as a consequence of their emotional structure (de-feminized). By contrast, high 2D:4D females are stereotypically female, bond well to males, are sexually reserved, and seek less masculinized males for LTMs, or when there is a high probability of conception."(Johnston, Victor S. "Mate choice decisions: the role of facial beauty." Trends in cognitive sciences 10.1 (2006): 9-13., Part 1, Part 2)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with lifelong premature ejaculation
"Totally 65 patients with lifelong premature ejaculation and 65 control cases without any ejaculatory complaints were enrolled in the study. (...) Individuals with lower digit ratios have higher risks of shorter intravaginal ejaculatory latency times. These results suggest that increased fetal androgen exposure may be a new risk factor for the development of lifelong premature ejaculation."
(Bolat, D., G. U. Kocabas, T. Kose, T. Degirmenci, M. E. Aydin, and C. Dincel. "The relationship between the second‐to‐fourth digit ratios and lifelong premature ejaculation: a prospective, comparative study." Andrology 5, no. 3 (2017): 535-540.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with higher enjoyment of competition, but not with more competitive behavior in itself
"[T]he associations between behavioral measures of competitiveness and digit ratios are not statistically significant. (...) In contrast to our results regarding the behavioral measure, we find a negative and statistically significant relationship between psychometric [self-reported] measures and 2D:4D in both studies. Our specific findings suggest that psychometric scales reflecting enjoyment of competition are significantly related to the right-hand digit ratio (R2D:4D). (...) Hence, our results imply that the digit ratio is, first and foremost, related to enjoyment of competition, suggesting that individuals with low (more masculine) digit ratios tend to select into competition not primarily for winning a competition but for the sake of competition itself."
(Bönte, Werner, Vivien D. Procher, Diemo Urbig, and Martin Voracek. "Digit Ratio (2D: 4D) Predicts Self-Reported Measures of General Competitiveness, but Not Behavior in Economic Experiments." Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience 11 (2017): 238.)
(Noser, Emilou, Jessica Schoch, and Ulrike Ehlert. "The influence of income and testosterone on the validity of facial width-to-height ratio as a biomarker for dominance." PLOS ONE 13, no. 11 (2018): e0207333.)
(Fisher, Helen E., Jonathan Rich, Heide D. Island, and Daniel Marchalik. "The second to fourth digit ratio: A measure of two hormonally-based temperament dimensions." Personality and Individual Differences 49, no. 7 (2010): 773-777. - full article)
(Isman, Cagla A., and Nimet U. Gundogan. "The influence of digit ratio on the gender difference in learning style preferences." Personality and Individual Differences 46, no. 4 (2009): 424-427.)
(Nadler, Amos, David Zava, Triana Ortiz, Neil Watson, Justin Carre, Colin Camerer, and Gideon Nave. "Does testosterone impair mens' cognitive empathy? Evidence from two large-scale randomized controlled trials." bioRxiv (2019): 516344.)
An "asset bubble " is when the price of an asset, such as housing, stocks or gold, become over-inflated. Prices rise quickly over a short period. They are not supported by an underlying demand for the product itself. It's a bubble when investors bid up the price beyond any real sustainable value.
(https://www.thebalance.com/asset-bubble-causes-examples-and-how-to-protect-yourself-3305908)
(Nadler, Amos, Peiran Jiao, Cameron J. Johnson, Veronika Alexander, and Paul J. Zak. "The bull of wall street: experimental analysis of testosterone and asset trading." Management Science (2017).)
(Togo, Shunta, Takashi Itahashi, Ryuichiro Hashimoto, Chang Cai, Chieko Kanai, Nobumasa Kato, and Hiroshi Imamizu. "Fourth finger dependence of high-functioning autism spectrum disorder in multi-digit force coordination." Scientific Reports 9, no. 1 (2019): 1737.)
704 subjects (478 females)
(Pablo, Brañas-Garza, Subhasish Chowdhury, Antonio M. Espín, and Jeroen Nieboer. ‘Born this Way’? Prenatal Exposure to Testosterone May Determine Behavior in Competition and Conflict. University Library of Munich, Germany, 2019.)
Stuttering associated with lower 2D:4D
No association between sex hormone levels at birth or 2D:4D, and economic preferences later in life (n=533)
No difference in 2D:4D ratio between students who regularily drink and those who don't drink at all. Positive correlation between left-hand 2D:4D ratio and smoking in women
"Purpose was to test the relationships between nicotine and alcohol intake and 2D:4D. (...)
2D:4D was positively related to smoking only in women.
We found no relationship between 2D:4D and alcohol drinking.
(...)
There was no significant difference in digit ratios between subjects regularly using both nicotine and alcohol and those who took none of them. When analyzing the two substances separately, there was no relationship between 2D:4D and alcohol drinking, whereas left hand 2D:4D was positively related to smoking only for women (nonsignificant trend was observed for right hand). Contrary to the previous study, our results indicate that there is no relationship between 2D:4D and alcohol drinking. There is, however, a subtle influence of prenatal testosterone levels for cigarette smoking habits in the case of women."
(Borkowska, Barbara, and Boguslaw Pawlowski. "Alcohol and nicotine intake and prenatal level of androgens measured by digit ratio." Personality and Individual Differences 55, no. 6 (2013): 685-687.)
Low 2D:4D associated with better results on Cognitive Reflection Test (mathematical questions)
The Cognitive Reflection Test consists of three mathematical questions for which the intuitive answer is false.
"The Cognitive Reflection Test (CRT) is a test introduced by S. Frederick (2005) Cognitive reflection and decision making, J Econ Perspect 19(4): 25-42. The task is designed to measure the tendency to override an intuitive response that is incorrect and to engage in further reflection that leads to the correct response. (...) This paper tests to what extent 2D:4D, as a proxy for prenatal exposure to testosterone, can predict CRT scores in a sample of 623 students. After controlling for sex, we observe that a lower 2D:4D (reflecting a higher exposure to testosterone) is significantly associated with a higher number of correct answers. The result holds for both hands’ 2D:4Ds. In addition, the effect appears to be sharper for females than for males."
(Bosch-Domènech, Antoni, Pablo Brañas-Garza, and Antonio M. Espín. "Fetal testosterone (2D: 4D) as predictor of cognitive reflection." (2013).)
More brain lateralisation in people with lower left-hand 2D:4D ratios, independent of sex
"In this study the relationship between 2D:4D ratio and strength of lateralisation to the right hemisphere for processing facial emotion is examined in a large sample (N = 475) of males and females. Left hand 2D:4D ratio was a significant predictor of strength of right hemisphere lateralisation for processing facial emotion, but particularly for the processing of facial expressions of disgust, happiness, sadness and surprise. Individuals with lower 2D:4D ratios, indicating higher levels of prenatal testosterone exposure, tended to be more strongly lateralised to the right hemisphere for the processing of both positive and negative facial emotion. However, there was no sex difference in this relationship, suggesting that the influence of prenatal testosterone is the same for males and females."
(Bourne, Victoria J. "Prenatal hormonal exposure (2D: 4D ratio) and strength of lateralisation for processing facial emotion." Personality and Individual Differences 58 (2014): 43-47.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with stronger right hemisphere dominance in various functions
"Lower 2D:4D ratios, which indicate high levels of prenatal testosterone exposure, were associated with stronger right hemisphere dominance. Later life hormonal exposure was not found to be associated with any of the lateralisation measures. This finding suggests a relationship between prenatal hormonal exposure and brain organisation."(Bourne, Victoria J., and Dawn L. Gray. "Hormone exposure and functional lateralisation: Examining the contributions of prenatal and later life hormonal exposure." Psychoneuroendocrinology 34, no. 8 (2009): 1214-1221.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with better results in Java programming, and less computer-related anxiety
"This study examined whether an index of prenatal exposure to testosterone, digit ratio (2D:4D), is related to successful involvement within a computer-technology context – performance in a Java programming course. Three studies (N = 73,75,65) identified a consistent negative correlation between 2D:4D digit ratio and attainment (r ≈ −0.2). A fourth study (N = 119) found that 2D:4D digit ratio positively correlated with two indices of computer-related anxieties, as well as anxiety sensitivity (r = 0.32/0.51). These results suggest that males and females who have been exposed to higher levels of testosterone within the womb perform better upon academic assessments of Java-related programming ability within computer science education, and have lower levels of computer-related anxieties outside computer science education."(Brosnan, Mark, Victoria Gallop, Nida Iftikhar, and Edmund Keogh. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D), academic performance in computer science and computer-related anxiety." Personality and Individual Differences 51, no. 4 (2011): 371-375.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with more mental visual representation of numbers
"This study examined a phenomenon known as the SNARC effect (Spatial Numerical Association of Response Codes), which is taken as evidence of a mental representation of magnitude along a left–right-oriented number line, with low magnitudes associated with the left side of space, and high numbers with the right side of space. (...)(Bull, Rebecca, and Philip J. Benson. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and the spatial representation of magnitude." Hormones and Behavior 50, no. 2 (2006): 194-199.)
Participants with lower (more masculine) digit ratios on the right hand showed a stronger SNARC effect compared to participants with high digit ratios. This pattern of results was also found when the analyses were conducted separately for men and women. Results from left hand digit ratios indicated that only low digit ratio females showed a significant SNARC effect."
Low 2D:4D associated with better number sense and visual-spatial skills in girls, and better arithmetic skills in boys
"This study investigated sex and individual differences and relationships between 2D:4D (...), visual-spatial memory, and numerical skills in 5-year-old children. No sex differences were found in any of the numerical or visual-spatial tasks. Visual-spatial memory was positively correlated with arithmetic score. Girls with a lower (more masculinised) 2D:4D had better number sense and visual-spatial skills, whilst boys with lower 2D:4D had better arithmetic skills. This suggests that prenatal testosterone exposure may have differential effects on the visual-spatial and numerical skills of girls and boys."(Bull, Rebecca, Wendy Anne Davidson, and Emily Nordmann. "Prenatal testosterone, visual-spatial memory, and numerical skills in young children." Learning and Individual Differences 20, no. 3 (2010): 246-250.)
Possible curvilinear relation between prenatal sex hormones and cognition in normal populations
"For the men, better performance on the measures, including mental rotation, verbal fluency, and verbal Scholastic Achievement Test score was associated with less of a male-typical finger-length ratio pattern, or higher ratios. For the women, better performance for mental rotation and verbal fluency was associated with less of a female-typical finger-length ratio pattern, or lower ratios. Thus, in this group of college students, better cognitive performance was associated with a less gender-typical finger-length ratio, for both men and women. These findings are discussed in the context of other similar reports and a possible curvilinear relation between hormones and cognition in normal populations."(Burton, Leslie A., Debra Henninger, and Jessica Hafetz. "Gender differences in relations of mental rotation, verbal fluency, and SAT scores to finger length ratios as hormonal indexes." Developmental neuropsychology 28, no. 1 (2005): 493-505.)
People with lower 2D:4D ratios use smiling and flirtation as mild forms of agression
"For 91 participants (55 female, 36 male), use of smiling and flirtation to make others receptive to one's ideas were associated with relational aggression and a more male-typical (smaller) right 2D:4D finger length ratio. The only significant relationship in the male sample alone was the relationship between smiling and relational aggression. In the female sample alone, use of smiling and flirtation to "make people receptive to my ideas" was associated with a more male-typical 2D:4D finger length ratio pattern, and there was a trend for flirtation to be associated with greater physical aggression. Both 2D:4D and physical aggression have been associated with higher prenatal androgen level. It is concluded that deliberate smiling and flirtation are mild forms of relational aggression, and are related to prenatal androgenic activity in a manner similar to physical aggression."(Burton, Leslie, Nicholas Bolt, Despina Hadjikyriacou, Nava Silton, Christine Kilgallen, and Janaina Allimant. "Relationships of smiling and flirtation to aggression and 2D: 4D, a prenatal androgen index." Evolutionary Psychology 9, no. 1 (2011): 147470491100900104.)
Testosterone administration disables trust in low 2D:4D women
"We use the economic trust game and compare one-shot games modelling trust problems in relations between strangers with repeated games modelling trust problems in ongoing relations between partners. As expected, subjects are more trustful in repeated than in one-shot games. In subjects prenatally relatively highly primed by testosterone, however, this effect disappears after testosterone administration. We argue that impairments in cognitive empathy may reduce the repeated game effect on trust after testosterone administration in subjects with relatively high prenatal testosterone exposure and propose a neurobiological explanation for this effect."(Buskens, Vincent, Werner Raub, Nynke Van Miltenburg, Estrella R. Montoya, and Jack Van Honk. "Testosterone administration moderates effect of social environment on trust in women depending on second-to-fourth digit ratio." Scientific reports 6 (2016): 27655.)
Women with a more masculine (lower) 2D:4D ratio use a more masculine-typical way of orientation
"Previous work suggests that males are better in the use of directional cues than females. In the present study, participants learned a target location in a virtual landscape environment, in conditions that contained either all directional (i.e., distant or compass bearing) cues, or all positional (i.e., local, small objects) cues. After a short delay, participants navigated back to the target location from a novel starting location. Males had higher accuracy in initial search direction than females in environments with all directional cues. Lower digit ratio was correlated with higher accuracy of initial search direction in females in environments with all directional cues. Mental rotation scores did not correlate with digit ratio in either males or females. These results demonstrate for the first time that a sex difference in the use of directional cues, i.e., the sense of direction, is associated with more male-like digit ratio."(Chai, Xiaoqian J., and Lucia F. Jacobs. "Digit ratio predicts sense of direction in women." PloS one 7, no. 2 (2012): e32816.)
Testosterone promotes behaviors intended to maintain and seek social status
"Recent research suggests that testosterone promotes behaviors intended to maintain and seek social status rather than simply inducing aggressive behavior (...). For example, testosterone potentiates aggressive responses to provocation, while it increases generosity in the absence of provocation in a modified Ultimatum Game (...)."(Front Neurosci. 2017; 11: 417, "Commentary: Winning a competition predicts dishonest behavior", Yin Wu, Philip R. Blue, and Luke Clark)
[Article]: the people most likely to cheat are those who are both aggressive (high testosterone) and stressed (high cortisol).
"Based on the researchers' findings, the people most likely to cheat are those who are both aggressive (high testosterone) and stressed (high cortisol)."(Forbes.com, Aug 5, 2015, "How Hormones Foretell Whether People Will Cheat", by Carmen Nobel)
Study finds no evidence for masculinization of limbic circuits in high fetal testosterone women
"we find no evidence for masculinization of the limbic circuits in women with high fetal testosterone."(Ciumas, C., A. Lindén Hirschberg, and I. Savic. "High fetal testosterone and sexually dimorphic cerebral networks in females." Cerebral Cortex 19, no. 5 (2008): 1167-1174.)
2D:4D ratio predicts monogamous/polyandrous inclinations in women
"Women vary with respect to monogamous/polyandrous inclinations, as indexed by the Sociosexual Orientation Inventory (SOI). Possible sources of SOI variation include variation in perceptions relating to the utility of different mating tactics and variation in one's degree of masculinity/femininity, among other things. In three studies with undergraduate participants SOI, an index of self-perceived attractiveness and two measures of masculinization, namely scores on the Vandenberg Mental Rotation test (V-MRT) and 2D:4D digit ratios, were measured. Self-perceived attractiveness predicted SOI in the first study, but not in the second study. Right 2D:4D did predict SOI in the second study. In the third study, both self-perceived attractiveness and right 2D:4D predicted SOI, and so did V-MRT scores."(Clark, Andrew P. "Self-perceived attractiveness and masculinization predict women's sociosexuality." Evolution and Human Behavior 25, no. 2 (2004): 113-124.)
Low 2D:4D ratio (in combination with emotional intelligence and parenting style of their parents) associated with agression in females
"The contributions of digit ratio (2D:4D), emotional intelligence (EI) and parenting styles to social aggression were examined. Females (n = 215 emerging adults) completed 5 aggression measures, an EI measure, 2 parenting measures, and had their hands measured. Aggression correlated with each of the predictors. Left hand 2D:4D, EI, and parental authoritarianism resulted in the most robust model for predicting aggression."(Cleveland, Emily Sutcliffe. "Digit ratio, emotional intelligence and parenting styles predict female aggression." Personality and individual differences 58 (2014): 9-14.)
Prenatal androgen exposure influences neural circuitry underlying visual spatial ability in men and women
"In agreement with a prenatal sex hormone hypothesis, line judgment accuracy in adults related to 2D:4D and sexual orientation, both of which are postulated to be influenced by early steroids. In both sexes, better visuospatial performance was associated with lower (more male-typical) digit ratios. For men, heterosexual participants outperformed homosexual/bisexual participants on the JLAP-15 and, for women, homosexual/bisexual participants outperformed heterosexual participants. In children aged 8–10 years, presumed to be a largely prepubertal group, boys also outperformed girls. These findings are consistent with the hypothesis that visuospatial ability is influenced by early sex steroids, although they do not rule out alternative explanations or additional influences. More broadly, such results support a prenatal sex hormone hypothesis that degree of androgen exposure may influence the neural circuitry underlying cognition (visuospatial ability) and sexual orientation as well as aspects of somatic (digit ratio) development."(Collaer, Marcia L., Stian Reimers, and John T. Manning. "Visuospatial performance on an internet line judgment task and potential hormonal markers: sex, sexual orientation, and 2D: 4D." Archives of sexual behavior 36, no. 2 (2007): 177-192.)
Low 2D:4D men more aggressive toward other men and their own partners; low 2D:4D women less possessive
"Low 2D:4D men (indicating higher prenatal testosterone exposure) were more likely to state that they threatened male competitors and used more threats and physical aggression toward their female partners. Men were particularly likely to use threats and physical aggression toward partners who cheated in the current relationship. In addition, women resisted mate guarding by men with high 2D:4D, particularly when women cheated on their partner. High 2D:4D women were more possessive toward their partner."(Cousins, Alita J., Madeleine A. Fugère, and Melissa Franklin. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D), mate guarding, and physical aggression in dating couples." Personality and Individual Differences 46, no. 7 (2009): 709-713.)
High 2D:4D ratio associated with higher volumes of total cerebral cortex and total cerebellar white matter in males
"Here we investigated the association between the 2D:4D ratio and several brain subvolumes. Seventy-five subjects between the ages of 18 and 30 were included in the study. (...) Finger ratio significantly positively correlated with total cerebral cortex, total cerebellar white matter and total cerebellar cortex in males but not in females. Our results indicate that prenatal testosterone, as estimated by the 2D:4D ratio has an effect on adult brain morphology in males."(Darnai, Gergely, Enikő Plózer, Gábor Perlaki, Gergely Orsi, Szilvia Anett Nagy, Réka Horváth, Attila Schwarcz et al. "2D: 4D finger ratio positively correlates with total cerebral cortex in males." Neuroscience letters 615 (2016): 33-36.)
Low left-hand 2D:4D ratio strongly associated with autistic features in girls
"This study assessed this association in a large sample of children with a variety of psychiatric disorders (n = 35 girls and n = 147 boys). Autistic features were assessed with a highly valid and reliable measure (Autism Diagnostic Observation Schedule—Generic). Correlations between the 2D:4D ratio and autistic features were computed separately for boys and girls. Some small negative correlations (r = —0.17 and r = —0.19) were found in the right hand for boys; however, particularly in girls, large negative correlations (r = —0.51 to r = —0.64) were found in the left hand. A low 2D:4D ratio in girls was highly predictive of the presence of autistic features."(De Bruin, Esther I., Pieter FA De Nijs, Fop Verheij, Debora H. Verhagen, and Robert F. Ferdinand. "Autistic features in girls from a psychiatric sample are strongly associated with a low 2D: 4D ratio." Autism 13, no. 5 (2009): 511-521.)
Higher prenatal and current testosterone in children with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD)
"Study on 2D:4D revealed lower 2D:4D ratio in children with ASD. Higher testosterone in prepubertal children with autism were found."(Ostatnikova, Daniela, Martin Hill, Katarina Šebeková, Hana Celušáková, Anna Pivovarčiová, Jaroslava Babková, and Peter Celec. "THE ROLE OF STEROIDS IN AUTISM PATHOGENESIS." Pathophysiology 25, no. 3 (2018): 192-193.)
Autism related to low levels of salivary oxytocin, oppositional defiant disorder and conduct disorder related to low levels of salivary oxytocin and high levels of salivary testosterone
"Across groups, higher levels of callous-unemotional (CU) traits were related to higher levels of cortisol and testosterone, however, proactive and reactive aggression were unrelated to all three hormonal levels. The current findings show that, regardless of cognitive ability or comorbid disorders, the diagnostic groups (autism spectrum disorder (ASD), oppositional defiant disorder (ODD)/conduct disorder (CD)) differ from each other by their hormonal levels, with the ASD group characterized by relative low level of oxytocin, and the ODD/CD group by a relative low level of oxytocin and high level of testosterone. These group effects were partly driven by differences in callous-unemotional (CU) traits between the groups."(Bakker-Huvenaars, M. J., C. U. Greven, P. Herpers, E. Wiegers, A. Jansen, R. van der Steen, A. E. van Herwaarden et al. "Saliva oxytocin, cortisol, and testosterone levels in adolescent boys with autism spectrum disorder, oppositional defiant disorder/conduct disorder and typically developing individuals." European Neuropsychopharmacology (2018).)
Correlation between higher meat consumption and lower 2D:4D ratio
"Based on the profiles of 29 countries, we managed to identify three groups of countries that differ in the consumption of key food products, i.e., meat, wheat, etc.. Cluster 1, which includes countries located in the Mediterranean and Black Sea region, is characterized by a plant-based diet (wheat and vegetables) and low consumption of animal source foods (all types of meat plus eggs). Cluster 3 includes mainly Scandinavian, Northern European and large non-European countries (such as Canada, Australia, and USA). The diet in these countries is based on meat (mainly beef, poultry, and fish), while the consumption of plant products (wheat and vegetables) and eggs is relatively low. Cluster 2 includes countries of Central and Western Europe. In these countries, the consumption of pork and eggs is high, and these products constitute the main components of the diet. However, overall meat consumption is significantly lower than in Cluster 3. These clusters have been examined with respect to correlation with the prevalent indicators of sex steroids levels, which influence prenatal development.
(...)
Our cluster analysis showed that countries with predominantly plant-based diets have high digit ratio values both in males and females, i.e., a low level of prenatal testosterone and/or a high level of prenatal oestrogen. By contrast, in countries with predominantly meat-based diets, the male pattern of the digit ratio is dominant in both sexes, suggesting high prenatal testosterone and/or low prenatal oestrogen exposure in utero. The remaining countries have average parameters for the clusters in question, with sex-typical digit ratios. These findings suggest a correlation between the type of diet and digit ratio distribution in a given population. A protein-rich, meat-based diet seems to be associated with the masculine 2D:4D, while a plant-based diet seems to be associated with the feminine 2D:4D. Since the digit ratio is believed to be determined in utero through the effects of prenatal sex steroids, we hypothesized that diet and the respective levels of these hormones may indeed be related. This study suggests that the diets involving a high or low intake of meat, in an indirect way, may shape the socio-economic profile of some populations."
(Modlinska, Klaudia, and Wojciech Pisula. "Selected Psychological Aspects of Meat Consumption—A Short Review." Nutrients 10, no. 9 (2018): 1301.)
Higher levels of testosterone increase effect of parental rejection on antisocial behavior
"Results (...) revealed that parental rejection and testosterone were independently associated with antisocial behavior and that the effect of parental rejection on antisocial behavior was stronger at higher levels of testosterone."(Woeckener, Matthias, Danielle L. Boisvert, Eric M. Cooke, Nicholas Kavish, Richard H. Lewis, Jessica Wells, Todd A. Armstrong, Eric J. Connolly, and James M. Harper. "Parental rejection and antisocial behavior: the moderating role of testosterone." Journal of Criminal Psychology (2018).)
Low 2D:4D associated with high social phobia
"There is a greater likelihood of developing social phobia in people with high exposure to fetal testosterone compared to people with low exposure."
(Celis, Elkin Rodrigo Lozada, Nidia Paez, Fred Gustavo Manrique-Abril, Mario Andres Valderrama, and Juan Manuel Ospina-diaz. "ASOCIACIÓN ENTRE EL ÍNDICE D2: D4 Y FOBIA SOCIAL EN HOMBRES. UN ESTUDIO DE CASOS Y CONTROLES." SALUD, HISTORIA Y SANIDAD ON-LINE 12, no. 2 (2017): 87-98.)
More years of training, not 2D:4D ratio, correlates with success in Olympic wrestling
"There were no differences between successful and non-successful wrestlers in 2D:4D (p=0.87 for right hand, and p=0.46 for left hand), whereas having high training experience supposed an increase up to 4.38,(1.70-11.01) times more likely to be successful. Our results suggest that 2D:4D fails in predicting wrestling success, whereas training background is a good predictor of competition prowess in highly trained wrestlers."(la Cruz-Sánchez, De, Jesús García-Pallarés, María Dolores Torres-Bonete, and José María López-Gullón. "Can our fingers alone raise us up to the sky? Analysis of the Digit Ratio Association with success in olympic wrestling." Collegium antropologicum 39, no. 3 (2015): 515-519.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with being more suspicious of others
"Trust game players (n = 144) trusted less when they had lower 2D : 4D (high prenatal testosterone), but their ability to detect the strategy of other players was constant (and better than chance) across all levels of digit ratio."(De Neys, Wim, Astrid Hopfensitz, and Jean-François Bonnefon. "Low second-to-fourth digit ratio predicts indiscriminate social suspicion, not improved trustworthiness detection." Biology Letters 9, no. 2 (2013): 20130037.)
High 2D:4D associated with more preoccupation and less avoidance, independent of gender
"In a sample of 285 Italian children aged 8–10 years, females scored lower in avoidance and higher in preoccupation, while no significant sex differences were observed in felt security. Consistent with our predictions, higher (feminized) digit ratios were significantly associated with lower avoidance and higher preoccupation scores in both males and females. In contrast, there was no significant association between digit ratio and felt security in either sex. These results corroborate the hypothesis that sex differences in attachment reflect the activation of sexually differentiated pathways organized in early development, and for the first time implicate sex hormones in the development of individual differences in attachment styles."(Del Giudice, Marco, and Romina Angeleri. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and attachment styles in middle childhood: Indirect evidence for an organizational effect of sex hormones." Adaptive Human Behavior and Physiology 2, no. 1 (2016): 1-10.)
Men rate women with lower right 2D:4D ratios as less faithfull, based on facial photographs; women's self-reports on faithfulness do not correlate with their 2D:4D ratios
"Results indicated a significant negative relationship between women's SOI scores [Sociosexual Orientation Inventory, the higher the score the more unrestricted the sexuality] and men's faithfulness ratings (more unrestricted sociosexuality was associated with lower faithfulness ratings). There was also a significant positive relationship between right (but not left) 2D:4D ratio and faithfulness ratings (women with female-like ratios were rated as being more faithful). The SOI scores of the women were not related to 2D:4D ratios. These results suggest that the potential for sexual infidelity can be gleaned from static facial cues."(DeLecce, Tara L., John P. Polheber, and Robert L. Matchock. "Sociosexual orientation and 2D: 4D ratios in women: Relationship to men’s desirability ratings as a long-term pair bond." Archives of sexual behavior 43, no. 2 (2014): 319-327.)
Differences in 2D:4D ratio correlate with differences in network properties of the brain
"A comparison between the mean map for the low 2D:4D digit ratio group (indicative of high exposure to testosterone during the prenatal period) and that for the high 2D:4D digit ratio group revealed a significant difference in the network properties of the medial parietal region for males and in the temporal region for females. The menstrual cycle affected network organization in the brain, which varied with the 2D:4D digit ratio."(Donishi, Tomohiro, Masaki Terada, and Yoshiki Kaneoke. "Effects of gender, digit ratio, and menstrual cycle on intrinsic brain functional connectivity: A whole‐brain, voxel‐wise exploratory study using simultaneous local and global functional connectivity mapping." Brain and behavior 8, no. 1 (2018): e00890.)
2D:4D correlates with nonverbal IQ in gifted girls
"Testing of between-subjects effects proved significant interactions between right and left 2D:4D ratio, genetic variability in androgen receptor, and also salivary testosterone level with non-verbal IQ in gifted girls. Our results point out that the variability in parameters of androgenicity contributes to the variability of nonverbal IQ in gifted girls."(Durdiaková, Jaroslava, Peter Celec, Jolana Laznibatová, Gabriel Minárik, and Daniela Ostatníková. "Testosterone metabolism: a possible biological underpinning of non-verbal IQ in intellectually gifted girls." Acta Neurobiol Exp 76 (2016): 66-74.)
Intellectually gifted boys have lower left 2D:4D and score lower on "reading the mind in the eyes" test
"Lower left 2D:4D (standing for higher prenatal testosterone level (...)) was observed in intellectually gifted boys compared to control boys surviving the correction for multiple testing. (...) Intellectually gifted boys achieved significantly lower score in reading mind in the eye test (...) that remained significant after correcting for multiple comparisons. It can be speculated that higher prenatal testosterone reflected by lower 2D:4D organizes the brain of gifted boys in a different way in comparison with controls."(Durdiaková, Jaroslava, Peter Celec, Jolana Laznibatová, Gabriel Minárik, Silvia Lakatošová, Aneta Kubranská, and Daniela Ostatníková. "Differences in salivary testosterone, digit ratio and empathy between intellectually gifted and control boys." Intelligence 48 (2015): 76-84.)
Prenatal testosterone has substantial role in determining cognitive performance
"The exclusive predictor for mental rotation was found to be sex, while 2D:4D was found to be the sole predictor of targeting, exhibiting a curvilinear relation, and figure-disembedding performance, showing a linear relation. These findings suggest a substantial role for prenatal testosterone but not current testosterone in determining cognitive performance."(Falter, C. M., M. Arroyo, and G. J. Davis. "Testosterone: Activation or organization of spatial cognition?." Biological psychology 73, no. 2 (2006): 132-140.)
High right-hand 2D:4D in boys associated with Specific Language Impairment, but not with behavioral problems
"A higher value of the biological 2D:4D ration (lower intrauterine exposure to testosterone) seems to be associated with language difficulties in boys with SLI (Specific Language Impairment), but not with their behavioural difficulties. Their behavioural difficulties seem to be a consequence of their linguistic difficulties and their level of cognition."(Font-Jordà, Antònia, Antoni Gamundí, María Cristina Nicolau Llobera, and Eva Aguilar-Mediavilla. "Use of the 2D: 4D digit ratio as a biological marker of specific language impairment." Anales de Pediatría (English Edition) (2018).)
High testosterone in men may be linked to higher earnings
"(...) Mendelian Randomization (MR), an approach which uses gene variants as instrumental variables for endogenous exposures, is used to investigate causal directionality. (...)(Hughes, Amanda, and Meena Kumari. "Testosterone, risk, and socioeconomic position in British men: Exploring causal directionality." Social Science & Medicine (2018).)
In observational models no social differences in testosterone are seen, but MR models suggest a positive influence of testosterone on earnings (...) and probability of being in work (...). Though MR estimates are less precise, results are consistent with previous literature linking testosterone with labour market success. The discrepancy may reflect suppression of observational associations by factors positively correlated with testosterone and negatively correlated with SEP, or indicate an influence of typical lifetime testosterone, which may be better indexed by genetic variants than by single testosterone measurements subject to noise."
Influence of prenatal steroid exposure on the need for power and achievement
"We obtained robustly significant sex-dimorphic effects of nPower (implicit need for power), and AI (activity inhibition) on [sic] between-hand digit ratio differences (right-hand 2D:4D ratio minus left-hand 2D:4D ratio) (...). Women high in both nPower and AI had a male-typical negative digit ratio difference, whereas those high only in nPower had a particularly female-typical positive digit ratio difference. In women, nAchievement (need for Achievement) was positively associated with digit ratio; in men, it was negatively related. No effects emerged for nAffiliation (need for affiliation). Thus, dispositional needs for power and achievement in adulthood appear to be shaped in part by the organizational effects of prenatal steroid exposure on brain development.
(...)
Implicit motives represent capacities for enjoying certain types of incentives, which in
turn makes individuals more likely to crave these incentives and act upon incentive-predicting
cues. (...) the needs (n) for power [are] defined as a capacity for deriving pleasure from having impact on others, achievement [is] defined as a capacity for getting a kick out of mastering challenging tasks, (...) and affiliation [is] defined as a capacity to enjoy establishing, maintaining, or restoring friendly, harmonious relationships.
(...)
This suggests that the seeds for individual differences in motivational needs are sown even before birth and that the link between implicit motives and the endocrine system is more pervasive than previously assumed (e.g., Schultheiss, 2013). Our findings also hint at a lateralization of the effects of prenatal sex steroids on the body and on brain systems supporting motivational functions."
"Activity inhibition" is defined as "a stable tendency to restrain or inhibit motivational impulses.
(source: Oxford Scholarship Online, description of Implicit Motives, Oliver Schultheiss and Joachim Brunstein)
(Schultheiss, Oliver C., Miriam Frisch, Dominik Özbe, Anna Ossmann, Maria Schultheiss, Sophie Lentz, Leon Martin, and Andreas G. Rösch. "Implicit motives show sex-dimorphic associations with digit ratio.")
Facial width-to-height ratio (fWHR) linked to testosterone exposure during adolescence
"Previous studies assumed testosterone to be the potential underlying mechanism of links between fWHR and dominance-related traits (...) It is plausible that fWHR is more closely tied to exposure to testosterone in adolescence: The link between fWHR and dominance-related behaviors and traits might emerge due to the common influence of testosterone on the craniofacial growth and the expression of behaviors and traits as part of sexual differentiation in puberty [7]. Indeed, administration of testosterone to males with delayed puberty affects various indices of craniofacial growth [50]. Moreover, Welker and colleagues found a positive association between fWHR and pubertal testosterone [33], and pubertal testosterone can bring about long-lasting effects on behavior and personality [51]. These findings provide indirect support for the assumption that fWHR and associated dominance-related traits may be more closely tied to pubertal testosterone exposure than to circulating concentrations in adulthood."
Lasting organizational effects of steroid hormones on nervous system structure
"This chapter summarizes recent evidence for organizational hormone effects (OHEs), that is, lasting organizational effects of steroid hormones on nervous system structure occurring during development (...), on the development of non-conscious motivational dispositions.(Köllner, Martin G., Kevin T. Janson, Kira Bleck, M. G. Köllner, K. T. Janson, and K. Bleck. "The social biopsychology of implicit motive development." Routledge international handbook of social neuroendocrinology. Abingdon, UK: Routledge.)
(...)
In sum, there is growing evidence from marker research for OHEs on the development of adult implicit motive levels. Several 2D:4D-studies consistently point to prenatal influences on nPower (the need for Power). Pubertal OHEs on further development and refinement of nPower are also likely, as our fWHR(facial Width-to-Height)-study suggests. AI consistently emerged as a moderator of these results, suggesting that brain lateralization is an important factor for further theorizing."
Lower 2D:4D ratio in men associated with higher facial attractiveness to women
"[M]ales' lower (more masculine) right 2D:4D and lower right-minus-left 2D:4D (Dr−l) were associated with a more attractive (and in some cases more symmetrical), but not more masculine, face. However, 2D:4D and Dr−l did not predict voice and body odour masculinity or attractiveness."(Ferdenzi, Camille, Jean-François Lemaître, Juan David Leongómez, and S. Craig Roberts. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) predicts facial, but not voice or body odour, attractiveness in men." Proceedings of the Royal Society of London B: Biological Sciences (2011): rspb20110544.)
More substance abuse in men with low 2D:4D ratios
"Results: Overall, the left 2D:4D digit ratio correlated significantly with frequency of drug use (...). The right 2D:4D digit ratio correlated significantly with the number of cigarettes smoked (...) and the frequency of drug use ...). For men, the left 2D:4D digit ratio correlated significantly with frequency of drug use (...). The right 2D:4D digit ratio in men correlated significantly with the number of cigarettes smoked (...) and the frequency of drug use (...). For women, none of the correlations between substance abuse and digit ratio were significant. Subjects with a right 2D:4D1. They also significantly more often were drug users (..., 33.6% of hawks versus 24.3% of doves). Conclusion: Subjects with a 2D:4D1. Although the strength of the associations is modest, subjects with a lower 2D:4D digit ratio tend to smoke more cigarettes and use drugs of abuse more frequently."(Fernstrand, A. M., L. Van den Borne, L. M. H. Lensvelt, L. L. A. Ribbert, L. X. Y. Goede, J. Garssen, and J. C. Verster. "The 2D: 4D digit ratio as biomarker for substance abuse." European Neuropsychopharmacology 25, no. S2 (2015): 616.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with better left-hand skill; high 2D:4D with better right-hand skill
"In right-handed children, high 2D:4D correlated with improved right-hand skill and low 2D:4D correlated with enhanced left-hand skill. Correlations were found to be similar for girls and for boys. Since low 2D:4D has been previously reported to be associated with faster left-hand speed compared to right in Afro-Caribbean children with very low mean 2D:4D, the present finding in a Caucasian population with high mean 2D:4D suggests that a tendency of improved left-hand performance due to prenatal testosterone may be found across ethnic groups."(Fink, Bernhard, John T. Manning, Nick Neave, and Uner Tan. "Second to fourth digit ratio and hand skill in Austrian children." Biological Psychology 67, no. 3 (2004): 375-384.)
Women find the dance of men with low 2D:4D ratio more attractive, dominant and masculine
"A panel of 104 female judges rated 12 clips of men with the lowest and highest finger-length ratios (2D:4D) for attractiveness, dominance, and masculinity. We found that dances by men with low (masculinised) 2D:4D ratios were rated significantly higher on attractiveness, dominance, and masculinity than dancers with high (feminised) 2D:4D. There were no significant differences between the two groups of dancers for age and other physical measures such as waist-to-hip ratio (WHR) and body-mass-index (BMI). Since there is evidence that finger-length ratios negatively correlate with testosterone exposure in utero, male dancing abilities may be organized early during development. Moreover, women’s ability to perceive differences in dance movement of men with low and high 2D:4D may indicate that dance provides some cues to phenotypic condition, relevant for sexual selection."(Fink, Bernhard, Hanna Seydel, John T. Manning, and Peter M. Kappeler. "A preliminary investigation of the associations between digit ratio and women’s perception of men’s dance." Personality and Individual Differences 42, no. 2 (2007): 381-390.)
About 5% of XX fetuses have "male" prenatal testosterone levels
"In both rats and humans, about 5% of XX fetuses have testosterone levels that are in the lower end of the male range during the prenatal testosterone surge, which is important for genital development. Since the incidence of discordance between the genitals and gonads is much lower than they would be if testosterone levels were the only determinant, thus it is conclude that there is sexual dimorphism in sensitivity levels to testosterone."(Khalid, Javaria Mona, Juliet M. Oerton, Carol Dezateux, Peter C. Hindmarsh, Christopher J. Kelnar, and Rachel L. Knowles. "Incidence and clinical features of congenital adrenal hyperplasia in Great Britain." Archives of disease in childhood 97, no. 2 (2012): 101-106.)
Skydivers with higher 2D:4D ratio do not take less risks, but when they take them, they take more precautions (more conscientiousness); and they are generally more agreeable
"Abstract:(Massimino, Simona, Sergio Rinella, Andrea Buscemi, Elisa Similia, Vincenzo Perciavalle, Valentina Perciavalle, Maria Cristina Petralia, Donatella Di Corrado, Annarita Laspina, and Marinella Coco. "Digit ratio, personality and emotions in skydivers." Biomedical Reports 10, no. 1 (2019): 39-46.)
The aim of the present study was investigate if there is an association between second‑to‑fourth digit length (2D:4D) ratio and personality factors capable of serving as predictors of individual choice towards high‑risk activities in a group of experts skydivers (...).
Lower 2D:4D ratios did not appear associated with a greater propensity for taking risks [deliberate risk-taking DRT (e.g., he/she actively seeks out dangerous situations)] but rather with a lower aptitude to assume precautions in unsafe conditions. In fact, the only sub‑dimensions of personality, analyzed by the BFQ‑2, correlated with the 2D:4D ratio were conscientiousness and agreeableness. Furthermore, prior to launch, the skydiver's level of stress (...) or state anxiety (...) was not significantly correlated with 2D:4D ratio; whereas there was significant positive correlation between 2D:4D values and trait anxiety. (...) The present results suggest that lower 2D:4D ratio may represent a significant predictor of less attentive precautionary behavior when risk‑taking.
(...)
Conscientiousness (efficient/organized vs. easy‑going/careless): Propensity to be organized and dependable, show self-discipline, act dutifully, aim for success, and prefer planned rather than spontaneous behavior. (...)
Agreeableness (friendly/compassionate vs. analytical/detached): Propensity to be empathetic and cooperative rather than suspicious and hostile towards others; it is also a measure of one's trusting and helpful nature, and whether an individual is generally well tempered or not.
(...)
A significant positive correlation was observed between 2D:4D and [precautionary behavior] PB [(e.g., he/she takes time to check for potential hazards)] (...) as well as between 2D:4D and trait anxiety (...). Therefore, skydivers with lower 2D:4D ratios were indicated to be less careful in taking precautions when deciding to take a risk. (...)
There were positive correlations between 2D:4D and the factors conscientiousness (...) and agreeableness (...). This implies that individuals with lower 2D:4D ratios are less conscientious."
Relation between genes, impulsivity, romantic relation quality and 2D:4D ratios in women
"The ratio between the second and fourth digits (2D:4D) has been widely used as a proxy for fetal exposure to androgens and has been linked to a number of sociosexual traits in humans. However, the role of genes in this equation remains unknown. Here (N=474), we test, firstly, for associations between 2D:4D and single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) in nine neurochemical receptor genes (AR, OXTR, AVPR1A, OPRM1, DRD1/2, ANKK1, 5HTR1A/2A), and secondly, whether digit ratios mediate the relationship between genetic variation and sociosexuality. We demonstrate significant associations between AR, OPRM1 and AVPR1A and 2D:4D. Moreover, mediation analysis indicates that, in women, AR and OPRM1 variation drives digit ratios, which are related positively to impulsivity and, for OPRM1, negatively to romantic relationship quality. Although these findings are subject to multiple testing issues, this study provides preliminary evidence that in women genetic factors may affect both impulsivity and perceived relationship quality through influencing factors indexed by digit ratios."(Pearce, E. H., Rafael Wlodarski, Anna Machin, and R. Dunbar. "Associations between neurochemical receptor genes, 2D: 4D, impulsivity and relationship quality." Biology Letters (2018).)
Low digit ratio strongly associated with more motor vehicle accidents in women
"Aim: To assess the prevalence and significance of Type 3 digit ratio in female motorcyclists involved in [Motor Vehicle Accident] MVA.(ABDULLAH, MUHAMMAD AZHAR, and MOHD IMRAN YUSOF. "Higher Risk of Motor Vehicle Accident in Female Motorcyclist with Type 3 Digit Ratio (2D: 4D)." Journal of Clinical & Diagnostic Research 12, no. 12 (2018).)
Materials and Methods: This study was a comparative crosssectional study that included 194 female motorcyclists which were equally divided into MVA and Non-MVA (control group). Radiograph of the right hand was used to calculate the digit ratio. The ratio were grouped into Type 1 (index>ring) common female pattern, Type 2 (index=ring) intermediate and Type 3 (index<ring) male pattern. (...)
Results: The result showed the MVA group was strongly associated with Type 3 pattern (...), while the non- MVA group was associated with Type 1 pattern (...).
Conclusion: The Type 3 digit ratio [(male pattern)] in female motorcyclists appears to be highly associated to involve in MVA."
People with high 2D:4D digit ratios have different biobehavioral traits compared with low 2D:4D ratios
"Constellations of biobehavioral traits are associated with activity in the testosterone and estrogen systems, due to fetal priming or hormonal alterations during the life course. Using these data, we developed two 14-item measures to investigate the traits associated with these hormone systems. To reach adequate internal consistency, we used participants of an Internet dating site; the final sample was 39,913 individuals. (...) Individuals who reported a longer 4th finger relative to 2nd expressed high scores on the proposed testosterone scale; individuals who reported a longer 2nd finger relative to 4th or 2nd and 4th digits of equal length expressed high scores on the proposed estrogen/oxytocin scale. These data are consistent with the hypothesis that these 2D:4D ratios are artifacts of hormonal priming in utero.
(...)
2. Traits associated with the testosterone and estrogen/oxytocinsystems in humans
[Editor's note: in the list below, "masculin" (testosterone-related) traits are marked in bold, and "feminine" (estrogen-related) traits are underlined.]In a meta-analysis of 150,000 Americans aged 13–22, thosewhose scores fell in the top 5–10% in math, geometry, mechanical reasoning and engineering were overwhelmingly male (e.g.,Hyde,Fennema, & Lamon, 1990). Questionnaire studies in several othercountries yielded similar results (e.g.,Mann, Sasanuma, Sakuma,& Masaki, 1990). Most young adult men express approximately eight to ten times more testosterone than most women; and it is widely hypothesized that this sex difference in hormone expression contributes to the above sex differences in cognition. Although adult sex differences in cognitive tasks are not sufficient evidence for hormonal effects, biological data support this hypothesized correlation. The brain architecture associated with these spatial/mathematical skills has been associated with fetal testosterone (e.g.,Geschwind & Galaburda, 1985; Grimshaw,1995); and bodily levels of testosterone also contribute to spatial/mathematical dexterity across the life span ( Janowsky et al.,1994). Further, it has been proposed that greater understanding of spatial, mechanical, mathematical, engineering and other rule-based systems is the result of more short-range and less long-distance neural connectivity, due to the exposure to prenatal androgens (e.g.,Manning, 2002).Other traits that may be linked with prenatal testosterone expression are heightened attention to detail, intensified focus, and restricted (narrow) interests (e.g.,Baron-Cohen, Knickmeyer,& Belmonte, 2005; Knickmeyer, Baron-Cohen, Raggatt, & Taylor,2005); and elevated adult levels of testosterone have also been associated with these traits(Dabbs&Dabbs, 2000). It has been suggested that prenatal testosterone expression is also linked with less emotion recognition, eye contact and social sensitivity (e.g.,Baron-Cohen et al., 2005), a poorer ability to judge what others are thinking or feeling (Baron-Cohen, 1995); and lack of empathy (Baron-Cohen et al., 2005). Adult expression of testosterone hasbeen correlated with being less polite, respectful, considerate or friendly (Dabbs, 1997; Harris, Rushton, Hampson, & Jackson,1996); and being more confident, forthright and bold (Nyborg,1994). Adult levels of testosterone have also been positively correlated with sensitivity to social dominance, drive for rank, the tendency to create dominance hierarchies (e.g.,Mazur, Susman, &Edelbrock, 1997), and aggressiveness (e.g.,Dabbs, 1990; Mazuret al., 1997). Poor verbal fluency and other language deficiencies have been associated with testosterone priming in the womb(e.g.,Baron-Cohen et al., 2005; Knickmeyer, Baron-Cohen, Raggatt, Taylor & Hackett, 2006; Knickmeyer et al., 2005; Geschwind & Galaburda, 1985; Manning, 2002). Last, a lower (masculinized) second to fourth digit ratio has been associated with high prenatal testosterone (Manning, 2002).
Women excel at several linguistic skills in US populations (e.g.,Halpern, 1992; McGuinness & Pribram, 1979) and other countries(Mannetal.,1990). Cross-culturally, women also excel at recognizing emotions in faces (e.g.,Hall, 1984; McClure, 2000), reading a person’s emotions from voice, gestures and other non-verbal cues (e.g.,Hall, 1984; McGuinness & Pribram, 1979) and interpreting a range of mental states (Baron-Cohen, Jolliffe, Mortimore, & Robertson, 1997). Although these sex differences are not sufficient evidence for hormonal effects, studies suggest that nurturance and other prosocial skills are associated with adolescent and adult estrogen activities in human females (Nyborg, 1994) and females of many other mammalian species (Carlson, 2001). Adult estrogen facilitates memory for emotional experiences (Canli, Desmond,Zhoa, & Gabrieli, 2002). Estrogen replacement therapy increases verbal memory (Hogervorst, Williams, Budge, Riedel, & Jolles,2000). In addition, estrogen receptor modulators can elevate adult working and episodic memory, executive function and verbal skills (Goekoop et al., 2005)."
(Fisher, Helen E., Jonathan Rich, Heide D. Island, and Daniel Marchalik. "The second to fourth digit ratio: A measure of two hormonally-based temperament dimensions." Personality and Individual Differences 49, no. 7 (2010): 773-777. - full article)
Behavioral differences ascribed to toxoplasmosis infection may actually be caused by prenatal testosterone
"Subjects with clinically asymptomatic life-long latent toxoplasmosis differ from those who are Toxoplasma free in several behavioural parameters. Case-control studies cannot decide whether these differences already existed before infection or whether they were induced by the presence of Toxoplasma in the brain of infected hosts. Here we searched for such morphological differences between Toxoplasma-infected and Toxoplasma-free subjects that could be induced by the parasite (body weight, body height, body mass index, waist-hip ratio), or could rather correlate with their natural resistance to parasitic infection (fluctuating asymmetry, 2D : 4D ratio). We found Toxoplasma-infected men to be taller and Toxoplasma-infected men and women to have lower 2D : 4D ratios previously reported to be associated with higher pre-natal testosterone levels. The 2D : 4D ratio negatively correlated with the level of specific anti-Toxoplasma antibodies in Toxoplasma-free subjects. These results suggest that some of the observed differences between infected and non-infected subjects may have existed before infection and could be caused by the lower natural resistance to Toxoplasma infection in subjects with higher pre-natal testosterone levels."(Flegr, J., M. HRŬSKOVÁ, Z. Hodný, M. Novotna, and J. Hanušová. "Body height, body mass index, waist-hip ratio, fluctuating asymmetry and second to fourth digit ratio in subjects with latent toxoplasmosis." Parasitology 130, no. 6 (2005): 621-628.)
Men and women with low 2D:4D ratios choose riskier financial options
"In an individual decision-making task with financial stakes, we find that both men and women with smaller 2D:4D ratios chose significantly riskier options. We further find that the 2D:4D ratio can partially explain the overall difference in risktaking between men and women. Moreover, for men and women at the extreme ends of the digitratio distribution the difference in risk-taking disappears entirely. Thus, the 2D:4D ratio can at least partially explain variation in financially motivated risk-taking behavior both within and between sexes and offers strong evidence of a biological basis of attitudes toward risk-taking."(Garbarino, Ellen, Robert Slonim, and Justin Sydnor. "Digit ratios (2D: 4D) as predictors of risky decision making for both sexes." Journal of Risk and Uncertainty 42, no. 1 (2011): 1-26.)
Low 2D:4D associated with more cognitive decline in elderly women
"We found that reduced prenatal exposure to testosterone in women may contribute to the prevention of cognitive decline in elderly women."(Gonçalves, Celina, Tiago Coelho, Sérgio Machado, and Nuno Barbosa Rocha. "2D: 4D digit ratio is associated with cognitive decline but not frailty in community‐dwelling older adults." American Journal of Human Biology 29, no. 5 (2017): e23003.)
Female-to-Male transgenders have lower 2D:4D ratio than female control group
"The finger length ratio 2D:4D in GID‐FtM [Gender Identity Disorder - Female to Male] was significantly lower than in female controls in the right hand in this study."(Hisasue, Shin‐ichi, Shoko Sasaki, Taiji Tsukamoto, and Shigeo Horie. "The Relationship Between Second‐to‐Fourth Digit Ratio and Female Gender Identity." The journal of sexual medicine 9, no. 11 (2012): 2903-2910.)
Meta-analysis finds no correlation between 2D:4D and agression in females, and only a weak (negative) correlation in males
"Here we meta-analyse these studies to determine the true size of the relationship between 2D:4D and aggression. We find no evidence of 2D:4D better predicting aggression at different levels of risk nor do we find evidence for a relationship between 2D:4D and aggression in females. Regarding males we find some evidence of a small, negative relationship between 2D:4D and aggression (r ≈ −.06) and no indication that either hand would predict aggression better than the other."(Hönekopp, Johannes, and Steven Watson. "Meta-analysis of the relationship between digit-ratio 2D: 4D and aggression." Personality and Individual Differences 51, no. 4 (2011): 381-386.)
Low 2D:4D ratio in men associated with higher number of sexual partners
"The number of sexual partners per individual (NSP) is an important component of sexual behaviour. Here, we report two studies concerning the relationship between a probable negative correlate of prenatal testosterone, the ratio of the length of 2nd and 4th digits (2D:4D), and NSP in men. The right hand 2D:4D ratio appears to be more strongly related to prenatal testosterone than does the left hand. Accordingly we found: (a) in a sample of 99 German heterosexual male undergraduates right hand 2D:4D (but not left hand 2D:4D) was significantly negatively associated with reported lifetime NSP. The relationship between NSP and 2D:4D was independent of free testosterone, but free testosterone also showed a weak positive association with NSP (b) in a sample of 79 heterosexual and 95 homosexual Austrian men we found a significant negative association between right hand 2D:4D (but not left hand 2D:4D) and reported NSP in past year for heterosexual but not for homosexual men. The association in heterosexuals was independent of age, years of education, occupation and relationship status. We conclude that male NSP is likely to be influenced by the long-term organisational effects of prenatal testosterone. The relationship between NSP and 2D:4D appears to be confined to heterosexual men."(Hönekopp, Johannes, Martin Voracek, and John T. Manning. "2nd to 4th digit ratio (2D: 4D) and number of sex partners: Evidence for effects of prenatal testosterone in men." Psychoneuroendocrinology 31, no. 1 (2006): 30-37.)
Low 2D:4D ratio correlates with higher grades in dentistry students, in males but not females
"Theoretical and practical grades were significantly negatively correlated to digit ratio in males (and this was particularly so after the influence of age and hours of study were removed, p = 0.02 and 0.004, respectively), but not in females (p = 0.89 and 0.77, respectively). This finding supports a link between high PT [Prenatal Testosterone] and intelligence in males. Our finding of no relationship between 2D:4D and examination marks in female students, suggests that PT may not influence intelligence in females."(Hopp, Renato Nicolás, Juliana Pucci de Moraes, and Jacks Jorge. "Digit ratio and academic performance in dentistry students." Personality and Individual Differences 52, no. 5 (2012): 643-646.)
Females with lower digit ratios less likely to worship celebrities
"[T]he digit ratios were positively correlated with CAS [Celebrity Attitude Scale] scores among female (r = 0.51, p < 0.001) but not male (r = −0.13, p = .394) participants. Our research found evidence of a significant positive correlation between 2D:4D ratios and celebrity worship in females but not in males, which indicated that females with lower digit ratios were less likely to worship celebrities."(Huh, HaengRyang. "Digit ratio and celebrity worship." Personality and Individual Differences 52, no. 3 (2012): 265-268.)
Of all armed military services, Marines have the lowest digit ratio (mean 0.94)
"We measured the 2D:4D on the participants’ right hands and explored its relationship to their selection of one of four branches of military service. Statistical analysis found no significant differences among the four branches of military service but supported our hypothesis of significant group differences in 2D:4D between Marines and all non-Marines. As expected, members of the Marine Corps demonstrated the lowest digit ratios, whereas those in the Army showed the highest. The average 2D:4D was 0.94 (SD = 0.05) for the Marine Corps, 0.95 (SD = 0.07) for the Air Force, 0.96 (SD = 0.06) for the Navy, and 0.97 (SD = 0.06) for the Army. Our research found evidence of small but significant group differences in 2D:4D among members of different branches of military service. We conclude that low 2D:4D is related to the risk and severity associated with the type of military training selected by recruits."(Huh, HaengRyang. "Born to be a Marine: Digit ratios and military service." Personality and Individual Differences 53, no. 3 (2012): 166-168.)
People with low 2D:4D prefer more aggressive and erotic content on media
"Our findings suggest that individuals with low 2D:4D prefer aggressive contents such as action films, sports telecast, killing and achieving games, hip-hop music, and erotic video clips rather than do individuals with high 2D:4D. Also individuals with low 2D:4D tend to demonstrate less preference for romance films than individuals with high 2D:4D. In addition, we found that low 2D:4D was associated with a preference for sports instead of other genres of entertainment products. Therefore, 2D:4D (a putative correlate of prenatal sex steroids) helps us to better understand the rationale of individuals’ preferences for media violence."(Huh, HaengRyang. "Digit ratios and preferences for aggressive content in entertainment." Personality and individual differences 51, no. 4 (2011): 451-453.)
Men and women with low digit ratios pay more attention to bodies than to faces
"Our findings indicate that individuals with low digit ratios tended to pay more attention to bodies than to faces compared with individuals with higher digit ratios, independently of sex. (...) Priority attention to bodies versus faces implies short- or long-term relationship orientation. (...) There is significant correlation between digit ratios and facial width-to-height ratios for females, not for males."(Huh, HaengRyang. "Digit ratios, but not facial width-to-height ratios, are associated with the priority placed on attending to faces versus bodies." Personality and Individual Differences 54, no. 1 (2013): 133-136.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with preference for unimodal learning style (in men and women)
"Lower 2D/4D ratios were determined to be associated with unimodal learning significantly in both genders."(Editor's note: Multimodal learning is eg. text and pictures, unimodal only text.)
(Isman, Cagla A., and Nimet U. Gundogan. "The influence of digit ratio on the gender difference in learning style preferences." Personality and Individual Differences 46, no. 4 (2009): 424-427.)
High 2D:4D associated with more harm avoidance
"A total of 728 healthy adults (330 men and 398 women) ranging in age from 20 to 45 years were tested. Subjects completed the Temperament and Character Inventory (TCI) and were examined by measuring the 2D:4D ratio using a direct measurement method. Correlations between the 2D:4D ratio and psychological characteristics were explored. For women only, significant positive correlations with the 2D:4D ratio were found in the TCI-Temperament dimension (TCI-T), particularly in the two subscales of harm avoidance scale. Women with higher 2D:4D ratios had higher fear of uncertainly scores (rpartial = 0.206, p = 0.028) and shyness with strangers scores (rpartial = 0.252, p = 0.024). The 2D:4D ratio shows stronger correlations with temperament than with character. A higher 2D:4D ratio of woman is expected to indicate harm avoidance."(Jeon, Sang Won, Ho-Kyoung Yoon, Changsu Han, Young-Hoon Ko, Yong-Ku Kim, and You Joon Won. "Second-to-fourth digit length ratio as a measure of harm avoidance." Personality and Individual Differences 97 (2016): 30-34.)
Mathematically inclined female teaching students have lower 2D:4D ratio
"This study found evidence that female pre-service teaching students who were inclined toward mathematics exhibited smaller, more masculine, digit ratios than those who were not as mathematically inclined. The right-hand 2D:4D ratios of the female pre-service teaching students who had a mathematics major or minor as their chosen field of study were compared to the right-hand 2D:4D ratios of the female pre-service teaching students who did not have a mathematics major or minor as their chosen field of study. The 2D:4D ratios of those with the mathematics major or minor was found to be statistically significantly less than those without. Please note that causality is not claimed, merely correlation."(Jordan-Steen, Maureen. "Correlation study between second/fourth digit ratio, number of older brothers and mathematics inclination in female pre-service teachers." In Proceedings of the World Congress on Engineering, vol. 2. 2009.)
Male (but not female) surgeons have significantly lower 2D:4D ratios
"We found that male surgeons had a significantly reduced 2D:4D ratio compared to the controls. There was no difference observed between female surgeons and the female control. We have demonstrated that male surgeons have a significantly lower 2D:4D ratio compared to an age and gender matched control."(Joyce, C. W., N. Mahon, J. C. Kelly, S. Murphy, M. McAllister, J. C. Chan, M. J. Kerin, and J. L. Kelly. "Hands of a surgeon: Second to fourth digit ratios in the surgical profession." Personality and Individual Differences 68 (2014): 28-31.)
Low 2D:4D digit ratio associated with more osteoporosis and osteoarthtritis
"The aim of this population-based study was to evaluate the association between the index to ring (2D:4D) finger length ratio and the osseographic score (OSS), the skeletal biomarker of biological aging. A sample included 802 males and 738 females who had participated in a Chuvashian skeletal aging study. (...) OSS is a skeletal biomarker that comprises osteoporotic and osteoarthritic changes observable on a hands X-ray. (...) Individuals with Type 3 finger length pattern (2D < 4D) showed significantly higher OSS that ones with Type 1 (2D > 4D) and Type 2 (2D=4D)."(Kalichman, Leonid, Valery Batsevich, and Eugene Kobyliansky. "2D: 4D finger length ratio and skeletal biomarker of biological aging." Anthropologischer Anzeiger; Bericht uber die biologisch-anthropologische Literatur 74, no. 3 (2017): 221-227.)
Low 2D:4D ratio in women associated with higher incidence of nose deformity caused by accidents
"This study compared 2D:4D and waist–hip ratio (WHR) in men and women with nose deformity caused by injuries suggesting risky behaviour with those of unaffected controls. This kind of facial trauma was accepted as an indicator of risk-taking behaviour. The study involved 100 patients (50 women aged 30.74±8.09 years and 50 men aged 30.98±10.86 years) who underwent rhinoplasty due to nose trauma (...). The results showed that women and men who had suffered nose injury had significantly higher values of WHR than controls. The 2D:4D in women with post-traumatic nose deformity was significantly different than the ratio in control women (p<0.0001) and presented the male pattern. It is concluded that in women risky behaviours seem to be associated with prenatal sex hormone influence, while differences in WHR suggest that this tendency is also related to postnatal hormonal factors. Risky behaviours in men should be linked to postnatal hormonal changes rather than to increased prenatal androgen exposure."(Kasielska-Trojan, Anna, Piotr Stabryła, and Bogusław Antoszewski. "Can body proportions serve as a predictor of risk-taking behaviours in women and men?." Journal of biosocial science 49, no. 5 (2017): 567-577.)
Low 2D:4D in men associated with higher number of children
"Five hundred and fifty-eight men from rural Poland (...) participated in this study. (...)(Klimek, Magdalena, Andrzej Galbarczyk, Ilona Nenko, Louis Calistro Alvarado, and Grazyna Jasienska. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) as an indicator of body size, testosterone concentration and number of children in human males." Annals of human biology 41, no. 6 (2014): 518-523.)
Results: Low 2D:4D was related to higher birth weight (p ¼ 0.04), higher birth length (p ¼ 0.01), higher body mass during childhood and adolescence (p ¼ 0.01), higher BMI (borderline significance, p ¼ 0.06), higher number of children among fathers (p ¼ 0.04) and higher testosterone levels during adulthood (p ¼ 0.04)."
High 2D:4D in women associated with higher number of children
"We studied 319 women aged 46–92, who went through a natural menopause and whose husbands were alive at least until their menopause were studied. Women were recruited at the Mogielica Human Ecology Study Site located in rural Poland.(Klimek, Magdalena, Andrzej Galbarczyk, Ilona Nenko, and Grazyna Jasienska. "Women with more feminine digit ratio (2D: 4D) have higher reproductive success." American journal of physical anthropology 160, no. 3 (2016): 549-553.)
Results
Women with more feminine 2D:4D had a higher number of children (P = 0.002), gave birth to their last child at a later age (P = 0.02), and had a longer reproductive lifespan (P = 0.04) than women with more masculine 2D:4D. Age and number of years of education were included as potential confounders in the analyses."
Female military students have male-typical 2D:4D digit ratios
"The cross-sectional study compared 59 female and 118 male students from the military courses and 53 females and 64 male students from the civil courses. (...) Among females, but not in males, the military cohort had a significantly lower, i.e. more 'masculine', 2D:4D for the left hand and right hand and average for both hands (t=3.290, p<0.001) than the civil cohort. This was not the case in males. However, the sex difference in 2D:4D was only significant among the civil students, and not among the military cadets."(Kociuba, Marek, Slawomir Kozieł, and Raja Chakraborty. "Sex differences in digit ratio (2D: 4D) among military and civil cohorts at a military academy in Wrocław, Poland." Journal of biosocial science 48, no. 5 (2016): 658-671.)
Women who choose judo/boxing instead of aerobics have lower 2D:4D ratio
"This cross-sectional study included 167 female students from a military academy in Wrocław, Poland. Of them, 119 had voluntarily chosen aerobic exercise, and 48 opted for judo/boxing. (...) The two groups showed similar physical fitness and body size. However, the judo/boxing group had significantly lower mean 2D:4D values than the aerobics group. It is proposed that voluntary choice of participation in a sport discipline by women could be linked to the 'organizational' effect of intrauterine testosterone exposure during prenatal growth."(Kociuba, Marek, Slawomir Kozieł, Raja Chakraborty, and Zofia Ignasiak. "Sports preference and digit ratio (2D: 4D) among female students in Wrocław, Poland." Journal of biosocial science 49, no. 5 (2017): 623-633.)
Low 2D:4D values are associated with problematic video gaming behavior in males
"Here, we quantified video gaming behavior in young males. We found lower mean 2D:4D values in subjects who were classified according to the CSAS-II as having at-risk/addicted behavior (n = 27) compared with individuals with unproblematic video gaming behavior (n = 27). Thus, prenatal androgen exposure and a hyper-male brain organization, as represented by low 2D:4D values, are associated with problematic video gaming behavior."(Kornhuber, Johannes, Eva-Maria Zenses, Bernd Lenz, Christina Stoessel, Polyxeni Bouna-Pyrrou, Florian Rehbein, Sören Kliem, and Thomas Mößle. "Low 2D: 4D values are associated with video game addiction." PloS one 8, no. 11 (2013): e79539.)
Daughters of mothers with lifetime bulimia nervosa have lower 2D:4D ratio
"This is the first study to investigate prenatal testosterone exposure in children at high‐risk for ED, using 2D:4D as a marker. We compared children whose mothers reported a lifetime ED (anorexia, bulimia, or both; N = 446) to children whose mothers did not (n = 5,367). Results: Daughters of women with lifetime bulimia nervosa (BN) had lower 2D:4D ratio (B: −0.01, 95% CI: −0.02 to −0.002, P = 0.02), indicating higher prenatal testosterone exposure, than daughters of mothers unaffected by ED. No differences were observed in the male children of women with an ED. Conclusions: Findings suggest that children at high‐risk for BN may be exposed to higher levels of testosterone in utero."(Kothari, Radha, Joseph Gafton, Janet Treasure, and Nadia Micali. "2D: 4D Ratio in children at familial high‐risk for eating disorders: The role of prenatal testosterone exposure." American Journal of Human Biology 26, no. 2 (2014): 176-182.)
Policewomen have male-typical 2D:4D ratio
"This study investigated whether 2D:4D differed between police officers and a control group of civilians in Wrocław, Poland. Participants were 147 male and 55 female police officers and 91 male and 75 female civilian controls. (...) The policewomen, compared with the female controls, were taller and had stronger hand grip strength, but had lower 2D:4D in the right hand and average 2D:4D of both hands. However, male and female police officers slightly differed only in the right hand digit ratio but not in the left hand ratio or the average for the two hands. However, the control group showed significant sex differences in all digit ratios with higher (feminine) mean values in females. The study provides further evidence that prenatal testosterone exposure, as reflected in the 2D:4D ratio, might have an association with choice of occupation, particularly among females."(Kozieł, Sławomir, Marek Kociuba, Raja Chakraborty, Aneta Sitek, and Zofia Ignasiak. "FURTHER EVIDENCE OF AN ASSOCIATION BETWEEN LOW SECOND-TO-FOURTH DIGIT RATIO (2D: 4D) AND SELECTION FOR THE UNIFORMED SERVICES: A STUDY AMONG POLICE PERSONNEL IN WROCŁAW, POLAND." Journal of biosocial science 50, no. 4 (2018): 527-539.)
Women with low 2D:4D ratio tend more towards homosexuality
"We examined a community-based sample of 409 subjects and calculated correlations of 2D:4D and sexual orientation as a continuum ranging from homosexual to heterosexual. Results: We found a significant negative correlation of 2D:4D with homosexual orientation (fantasy, attraction, activity and general score) in women, but not in men. Conclusions: Our results indicate that with higher prenatal testosterone levels in women, the likelihood of homosexual orientation might increase. We hypothesize a continuous neurohormonal sexual differentiation of the brain, most notably for women, that overrides categories and results in varying dimensions of sexual orientation. This hypothesis contrasts with the predominant suggestion of fixed organizational effects of androgens in the brain and a categorical sexual orientation."(Kraemer, Bernd, Thomas Noll, Aba Delsignore, Gabriella Milos, Ulrich Schnyder, and Urs Hepp. "Finger length ratio (2D: 4D) and dimensions of sexual orientation." Neuropsychobiology 53, no. 4 (2006): 210-214.)
Male-to-Female, and right-handed Female-to-Male, transgenders have female-typical 2D:4D ratios
"We compared 2D:4D of 56 GID [Gender Identity Disorder] patients (39 MtF[Male-to-Female]; 17 female-to-male GID patients, FtM) with data from a control sample of 176 men and 190 women. Bivariate group comparisons showed that right hand 2D:4D in MtF was significantly higher (feminized) than in male controls, but similar to female controls. The comparison of 2D:4D ratios of biological women revealed significantly higher (feminized) values for right hands of right handed FtM."(Kraemer, Bernd, Thomas Noll, Aba Delsignore, Gabriella Milos, Ulrich Schnyder, and Urs Hepp. "Finger length ratio (2D: 4D) in adults with gender identity disorder." Archives of Sexual Behavior 38, no. 3 (2009): 359-363.)
Boys with autism have lower 2D:4D ratio
"In this study, 2D:4D in 56 boys with ASD [Autism Spectrum Disorder] and in 32 control boys was measured. We found that the 2D:4D in ASD boys were lower than the ratio in control boys."(Krajmer, P., M. Spajdel, A. Kubranska, and D. Ostatnikova. "2D: 4D finger ratio in Slovak autism spectrum population." Bratislavske lekarske listy 112, no. 7 (2011): 377-379.)
Men self-report lower trait aggression than they actually have; low 2D:4D associated with higher aggression in males but not females
"A total number of 171 healthy subjects (98 men, 73 women) ranging in age from 20 to 30 years were tested. Participants were subjected to a modified version of a competitive reaction-time task, a commonly used and well-established tool to elicit and measure aggression (Taylor paradigm). They also completed self-report scales on trait aggression. (...) [I]n contrast to questionnaire data, men reveal higher levels of aggression in the computer task compared to women. Finally, a negative correlation between 2D:4D and aggression was found in males but not in females."(Kuepper, Yvonne, and Jürgen Hennig. "Behavioral aggression is associated with the 2D: 4D ratio in men but not in women." Journal of Individual Differences 28, no. 2 (2007): 64-72.)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with lower taste sensitivity, liking sweets, and more caries in children
"A total of 500 children 6‒14 years of age, of both genders, who reported to the Department of Oral Medicine and Radiology, were included. Propylthiouracil (PROP) sensitivity test was carried out and the subjects whose perception was bitter were grouped as tasters, whereas those who were unable to perceive any taste were grouped as non-tasters. The 2D:4D ratio was obtained by measuring the length ratio of index finger to ring finger with the help of a digital Vernier caliper. (...)
The results suggested a positive relation between low digit ratio (2D:4D), non-tasters, sweet likers and high caries index among the participants with a highly significant statistical difference."
(Lakshmi, Chintamaneni Raja, Doppalapudi Radhika, Mpv Prabhat, Sujana mulk Bhavana, and Nallamilli Sai Madhavi. "Association between genetic taste sensitivity, 2D: 4D ratio, dental caries prevalence, and salivary flow rate in 6-14-year-old children: a cross-sectional study." Journal of dental research, dental clinics, dental prospects 10, no. 3 (2016): 142.)
Female-to-Male transgender have male-typical 2D:4D ratio; Male-to-Female transgender digit ratios are equal to control group
"We prospectively recruited 118 transgender subjects undergoing hormonal therapy (50 female to male [FTM] and 68 male to female [MTF]) for finger length measurement. The control group consisted of 37 cisgender volunteers (18 females, 19 males). The length of the second and fourth digits were measured using digital calipers. (...)(Matthew Leinung and Christina Wu (2017) THE BIOLOGIC BASIS OF TRANSGENDER IDENTITY: 2D:4D FINGER LENGTH RATIOS IMPLICATE A ROLE FOR PRENATAL ANDROGEN ACTIVITY. Endocrine Practice: June 2017, Vol. 23, No. 6, pp. 669-671.)
FTM subjects had a smaller dominant hand 2D:4D ratio (0.983 ± 0.027) compared to cisgender female controls (0.998 ± 0.021, P = .029), but a ratio similar to control males (0.972 ± 0.036, P =.19). There was no difference in the 2D:4D ratio of MTF subjects (0.978 ± 0.029) compared to cisgender male controls (0.972 ± 0.036, P = .434).
Conclusion: Our findings are consistent with a biologic basis for transgender identity and the possibilities that FTM gender identity is affected by prenatal androgen activity but that MTF transgender identity has a different basis."
No correlation between 2D:4D digit ratio and ADHD
"Method: A clinically referred group of 64 children who fulfilled DSM‐IV‐TR criteria for ADHD (47 males, 17 females; mean age 8y 8mo, SD 1y 8mo, range 7–12y) and 46 comparison children (25 males, 21 females; mean age 9y 2mo; SD 1y 10mo, range 7–12y) were included in the study. The length of the second and fourth digits was measured by two independent raters. The Child Behaviour Checklist (CBCL) and the Test of Everyday Attention for Children (TEA‐Ch) were used to assess behavioural problems and different aspects of attention.(Lemiere, Jurgen, Bart Boets, and Marina Danckaerts. "No association between the 2D: 4D fetal testosterone marker and multidimensional attentional abilities in children with ADHD." Developmental Medicine & Child Neurology 52, no. 9 (2010): e202-e208.)
Results: No group differences in 2D:4D ratio were observed between children with (combined, inattentive, or hyperactive‐impulsive subtype of) ADHD and comparison children. The ratio did not show the postulated relation with cognitive and behavioural aspects of ADHD.
Interpretation: These findings challenge the hypothesis that fetal testosterone exposure plays a prominent role in the aetiology of ADHD."
Low 2D:4D associated with lower life expectancy, more incidence of suicide, higher death rates from communicable, maternal, perinatal, and nutritional conditions, and more respiratory infections, asthma, neurological conditions, and Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias
"Normalized male 2D:4D correlated positively with normalized male life expectancy (at birth, r = 0.46, p = 0.029; at the age of 60, r = 0.44, p = 0.038) and negatively with normalized male suicide rates (r = − 0.49, p = 0.017). In the exploratory analyses, the normalized male 2D:4D values were negatively associated with the normalized male deaths rates from communicable, maternal, perinatal, and nutritional conditions [r = − 0.65, p(FDR) = 0.011], respiratory infections [r = − 0.69, p(FDR) = 0.008], asthma [r = − 0.65, p(FDR) = 0.011], neurological conditions [r = − 0.56, p(FDR) = 0.046], and Alzheimer’s disease and other dementias [r = − 0.59, p(FDR) = 0.036]. The normalized female parameters showed the same cross-national correlations. In line with the previous individual level findings, the results suggest that prenatal sex hormone effects are sex-specifically involved in suicide and neurological conditions. Moreover, we provide novel national level evidence that prenatal sex hormone priming may sex-specifically influence life expectancy and death risk from respiratory diseases."(Lenz, Bernd, and Johannes Kornhuber. "Cross-national gender variations of digit ratio (2D: 4D) correlate with life expectancy, suicide rate, and other causes of death." Journal of Neural Transmission 125, no. 2 (2018): 239-246.)
Low 2D:4D associated with alcohol dependence and alcohol withdrawal severity in males
"We quantified prenatal androgen markers (e.g., second‐to‐fourth finger length ratio [2D : 4D]) and blood androgens in 200 early‐abstinent alcohol‐dependent in‐patients and 240 controls (2013–2015, including a 12‐month follow‐up). We also surveyed 134 women during pregnancy (2005–2007) and measured the 2D : 4D of their children (2013–2016).(Lenz, B., C. Mühle, B. Braun, C. Weinland, P. Bouna‐Pyrrou, J. Behrens, S. Kubis et al. "Prenatal and adult androgen activities in alcohol dependence." Acta Psychiatrica Scandinavica 136, no. 1 (2017): 96-107.)
Results
The prenatal androgen loads were higher in the male alcohol‐dependent patients compared to the controls (lower 2D : 4D, P = 0.004) and correlated positively with the patients’ liver transaminase activities (P < 0.001) and alcohol withdrawal severity (P = 0.019). Higher prenatal androgen loads and increasing androgen levels during withdrawal predicted earlier and more frequent 12‐month hospital readmission in alcohol‐dependent patients (P < 0.005). Moreover, stress levels (P = 0.002), alcohol (P = 0.010) and tobacco consumption (P = 0.017), and lifetime stressors (P = 0.019) of women during pregnancy related positively to their children's prenatal androgen loads (lower 2D : 4D)."
Sex hormones may have organizational and activational effect on alcohol addiction
"Sex hormones exert both permanent (organizational) and transient (activational) effects on the human brain. The sensitive period for these effects lasts throughout life. In this article, we present a novel early sex hormone activity model of alcohol addiction. We propose that early exposure to sex hormones triggers structural (organizational) neuroadaptations. These neuroadaptations affect cellular and behavioral responses to adult sex hormones, sensitize the brain's reward system to the reinforcing properties of alcohol and modulate alcohol addictive behavior later in life. This review outlines clinical findings related to the early sex hormone activity model of alcohol addiction (handedness, the second-to-fourth-finger length ratio, and the androgen receptor and aromatase) and includes clinical and preclinical literature regarding the activational effects of sex hormones in alcohol drinking behavior. Furthermore, we discuss the role of the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal and -gonadal axes and the opioid system in mediating the relationship between sex hormone activity and alcohol dependence.(Lenz, Bernd, Christian P. Müller, Christina Stoessel, Wolfgang Sperling, Teresa Biermann, Thomas Hillemacher, Stefan Bleich, and Johannes Kornhuber. "Sex hormone activity in alcohol addiction: integrating organizational and activational effects." Progress in Neurobiology 96, no. 1 (2012): 136-163.)
We conclude that a combination of exposure to sex hormones in utero and during early development contributes to the risk of alcohol addiction later in life."
Homosexual and bisexual Chinese men have higher mean 2D:4D ratio
"(a) homosexual and bisexual men had higher mean 2D:4D ratios on their right hands than heterosexual men; (c) there was no difference between homosexual men and bisexual men in the 2D:4D ratio; (d)there was no difference between right and left hands in the same group in the 2D:4D ratio."(Li, Caixia, Manhong Jia, Yanling Ma, Hongbing Luo, Qi Li, Yumiao Wang, Zhenhui Li et al. "The relationship between digit ratio and sexual orientation in a Chinese Yunnan Han population." Personality and Individual Differences 101 (2016): 26-29.)
High 2D:4D digit ratio associated with less emotional stability in women
"We correlated 2D:4D of 184 women and 101 men with their scores in Cattell's 16 Personality Factor (16PF) Questionnaire. We found women with a higher (more ‘feminine’) right hand 2D:4D to score lower in emotional stability and social boldness and higher in privateness. Mediator analysis showed emotional stability to be probably primarily correlated with 2D:4D and to act as a mediator between 2D:4D and social boldness. Privateness appears to be mediated by an even more complex path."(Lindová, Jitka, Martina Hrušková, Věra Pivoňková, Aleš Kuběna, and Jaroslav Flegr. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and Cattell's personality traits." European Journal of Personality: Published for the European Association of Personality Psychology 22, no. 4 (2008): 347-356.)
Women with lower 2D:4D digit ratios may be more impulsive
"The propensity to value a reward less as the delay to receive that reward increases is known as delay discounting and is typical of many forms of impulsive behavior. The current study investigated the relationship between delay discounting and the 2D:4D ratio, a proposed marker of prenatal androgen exposure, in 184 male and female college students. While male 2D:4D ratios were significantly lower than female ratios, there was no sex difference in delay discounting and no overall relationship between digit ratio and delay discounting. There was a significant negative correlation between the right 2D:4D ratio and delay discounting in women, with lower ratios associated with greater delay discounting."(Lucas, Margery, and Elissa Koff. "Delay discounting is associated with the 2D: 4D ratio in women but not men." Personality and Individual Differences 48, no. 2 (2010): 182-186.)
No association between 2D:4D ratio and health risk-taking in post-menopausal women
"We investigated health and sexual risk and 2D:4D in post-menopausal women.(Lyons, Minna, and Samuli Helle. "Digit ratio and risk taking in post-menopausal Finnish women." Personality and Individual Differences 55, no. 5 (2013): 591-594.)
2D:4D did not relate to alcohol or nicotine consumption in our sample.
2D:4D did not relate to lifetime sexual partners in our sample.
Prenatal hormones may not affect risk taking at an older age."
Professional junior soccer players with low 2D:4D are not better at sports, but commit more foul play
"In this study, we analyze the relationship between second‐to‐fourth digit (2D:4D) ratios—a proxy for prenatal androgen levels—and foul play and sporting performance in a sample of junior soccer players from a professional Uruguayan soccer club. Our results show that the most aggressive players (i.e., those awarded one or more red cards) have a more masculine finger pattern (lower 2D:4D ratio), while no relationship could be found between sporting performance and 2D:4D ratios."(Mailhos, Alvaro, Abraham P. Buunk, Denise Del Arca, and Verónica Tutte. "Soccer players awarded one or more red cards exhibit lower 2D: 4D ratios." Aggressive behavior 42, no. 5 (2016): 417-426.)
High performance of low 2D:4D men in different domains may be explained by need for achievement
"Recently, it has been shown that low-2D:4D men react much more strongly on performance feedback than high-2D:4D men, irrespective of the performance itself (5). When men with a low 2D:4D ratio find themselves in a subordinate status position (e.g., when they lose a game), they might react strongly, e.g., by acting impulsively, or perhaps even abandoning the activity if possible (5). Following this rationale, my hypothesis is that low-2D:4D men want to excel and therefore will look for a specific domain (in both hobbies and jobs) where they have the abilities to excel. This idea might help to explain why a low 2D:4D ratio in men is related to better performance in completely different domains such as sports (2, 3) and music (4).The same mechanism might also lead to a better performance in trading in the financial world but needs not be limited to this type of job. I expect low-2D:4D people to outperform high-2D:4D people in all kind of competitive jobs, sports, and other activities, not because of specific physical characteristics, but because of one specific psychological characteristic: a higher need for achievement."(Millet, Kobe. "Low second-to-fourth-digit ratio might predict success among high-frequency financial traders because of a higher need for achievement." Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences (2009): pnas-0900396106.)
Low 2D:4D men may be primarily motivated by status seeking, not performance as such
"We provide evidence for the idea that status relevance of the particular situation at hand influences the attitude towards performance-enhancing means for low 2D:4D men, but not for high 2D:4D men. We argue that 2D:4D may be related to any behavior that is functional to attain status in a specific context. (...)(Millet, Kobe, and Florian Buehler. "A Context Dependent Interpretation of Inconsistencies in 2D: 4D findings: The moderating role of status relevance." Frontiers in behavioral neuroscience 11 (2018): 254.)
In line with a status drive perspective on 2D:4D, our findings indicate that low 2D:4D men are generally more positive towards performance-enhancing means to win a cycling competition when they believe that the competition at hand is important, but not so when the competition is not important. If low 2D:4D men would take legalness of means into account in their need to achieve status, a three-way interaction should have been observed. However, we did not find any evidence for a differentiation between legal (nutrition supplements) and illegal (EPO, a hidden engine in the bike) means thereby suggesting that low 2D:4D men may be more inclined “to do whatever it takes to win” when stakes are high, but not when the outcome is irrelevant to attain personal status.
If this conclusion is correct, relationships between 2D:4D and any attitude, trait or behavior (be it greedy, impulsive, unethical, altruistic, selfish,…) may emerge as long as these particular attitudes, traits and behaviors help to attain status in that specific situation. However, if the focal behavior is related to an outcome irrelevant to one’s own status position, we do not expect any relationship between 2D:4D and the specific behavior at hand."
Overview of association between (prenatal) testosterone and psychopathy
"Alongside other social and development dynamics, one potential risk factor for the emergence of psychopathic behaviour is increased in utero exposure to testosterone (see Yildirim & Derksen, 2012); a hormone released by the hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis. Testosterone is considered a biological marker of traits and behaviours associated with psychopathy, such as deficits in empathy and emotional arousal (Helleday et al., 1993; Josephs et al., 2006), as well as dominant, cold, and antisocial behaviour (Archer et al., 2005; Eisenegger et al., 2011; Turan et al., 2014). Testosterone has also been associated with psychopathic traits, specifically, with participants evidencing positive correlations between testosterone and psychopathy after being asked to lie on film (Dane et al., 2018); possibly indicative of enjoyment derived through deception. Moreover, a proxy measure of foetal testosterone, the second-to-fourth digit ratio, was found to positively relate to scores of psychopathy in females and callous affect in males (Blanchard & Lyons, 2010). In forensic samples, increased levels of testosterone have been found in offenders characterised by extreme violence and sexual deviancy (Aromäki et al., 1999; 2002; Räsänen et al., 1999), and has further been associated with the presence of anti-social personality disorder and psychopathy-related traits (Stålenheim et al., 1998). Further, and in the general population, increased testosterone predicted psychopathic traits in Glenn et al. (2011). However, this association was only evident as a function of low cortisol, and so potentially lends support to a proposed dual-hormone model of social behaviour whereby testosterone and cortisol are mutually inhibitive of each other (see Mehta & Prasad, 2015 for a review). Taken together, although this evidence presents a compelling argument for the relationship between testosterone and psychopathy, this association has yet to be explored in a sample characterised by a pre-disposition for increased testosterone."(Fido, D., S. Williams, I. R. Hume, and Dean Fido. "A comparison of the manifestation of psychopathic traits between women with and without 4 Polycystic Ovary Syndrome (PCOS) 5 6.")
Low and high androgen exposure increase androphilic sexual attraction in men
"[R]ecent findings indicate that high level androgen exposure may contribute to the sexual orientation of a subset of gay men who prefer insertive anal sex and report more male-typical gender traits, whereas gay men who prefer receptive anal sex, and who on average report more gender nonconformity, present with biomarkers suggestive of low androgen exposure. Together, the evidence indicates that for both mice and men there is an inverted-U curvilinear relationship between androgens and sexual preferences, such that low and high androgen exposure increases androphilic sexual attraction, whereas relative mid-range androgen exposure leads to gynephilic attraction."(Swift-Gallant, Ashlyn. "Individual differences in the biological basis of androphilia in mice and men." Hormones and Behavior (2018).)
Certain aspects of sexual differentiation of the brain due to sexual hormones, others to sex chromosomes
"Recent studies using magnetic resonance imaging have shown that several sexually differentiated aspects of brain structure and function are female-typical in women with complete androgen insensitivity syndrome (CAIS), who have a 46 XY karyotype but a female phenotype due to complete androgen resistance, suggesting that these sex differences most likely reflect androgen action, although feminizing effects of estrogens or female-typical socialization cannot be ruled out. By contrast, some male-typical neural characteristics were also observed in women with CAIS suggesting direct effects of sex chromosome genes in the sexual differentiation of the human brain. In conclusion, the sexual differentiation of the human brain is most likely a multifactorial process including both sex hormone and sex chromosome effects, acting in parallel or in combination."(Bakker, Julie. "The Sexual Differentiation of the Human Brain: Role of Sex Hormones Versus Sex Chromosomes." (2018): 1-23.)
Sex differences in cognition, gender identity, sexual orientation, and the risks of developing neuropsychiatric disorders programmed in early fetal development; no evidence that postnatal social environment plays crucial role
"During the intrauterine period a testosterone surge masculinizes the fetal brain, whereas the absence of such a surge results in a feminine brain. As sexual differentiation of the brain takes place at a much later stage in development than sexual differentiation of the genitals, these two processes can be influenced independently of each other. Sex differences in cognition, gender identity (an individual’s perception of their own sexual identity), sexual orientation (heterosexuality, homosexuality or bisexuality), and the risks of developing neuropsychiatric disorders are programmed into our brain during early development. There is no evidence that one’s postnatal social environment plays a crucial role in gender identity or sexual orientation. We discuss the relationships between structural and functional sex differences of various brain areas and the way they change along with any changes in the supply of sex hormones on the one hand and sex differences in behavior in health and disease on the other.(Bao, Ai-Min, and Dick F. Swaab. "Sexual differentiation of the human brain: relation to gender identity, sexual orientation and neuropsychiatric disorders." Frontiers in neuroendocrinology 32, no. 2 (2011): 214-226.)
Research highlights
► Gender identity and sexual orientation are permanently programmed in the fetal brain. ► Testosterone in the fetal stage determines sexual differentiation of the human brain. ► The degree of genital masculinization does not necessarily reflect that of the brain. ► No evidence indicates social environment affect gender identity or sexual orientation. ► Sex differences in the brain determine sex-specific prevalence of brain disorders."
Nigerian male students have higher 2D:4D ratio than their female counterparts; low 2D:4D associated with better mathematical abilities
"462 students were selected to participate in the study (Males n = 239 and Females n = 223). (...) Mean 2D:4D for males was 0.96 ± 0.04 and for females 0.95 ± 0.04. This sex difference in 2D:4D was in the unexpected direction as most digit ratio studies reported lower ratios in favour of the male subject. (...) Mathematics performance is higher in female student subjects than in male students counterparts. (...) Contrary to most studies that reported lower 2D:4D in favor of the males and higher ratio to females, this present study found lower 2D:4D ratio in favour of females and higher ratio to(Rayyan, Muhammad Kabir, Ramatu Salisu, Ibrahim Ahmad Atiku, and Barnabas Danborno. "2nd TO 4th DIGIT RATIO (2D: 4D) AND MATHEMATICS PERFORMANCE AMONG SECONDARY SCHOOL STUDENTS IN KADUNA, NIGERIA.")
males this explained why the females students perform better in Mathematics than their males counterpart."
Large study finds no association between 2D:4D (left, right and average), testosterone levels, and cognitive empathy in young men (Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test)
"The capacity to infer the mental states of others (known as “cognitive empathy”) is essential for social interactions, and a well-known theory proposes that it is negatively affected by intrauterine testosterone exposure. Furthermore, previous studies reported that testosterone administration impaired cognitive empathy in healthy adults, and that a biomarker of prenatal testosterone exposure (finger digit ratios) moderated the effect. However, empirical support for the relationship has relied on small-sample studies with mixed evidence. We investigate the reliability and generalizability of the relationship in two large-scale double-blind placebocontrolled experiments in young men (N=243 and N=400), using two different testosterone administration protocols. We find no evidence that cognitive empathy is impaired by testosterone administration or associated with digit ratios. With an unprecedented combined sample size, these results counter current theories and previous high-profile reports, and demonstrate that previous investigations of this topic have been statistically underpowered."Note: this study used the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test to measure cognitive empathy.
(Nadler, Amos, David Zava, Triana Ortiz, Neil Watson, Justin Carre, Colin Camerer, and Gideon Nave. "Does testosterone impair mens' cognitive empathy? Evidence from two large-scale randomized controlled trials." bioRxiv (2019): 516344.)
Testosterone administration to male traders causes asset bubbles to be larger and longer
"Growing evidence shows that biological factors affect individual financial decisions that could be reflected in financial markets. Testosterone, a chemical messenger especially influential in male physiology, has been shown to affect economic decision making and is taken as a performance enhancer among some financial professionals. This is the first experimental study to test how testosterone causally affects trading and prices. We exogenously elevated testosterone in male traders and tested testosterone’s effect both on their trading behavior in experimental asset markets and on the size and duration of asset price bubbles. Using both aggregated and individual trading data, we find that testosterone administration generated larger and longer-lasting bubbles by causing high bids and the slow incorporation of the asset’s fundamental value."
An "asset bubble " is when the price of an asset, such as housing, stocks or gold, become over-inflated. Prices rise quickly over a short period. They are not supported by an underlying demand for the product itself. It's a bubble when investors bid up the price beyond any real sustainable value.
(https://www.thebalance.com/asset-bubble-causes-examples-and-how-to-protect-yourself-3305908)
(Nadler, Amos, Peiran Jiao, Cameron J. Johnson, Veronika Alexander, and Paul J. Zak. "The bull of wall street: experimental analysis of testosterone and asset trading." Management Science (2017).)
Child sexual offenders have lower right-hand 2D:4D ratio
"Independent of their sexual preference, child sexual offenders showed signs of elevated prenatal androgen exposure compared with non-offending pedophiles and controls. (...) The findings support theories of testosterone-linked abnormalities in early brain development in delinquent behavior (...).(Kruger, Tillmann HC, Christopher Sinke, Jonas Kneer, Gilian Tenbergen, Abdul Qayyum Khan, Alexandra Burkert, Linda Müller-Engling et al. "Child sexual offenders show prenatal and epigenetic alterations of the androgen system." Translational Psychiatry 9, no. 1 (2019): 28.)
[C]hild sexual offenders (CSO) had a lower 2D:4D ratio of the right hand compared with non-child sexual offenders (−CSO), indicating a higher level of prenatal testosterone. (...) [C]hild sexual offenders showed significantly lower lateralization scores [2D4DR - 2D4DL] as an additional measure of prenatal androgenization"
Individuals with autism spectrum disorder have slightly lower 2D:4D ratio, but on average within typically developing range
"A meta-analysis study(6) confirmed the reliability of a low 2D:4D ratio in ASD (Autism Spectrum Disorder) across different research groups and measurement methods. However, the meta-analysis estimated that the 2D:4D ratio is lowered by approximately 0.5–0.6 SD in individuals with ASD in comparison to TD (Typically Developing) controls. Based on this estimation, the same study pointed out that a difference of approximately 0.5 SD indicates that most individuals with ASD have a 2D:4D ratio within the normal (TD) range.
(...)
(6) Hönekopp, J. & Watson, S. Meta-analysis of digit ratio 2D:4D shows greater sex difference in the right hand. Am J Hum Biol 22, 619–630, https://doi.org/10.1002/ajhb.21054 (2010)."
(Togo, Shunta, Takashi Itahashi, Ryuichiro Hashimoto, Chang Cai, Chieko Kanai, Nobumasa Kato, and Hiroshi Imamizu. "Fourth finger dependence of high-functioning autism spectrum disorder in multi-digit force coordination." Scientific Reports 9, no. 1 (2019): 1737.)
High prenatal testosterone (in amniotic fluid) associated with smaller delay of gratification, and more attention problems/overactive behavior in 3-year-old boys
"Highlights(Körner, Lisa M., Bettina M. Pause, Gunther Meinlschmidt, Marion Tegethoff, Susanne Fröhlich, Peter Kozlowski, Noëllie Rivet et al. "Prenatal testosterone exposure is associated with delay of gratification and attention problems/overactive behavior in 3-year-old boys." Psychoneuroendocrinology (2019).)
• Girls are better able to delay gratification than boys.
• Boys with higher prenatal testosterone levels are less able to delay gratification.
• Boys with higher prenatal testosterone levels show more attentions problems/overactive behavior.
• Boys with more attention problems/overactive behavior are less able to delay gratification.
Abstract
Sex differences in self-control become apparent during preschool years. Girls are better able to delay their gratification and show less attention problems and overactive behavior than boys. In this context, organizational effects of gonadal steroids affecting the neural circuitry underlying self-control could be responsible for these early sex differences. In the present study testosterone levels measured in amniotic fluid (via ultra performance liquid chromatography and tandem mass spectrometry) were used to examine the role of organizational sex hormones on self-control. One hundred and twenty-two 40-month-old children participated in a delay of gratification task (DoG task) and their parents reported on their attention problems and overactive behavior. Girls waited significantly longer for their preferred reward than boys, and significantly more girls than boys waited the maximum period of time, providing evidence for sex differences in delay of gratification. Moreover, there was a trend towards more attention problems and overactive behavior in boys than in girls. Boys that were rated as suffering from more attention problems and overactive behavior waited significantly shorter in the DoG task. Amniotic testosterone measures were reliable in boys only. Most importantly, boys who waited shorter in the DoG task and boys who were reported to suffer from more attention problems and overactive behavior had higher prenatal testosterone levels. These findings extend our knowledge concerning organizational effects of testosterone on the brain circuitry underlying self-control in boys, and are of relevance for understanding how sex differences in behavioral disorders are connected with a lack of self-control."
Testosterone differences in women robustly predict sociosexuality and general sexual desire in women
"Here, we examined associations between steroid hormones and two facets of sexual psychology with putatively different adaptive functions, sociosexual orientation and general sexual desire, in a sample of naturally cycling women (NC; n = 348, 87 of whom completed 2 sessions) and hormonally contracepting women (HC; n = 266, 65 of whom completed 2 sessions). Across two sessions, increases in estradiol predicted elevated sociosexual desires in NC women, and this relationship was stronger in women whose progesterone simultaneously decreased across sessions. Changes in hormones were not associated with changes in general sexual desire. Between-subjects differences in testosterone robustly, positively predicted sociosexuality and general sexual desire among NC women. Hormones were not consistently related to changes or differences in sexual psychology among HC women. The present results are consistent with testosterone contributing to individual differences, or modulating relatively long-term changes, in women's mating psychology."(Shirazi, Talia N., Heather Self, Khytam Dawood, Kevin A. Rosenfield, Lars Penke, Justin M. Carré, Triana Ortiz, and David A. Puts. "Hormonal predictors of women's sexual motivation." Evolution and Human Behavior (2019).)
Pro-environmental behavior as a competition between men
"Differences between men and women in terms of pro-environmental behaviour have been attributed to differences in perceived threats to gender identity; pro-environmental behaviours being viewed as more feminine than masculine. Conversely, if pro-environmental behaviour is framed in terms of competition with peers, men might be expected to engage more than women. This paper explores how far such behaviours are related to a suggested source of gender related attitude/behaviour differences: pre-natal exposure to testosterone and estrogen, employing a suggested biomarker, the ratio of the length of the second and fourth digits of the hand (2D,4D). A stratified sample of UK households containing 880 adults (400 male and 480 female) drawn from the Understanding Society Survey Innovation Panel is used. A small but significant difference between men's and women's environmental behaviour is found whilst greater engagement with pro-environmental behaviour is associated with more masculine ratio in men, but not women."(Hand, Chris. "Biology and being green: The effect of prenatal testosterone exposure on pro-environmental consumption behaviour." Journal of Business Research (2019).)
Low (right hand) 2D:4D men become less prosocial when they are more intuitive and less deliberate; high 2D:4D men are always equally prosocial, whether they deliberately try or not
"we observe in the data that for low (right) 2D:4D men, the more intuitive they are, the less prosocial they become, whereas for high (right) 2D:4D men the thinking style does not affect their prosociality."(Millet, Kobe, and Aylin Aydinli. "Cognitive reflection, 2D: 4D and social value orientation." PloS one 14, no. 2 (2019): e0212767.)
Null Effects of Game Violence, Game Difficulty, and 2D:4D Digit Ratio on Aggressive Behavior
"Researchers have suggested that acute exposure to violent video games is a cause of aggressive behavior. We tested this hypothesis by using violent and nonviolent games (...). (...) Incidentally, we found that 2D:4D digit ratio, thought to index prenatal testosterone exposure, did not predict aggressive behavior. Results do not support acute violent-game exposure and low 2D:4D ratio as causes of aggressive behavior."(Hilgard, Joseph, Christopher R. Engelhardt, Jeffrey N. Rouder, Ines L. Segert, and Bruce D. Bartholow. "Null Effects of Game Violence, Game Difficulty, and 2D: 4D Digit Ratio on Aggressive Behavior." Psychological Science (2019): 0956797619829688.)
Men with low 2D:4D are more aggressive towards everyone, in women everyone is aggressive towards those with high 2D:4D (who are less aggressive)
"We find that Low type (higher exposure to testosterone) males expend significantly higher conflict effort than High type males, that is, they are more aggressive, which reduces their opponents’ earnings. Among females, however, everyone is more aggressive against the High type (who respond less aggressively).
(...)
We find that L (DR) type males expend higher effort, but do not earn more than H type males. Anybody matched with L type males earns less than when matched with H type males. In addition, all females exert more effort against H types, and consequently H type females earn less than L type females. (...) Our main result thus shows that males act primarily according to their own type and react weakly to their opponent’s type while, in sharp contrast, females (re)act primarily according their opponent’s type. Although gender differences in attitudes toward competition have been documented before (...), our findings suggest that (i) biological factors matter for both genders and (ii) although the observed competitive behavior is to some sense intuitive (L type men being more aggressive; H type women encountering more aggression from others), men and women have a fundamentally different approach to dyadic competition."
704 subjects (478 females)
(Pablo, Brañas-Garza, Subhasish Chowdhury, Antonio M. Espín, and Jeroen Nieboer. ‘Born this Way’? Prenatal Exposure to Testosterone May Determine Behavior in Competition and Conflict. University Library of Munich, Germany, 2019.)
Men with low 2D:4D approach same-sex rivals more, and with a higher testosterone level
"Findings suggest that responses to infidelity threats in adulthood are shaped by hormonally mediated masculinization of the brain in utero. 2D:4D digit ratio (widely regarded as an index of prenatal testosterone exposure) moderated behavioral and endocrinological responses to infidelity threat. After an infidelity prime (but not a control prime), lower (more masculine) 2D:4D was associated with a greater tendency to approach attractive same-sex targets (intrasexual rivals) and with heightened increases in circulating testosterone, a hormone related to a variety of aggressive and confrontational behaviors."(Maner, Jon K., Saul L. Miller, Jacqueline M. Coyle, and Michael P. Kaschak. "Confronting intrasexual rivals: 2D: 4D digit ratio predicts behavioral and endocrinological responses to infidelity threat." Social Psychological and Personality Science 5, no. 1 (2014): 119-128.)
Feminine preschool play behavior associated with male-to-female transition in adulthood; masculine preschool behavior associated with female-to-male transition, and cisgender men
"Preschool play behaviors have been frequently shown to be associated with prenatal androgens. It has also been proposed that incongruent sex-typed play behaviors in childhood is associated with gender dysphoria in adulthood in both men and women. Most of these studies, however, have been conducted in western countries. In this study, we investigated the recalled childhood play behavior among a total number of 339 Iranian participants (n = 72 transwomen, n = 92 transmen, n = 75 cisgender men and n = 100 cisgender women) using Preschool Activity Inventory (PSAI). We found that PSAI mean scores of the four groups were significantly different (F(3,335 = 223.5, p < 0.001)). Both transmen and cisgender men scored significantly more masculine than transwomen and cisgender women but had no different with each other. Transwomen scored significantly more feminine than cisgender men and cisgender women."(Ghasem, Roshan, and Talaei Ali. "Recalled Pre-School Activities among adults with gender dysphoria who seek gender confirming treatment–an Iranian study." Asian Journal of Psychiatry (2019).)
High 2D:4D in female cynomolgus monkeys associated with depression
"This research aimed to provide evidence of a relationship between digit ratio and depression status in the cynomolgus monkey (Macaca fascicularis). In stable cynomolgus monkey social groups, we selected 15 [female] depressed monkeys based on depressive-like behavioral criteria and 16 [female] normal control monkeys. (...) Our findings revealed significant differences in finger lengths and digit ratios between depressed monkeys and healthy controls, which concords with our view that relatively high fetal testosterone exposure may be a protective factor against developing depressive symptoms (or that low fetal testosterone exposure is a risk factor)."(Li, Wei, XunYang Ling-YunLuo, Bin Lian YongHe, Qing-YuanWu Chao-HuaQu, and Peng Xie Jian-GuoZhang. "Depressed female cynomolgus monkeys (Macaca fascicularis) display a higher second-to-fourth (2D: 4D) digit ratio." 动物学研究: 47.)
Large study finds no correlation between cognitive empathy, digit ratio and testosterone administration
"The capacity to infer the mental states of others (known as cognitive empathy) is essential for social interactions, and a well-known theory proposes that it is negatively affected by intrauterine testosterone exposure. Furthermore, previous studies reported that testosterone administration impaired cognitive empathy in healthy adults, and that a biomarker of prenatal testosterone exposure (finger digit ratios) moderated the effect. However, empirical support for the relationship has relied on small-sample studies with mixed evidence. We investigate the reliability and generalizability of the relationship in two large-scale double-blind placebo-controlled experiments in young men (N=243 and N=400), using two different testosterone administration protocols. We find no evidence that cognitive empathy is impaired by testosterone administration or associated with digit ratios. With an unprecedented combined sample size, these results counter current theories and previous high-profile reports, and demonstrate that previous investigations of this topic have been statistically underpowered."(Nadler, Amos, David Zava, Triana Ortiz, Neil Watson, Justin Carre, Colin Camerer, and Gideon Nave. "Does testosterone impair mens' cognitive empathy? Evidence from two large-scale randomized controlled trials." bioRxiv (2019): 516344.)
2D:4D ratio associated with mating behaviour, dominance, social style (tolerance), and certain personality traits in humans and non-human primates
"The ultimate causes of variation in primate behaviour and social systems have been well studied, but less attention has been paid to the underlying role of proximate mechanisms. Using the second-to-fourth digit ratio (2D:4D ratio) as a biomarker for prenatal androgen effects (PAE) and phylogenetic comparative methods where appropriate, this thesis aims to complement the ultimate perspective by assessing the degree to which variation in PAE may provide a proximate explanation for the observed variation in primate behaviour. Specifically, this study examines 1) the role of PAE in male intrasexual competition and mating behaviour in non-human primates, 2) the relationship between PAE and human marriage systems, 3) the role of PAE in female intrasexual competition and social relationships in non-human primates and 4) the role of PAE in the expression of aspects of human and non-human primate personality.(Howlett, Caroline. "The Expression of the 2D: 4D ratio across the Order Primates." PhD diss., University of Kent,, 2019.)
In study 1 (...), [m]ale digit ratios (...) [varied] across species characterised by different types of mating systems; males of species characterised by monogamous mating had the highest 2D:4D ratios, followed closely by polyandrous males (low inferred PAE), while polygynandrous and polygynous males had the lowest 2D:4D ratios (high inferred PAE). Male 2D:4D ratios also varied with the form of polygyny and polygynandry corresponding to the need for males to display competitive over cooperative behaviours in each mating system. Higher PAE may therefore be adaptive for male non-human primates which experience high levels of direct intrasexual competition. This pattern was also evident in female non-human primates (Study 3), but was not mirrored in analysis of humans, where no associations were found between male or female 2D:4D ratios and marriage system (Study 2). (...) However, as the sample was biased in favour of monogamous populations, a more balanced dataset encompassing a wider range of marriage systems may provide further insights.
PAE were also implicated in the maintenance of intersexual dominance relationships, particularly female dominance, as evidenced by lower female 2D:4D ratios in species characterised by female dominance than in species characterised by male dominance or codominance (Study 3). (...) [I]n a more taxonomically-narrow analysis conducted with macaque species (Macaca spp.), female 2D:4D ratio varied according to social style, with more "tolerant" species having higher 2D:4D ratios than less tolerant species, suggesting that PAE may contribute to this variation. Results indicate that PAE may act as a proximate mechanism underlying behavioural expression in male and female non-human primates in ways that are ultimately adaptive to their social system.
In study 4, PAE on behavioural variation within species was explored using personality traits (boldness, exploration tendency/curiousness, persistency, competitiveness) in three species: ring-tailed lemurs (Lemur catta), robust capuchins (Sapajus spp.) and human children (Homo sapiens). 2D:4D ratios were not associated with any trait in ring-tailed lemurs or with persistency in any species, suggesting that expression of this trait may not be influenced by PAE. Boldness and exploration tendency in boys correlated negatively with 2D:4D ratios, as did competitiveness in robust capuchins, suggesting that PAE play a role in the expression of these traits in these and perhaps also in other haplorhine primates. In addition to broad cross-species influences, PAE thus appear to underlie inter-individual differences in the expression of some adaptive behavioural traits, highlighting the importance of considering proximate as well as ultimate causes in studies of primate behaviour."
Association between low 2D:4D digit ratio, high competitiveness, low anxiety, low stress and surgical vs. non-surgical study choice among medical students
"This study examined a possible link between the elective preferences of medical students (surgical vs. non-surgical) and their emotional and hormonal responses to a psychological stressor. Forty medical students completed a laboratory stressor comprising of 10 puzzles in a time-limited format. Emotional state was assessed before (competitiveness, anxiety) and after (stress, enjoyment) testing, along with changes in salivary testosterone (ΔT) and cortisol (ΔC). Comparisons were made according to individual preferences for a surgical (n = 16) or non-surgical (n = 24) elective. Those seeking surgery had a lower 2D:4D (d = -2.0) with higher competitiveness scores (d = 2.7), but less anxiety (d = -0.9) and stress (d = -0.8). They also had a larger ΔT (17% vs. 6%) and smaller ΔC (7% vs. 12%) from the non-surgical cohort. Significant interrelationships were observed between 2D:4D, competitiveness, anxiety, stress and hormones."(Crewther, Blair T., and Christian J. Cook. "Medical students preferring a surgical or non-surgical elective differ in their emotional and hormonal responses to a psychological stressor." The American Journal of Surgery (2019).)
Testosterone has a negative impact on the detection of emotions in men
"The subject of the present work was to investigate connections between the sex hormone testosterone and the emotion recognition performance of young men. For this purpose, a study was carried out with 40 male volunteers, in which mimic expressive emotions had to be recognized, at the same time the testosterone level was determined. The FEEL test (Facially Expressed Emotion Labeling test) served as a test instrument for measuring the emotion recognition performance. It was of particular interest whether testosterone influenced the emotional recognition eg. negatively and the detection of which of individual emotions it influences.(Sachsenweger, Frauke. "Der Einfluss des Sexualhormons Testosteron und weiterer psychometrischer Faktoren auf die Emotionserkennung bei Männern." PhD diss., Universität Ulm, 2019, translation by bva)
The following main results came out:
Testosterone generally influences facial expression detection negatively when the emotions are presented with full intensity (100%). Besides, the sexual hormone has a specific negative impact on the detection of grief (at 100% intensity), disgust (at 50% intensity) and anxiety (at 50% intensity). The results are consistent with the established hypothesis and thus confirm the theory that testosterone promotes antisocial behavior and thereby negatively affects emotion recognition.
In addition, in this study, the relationship between other psychometric factors (gender role identity, empathizing, Ten Item Personality Inventory (TIPI) Personality Dimensions) and emotion recognition performance were examined.
The results were as follows: There is no correlation between gender role identity (measured with the Bem Sex Role Inventory (BSRI)) and emotion recognition performance, subjects with high "Empathizing" results recognize the emotion disgust better, and there is a positive relationship between the personality dimension "extraversion" and emotion recognition performance."
2D:4D ratio correlates negatively with severity of problem drinking and nicotine dependency
"We investigated the independent relationship of 2D:4D ratios and problem drinking and nicotine dependence. 2D:4D ratios associated independently with the severity of problem drinking and nicotine dependence."(Canan, Fatih, Cuneyt Tegin, and Omer Gecici. "The second to fourth digit (2D: 4D) ratios, smoking, and problem drinking in a young adult university student sample." Neurology, Psychiatry and Brain Research 32 (2019): 63-67.)
Meta-analysis finds association between low 2D:4D ratio and substance and computer dependency
"Human studies have reported inconsistent associations between the length ratio of the second finger to the fourth finger (2D:4D), which is a proxy for prenatal androgen load, and substance or computer use in adolescents and adults. This meta-analysis quantifies the magnitude of this relationship and investigates the roles of sex, definition of caseness, different forms of addiction, the hand measured (right hand versus left hand), and other cohort characteristics. Univariate random-effects meta-analyses were performed, and moderators were tested with Bonferroni-corrected meta-regression analyses. The study included 18 independent samples with a total of 175,955 participants (96,316 males and 79,639 females). There was a significant difference in 2D:4D between the substance and computer-using subjects and the controls for the combined sample (Hedge’s g = − 0.178 [− 0.291; − 0.064]) and for males (Hedge’s g = − 0.260 [− 0.399; − 0.122]), but not for females. These effects were amplified when only analyzing studies that compared dependent versus non-dependent subjects (combined sample: g = − 0.325 [− 0.492; − 0.157]; males: g = − 0.427 [− 0.564; − 0.291]), but did not reach significance in the subgroup of studies examining other parameters of substance and computer use. When analyzing different forms of substance and computer use separately, alcohol intake and computer use revealed a significant difference in the standardized mean. Again, the effects were amplified when analyzing the subgroup of males and the subgroup of studies comparing dependent versus non-dependent subjects, with effect sizes showing Hedge’s g values as many as − 0.552 [− 0.785; − 0.319] (alcohol-dependent males). Thus, this meta-analysis confirms that lower 2D:4D is associated with substance and computer dependency."(Siegmann, Eva-Maria, Polyxeni Bouna-Pyrrou, Bernd Lenz, and Johannes Kornhuber. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) in relation to substance and computer use: a meta-analysis." Journal of Neural Transmission (2019): 1-14.)
Higher levels of steroid metabolites in Asperger's (high-functioning autism), even higher in Kanner's syndrome (low-functioning autism)
"Abstract:(GASSER, Benedikt Andreas, et al. Steroid Metabolites Support Evidence of Autism as a Spectrum. Behavioral Sciences, 2019, 9.5: 52.)
Objectives: It is common nowadays to refer to autism as a spectrum. Increased evidence of the involvement of steroid metabolites has been shown by the presence of stronger alterations in Kanner’s syndrome compared with Asperger syndrome.
Methods: 24 h urine samples were collected from 20 boys with Asperger syndrome, 21 boys with Kanner’s syndrome, and identically sized control groups, each matched for age, weight, and height for comprehensive steroid hormone metabolite analysis via gas chromatography–mass spectrometry. Results: Higher levels of most steroid metabolites were detected in boys with Kanner’s syndrome and Asperger syndrome compared to their matched controls. These di fferences were more pronounced in a ected individuals with Kanner’s syndrome versus Asperger syndrome. (...)
Conclusions: Due to di fferences in the level of alteration, the premise that Asperger syndrome is on the mild side of the autism spectrum and that Kanner’s syndrome is on the severe side is supported, but alteration patterns yield di erent phenotypic expressions."
High right-hand 2D:4D digit ratio associated with bipolar disorder
"Background: The 2th- to 4th-finger ratio (2D:4D) has been proposed as a potential indicator of greater androgen exposure during fetal development (1). While smaller digit ratios, suggestive of stronger perinatal androgen action, have been associated with male-linked disorders (e.g., autism), problematic video gaming behavior (2), larger digit ratios, suggestive of weaker perinatal androgen action, have been associated with depression, schizophrenia, and eating disorders (3,4,5).(Cuneyt Tegin, Fatih Canan, Rif El-Mallakh, "T145. Association Between Hand Digit Ratio and Bipolar Disorder", Biological Psychiatry, May 15, 2019Volume 85, Issue 10, Supplement, Page S185)
Objective: We investigated association between hand digit ratio (2D:4D) and Bipolar Disorder.
Methods: 53 bipolar subjects were invited among Bipolar clinic patients. 52 non-bipolar subjects were invited. Data was collected between February 2017- February 2018. A structured interview (M.I.N.I.) was performed on both bipolar group and control group to assess bipolar sign and symptoms, substance use, personality traits. Impulsivity was assessed with Barratt impulsivity Scale. Both hands of subjects were scanned by photocopier and measured with following Digit Ratio Measurement Guide.
Results: Bipolar group has higher impulsivity scores in all impulsivity sub-types compared to control group. Right hand 2D:4D ratio is significantly higher in Bipolar group. There is no difference on left 2D:4D ratio between Bipolar group and Control group. Conclusion: Our findings indicate that right hand 2th- to 4th-finger ratio is significantly higher in Bipolar group."
Females that choose uniformed careers have lower 2D:4D digit ratio
"The cross sectional study included 50 boys and 42 girls enrolled in the uniformed course and other 56 boys and 50 girls of a general course in an upper-secondary School. The lengths of the second (2D) and fourth fingers (4D) of each hand were measured to have the 2D:4D ratio. Height and weight were also recorded. Overall, as well as among the civil course students, males showed significantly lower mean 2D:4D compared to the females. But there was no significant sex difference in digit ratio among the uniformed course students. Besides, the females under uniformed course showed lower 2D:4D than the females in civil course, whereas, the male uniformed students had similar or almost same 2D:4D values with the male civil course students. Increased prenatal testosterone exposure might have a role in determining the choice towards a challenging future occupation and such effect is perhaps more pronounced in women than in males."(Kociuba, Marek, Raja Chakraborty, Zofia Ignasiak, and Sławomir Kozieł. "Is digit ratio (2D: 4D) associated with the choice for the uniformed versus a civil study course by the Polish youth?." Anthropological Review 82, no. 2 (2019): 177-190.)
2D:4D lower in Asian populations than populations more to the West; positive association between agreeableness and 2D:4D
"The study was conducted on 263 young men (age range 17–30 years), including Russians, Armenians, Ob-Ugric and Buryats. The results revealed significant population differences in 2D:4D ratios on both hands, with lowest ratios for Asian sample, increasing in populations to the West. Significant ethnic dif-ferences were found for Openness to New Experience, Conscientious-ness, and Neuroticism. Positive association between 2D:4D ratios on the right hand and Agreeableness in men with no respect to population origin was detected. This relationship becomes stronger, when controlling for aggressiveness."(Rostovtseva, Victoria, Marina Butovskaya, and Ruzan Mkrtchjan. "2d: 4d, Big Fives and Aggression in Young Men of Caucasian, Ural and Asian Origin." (2019).)
Stuttering associated with lower 2D:4D
"Right 2D:4D was significantly lower in stuttering boys than in control boys, and in stuttering girls than control girls. (...) Our results suggest that lower right 2D:4D and DR-L were related to the presence and severity of stuttering in children, i.e. CWS (Children Who Stutter) had lower 2D:4D and DR-L than CWNS (Children Who do Not Stutter)."(YUKSEL, Tugba; SIZER, Esra; DURAK, Hasan. 2D: 4D ratios as an indicator of intrauterine androgen exposure in children who stutter. Early Human Development, 2019, 135: 27-31.)
Lower 2D:4D associated with more physical aggression in boys
"Background(Butovskaya, M., et al. "The association between 2D: 4D ratio and aggression in children and adolescents: Cross-cultural and gender differences." Early Human Development 137 (2019): 104823.)
Two recent meta-analyses have suggested the association between digit ratio (2D:4D) and aggression is weak. This conclusion has been criticised because the meta-analyses conflate forms of aggression that show strong sex differences with those that do not, and most studies have considered post-pubertal participants.
Aims
We test the influence of 2D:4D and ethnicity in the expression of aggression in children and adolescents in four ethnic groups of European and African origin.
Study design
Buss and Perry aggression questionnaire. Direct measurement of the 2nd and 4th digits.
Subjects
1296 children and adolescents from Tanzania and Russia from 4 ethnic groups – Datoga, Meru, Russians, Tatars.
Results
There were ethnic and gender differences in ratings on aggression with boys consistently reporting more physical aggression. In all four samples right 2D:4D was significantly lower in boys, compared to girls. With regard to our total sample of boys, the right 2D:4D was significantly and negatively associated with self-ratings on physical aggression, but no association was found for left 2D:4D. No associations between 2D:4D and physical aggression were found for girls. Hostility was negatively correlated with 2D:4D for boys, and anger was positively correlated with 2D:4D in girls."
Low 2D:4D (weakly) associated with depression in adolescents
"Mean 2D: 4D ratio of the study population was 0.97±0.082. There was no significant difference in mean 2D: 4D ratios (Males=Females) and mean depression scores between sexes (Males >Females). Mean 2D: 4D ratios of the depressed individuals were lower than that of the non-depressed individuals. (p=0.05)There was no significant correlation between 2D: 4D ratio and the depression scores. (...) The present study revealed borderline significance in difference in 2D: 4D ratios between the depressed and non-depressed individuals among the study population."
(Jeevanandam, Saravanakumar, K. Muthu Prathibha, and K. Raman. "Relevance of 2D: 4D Ratio as a Marker of Depression in Adolescents of a South Indian Medical College-A Cross Sectional Study." International Journal of Physiology 7.2 (2019): 80-85.)
(direct link to PDF)
No association between 2D:4D and generosity, bargaining or trust-related behaviours in economic games
Sexual orientation not directly linked to prenatal testosterone levels
"Convergent evidence from experiments of nature and indirect markers of prenatal hormones strongly support a role for prenatal androgens in same-same sexual orientations in women, although this finding is specific to a subset of lesbians who are also gender nonconforming (“butch”). More gender-conforming lesbians (“femmes”) do not show evidence of increased prenatal androgens. The literature has been more mixed for male sexual orientation: some report evidence of low prenatal androgen exposure, while others report evidence of high androgen levels and many other studies find no support for a role of prenatal androgen exposure in the development of androphilia in males. Recent evidence suggests there may be subgroups of gay men who owe their sexual orientation to distinct biodevelopmental mechanisms, which could account for these mixed findings. Although this research is young, it is similar to findings from lesbian populations, because gay men who are more gender nonconforming, and report a preference for receptive anal sex, differ on markers of prenatal development from gay men who are more gender conforming and report a preference for insertive anal sex."(Swift-Gallant, Ashlyn, and S. Marc Breedlove. "Neuroendocrine Influences on Human Sexuality." Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Neuroscience. 2019.)
Correlation between lower digit ratios and psychopathy (primary and secondary) in males
"Using data from an undergraduate sample at a southwestern university, the current study examines the relationship between prenatal testosterone measured by the 2D:4D ratio, and a two-factor model of primary and secondary psychopathy between sex in order to identify potential biological vulnerabilities of later adult psychopathy. Findings are consistent with theory and previous literature, where a significant correlation was identified between the 2D:4D ratio and primary psychopathy for the entire sample, and a significant relationship was identified with the 2D:4D ratio and secondary psychopathy for males while controlling for age, race/ethnicity, parental criminality, and child sexual and physical abuse. (...)
Pearson’s correlation coefficients among the full sample revealed a significantly negative relationship between the 2D:4D ratio and primary psychopathy (r = -0.10, p < .05), whereby individuals with lower ratios were significantly more likely to report primary psychopathy. (...)
The multivariate regression analysis further revealed the importance of the 2D:4D ratio as a significant predictor of secondary psychopathy in males, while controlling for sex, race, age, child sex abuse, child physical abuse, and parental criminality. (...) This indicates that males with more masculinized digit ratios may report greater levels of secondary psychopathy.
For the female sample, the 2D:4D ratio was not significantly correlated with either primary (r = -0.03, p > .05) or secondary (r = 0.07, p > .05) psychopathy. (...) [T]he current study did not find a significant relationship between the 2D:4D ratio and psychopathy for females."(Perez, Katherine L. "The Influence of Prenatal Androgen Exposure on Psychopathy." PhD diss., 2019.)
(direct link to PDF)
Correlation between low 2D:4D digit ratio and alcohol dependence in men
"The mean of right‐hand 2D:4D and left‐hand 2D:4D was lower in men with DSM‐IV alcohol depen-dence than in those without (0.975 vs 0.981,P= .035) and lower in men with moderateto severe (0.974) than in those with mild (0.982,P= .001) or no (0.981,P= .003) DSM‐5 alcohol use disorder. Moreover, mean 2D:4D was lower in those reporting recent useof health services due to substance use problems (0.968 vs 0.981,P= .046). Lowermean 2D:4D correlated with a stronger anticipation to feel high following alcohol con-sumption (total cohort:ρ=−0.033,P= .026) and with a willingness to purchase morehigher‐priced alcoholic drinks (DSM‐IV alcohol dependence subgroup:ρmin=−0.162,P= .002). This is the first population‐based study on young males to demonstrate lower2D:4D in DSM‐IV alcohol dependence, DSM‐5 alcohol use disorder, and the related use of health care services."(Lenz, Bernd, Christiane Mühle, Cohort Study on Substance Use Risk Factors, and Johannes Kornhuber. "Lower digit ratio (2D: 4D) in alcohol dependence: Confirmation and exploratory analysis in a population‐based study of young men." Addiction Biology: e12815.)
No association between 2D:4D and generosity, bargaining or trust-related behaviours in economic games
"Prenatal exposure to sex hormones exerts organizational effects on the brain which have observable behavioural correlates in adult life. There are reasons to expect that social behaviours—fundamental for the evolutionary success of humans—might be related to biological factors such as prenatal sex hormone exposure. Nevertheless, the existing literature is inconclusive as to whether and how prenatal exposure to testosterone and oestrogen, proxied by the second-to-fourth digit ratio (2D : 4D), may predict non-selfish behaviour. Here, we investigate this question using economic experiments with real monetary stakes and analyse five different dimensions of social behaviour in a comparatively large sample of Caucasian participants (n = 560). For both males and females, our results show no robust association between right- or left-hand 2D : 4D and generosity, bargaining or trust-related behaviours. Moreover, no differences in behaviour were found according to sex. We conclude that there is no direct correlation between 2D : 4D and these social behaviours."(Brañas-Garza, Pablo, Antonio M. Espín, Teresa García-Muñoz, and Jaromír Kovářík. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and prosocial behaviour in economic games: no direct correlation with generosity, bargaining or trust-related behaviours." Biology Letters 15, no. 8 (2019): 20190185.)
Higher facial widt-to-height ratio predicts higher social dominance in bonobos of both sexes
"Facial width-to-height ratio (fWHR) is associated with social dominance in human and non-human primates, which may reflect the effects of testosterone on facial morphology and behaviour. Given that testosterone facilitates status-seeking motivation, the association between fWHR and behaviour should be contingent on the relative costs and benefits of particular dominance strategies across species and socioecological contexts. We tested this hypothesis in bonobos (Pan paniscus), who exhibit female dominance and rely on both affiliation and aggression to achieve status. We measured fWHR from facial photographs, affiliative dominance with Assertiveness personality scores and agonistic dominance with behavioural data. Consistent with our hypothesis, agonistic and affiliative dominance predicted fWHR in both sexes independent of age and body weight, supporting the role of status-seeking motivation in producing the link between fWHR and socioecologically relevant dominance behaviour across primates."(Martin, J. S., N. Staes, A. Weiss, J. M. G. Stevens, and A. V. Jaeggi. "Facial width-to-height ratio is associated with agonistic and affiliative dominance in bonobos (Pan paniscus)." Biology Letters 15, no. 8 (2019): 20190232.)
Testosterone supplementation more common in younger males with high 2D:4D and older females with low 2D:4D
"We considered the relationship between prenatal sex steroids, as measured by the digit ratio (2D:4D), and testosterone supplementation (T or Hormone Replacement Therapy with T)
Our sample is drawn from a large online survey (the BBC Study). T supplementation was most common in young males and HRTwT most common in older females.
Males who took T and HRTwT had higher right 2D:4D and higher right-left 2D:4D than their counterparts in the population.
Effects sizes for females were much smaller and in general in the opposite direction to that of males.
We conclude that T and HRTwT tend to be taken by high 2D:4D males, who likely have experienced low T and high estrogen in utero."
(Manning, John, Christian Cook, and Blair Crewther. "Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and testosterone supplementation." Early Human Development 139 (2019): 104843.)
In rats, there is a sex difference where males have less impulse control than females. When just after birth (neonatally) the female rats were treated with testosterone, this sex difference disappeared however, and the impulse control in female rats became like that in male rats. When the female rats were treated with testosterone in puberty or as adults, there was no difference in impulse control. In other words, neonatal testosterone treatment made female rats, for the rest of their lives, behave as male rats as far as impulse control is concerned.
Male sex, autism, gender dysphoria and non-right-handedness caused by high levels of maternal first-trimester intrauterine testosterone
"We present evidence that male sex, autism, gender dysphoria and non-right-handedness share a common cause, viz. high levels of maternal first-trimester intrauterine testosterone. This provides an explanation for the (as yet unexplained) co-occurrences and co-morbidities between these conditions and pathologies."(James, William H., and Victor Grech. "Is exposure to high levels of maternal intrauterine testosterone a causal factor common to male sex, autism, gender dysphoria, and non-right-handedness?." Early Human Development (2019): 104872.)
Testosterone administration linked to functional amygdala lateralization
"As expected, the lateralization index in trans boys shifted towards the right amygdala after testosterone treatment, and the cumulative dose of testosterone treatment correlated significantly with amygdala lateralization after treatment. However, we did not find any significant group differences in lateralization and endogenous testosterone concentrations predicted rightward amygdala lateralization only in the cis boys, but not in cis girls or trans boys. These inconsistencies may be due to sex differences in sensitivity to testosterone or its metabolites, which would be a worthwhile course for future studies."(Beking, T., S. M. Burke, R. H. Geuze, A. S. Staphorsius, J. Bakker, A. G. G. Groothuis, and B. P. C. Kreukels. "Testosterone effects on functional amygdala lateralization: a study in adolescent transgender boys and cisgender boys and girls." Psychoneuroendocrinology (2019): 104461.)
Higher prenatal testosterone associated with premature ejaculation
"Many diseases have been associated with anogenital distance, as an indicator of intrauterine androgen exposure. (...)(Toprak, Tuncay, Aytaç Şahin, Korhan Akgul, Musab Ali Kutluhan, Mehmet Akif Ramazanoglu, Mehmet Yilmaz, Ahmet Sahan, and Ayhan Verit. "The relationship between anogenital distance and lifelong premature ejaculation." Andrology (2019).)
[The] results suggest that longer AGD [AnoGenital Distance] is associated with higher possibility of lifelong premature ejaculation."
Low 2D:4D associated with carelessness, disorganization, revenge planning, and lower openness
"The personality traits, namely openness to new experiences, carelessness, and self‐discipline were significantly differed between lower‐half and higher‐half of 2d:4d by median split. The right hand 2d:4d was positively correlated with open to new experiences and negatively correlated with disorganization, carelessness, and revenge planning. The left hand 2d:4d was positively correlated with aggression. On binary logistic regression, openness was positively associated while carelessness was negatively associated with the right hand 2d:4d and self‐discipline trait was negatively associated with the left hand 2d:4d.(Bagepally, Bhavani S., Joydeep Majumder, and Sanjay M. Kotadiya. "Association between second to fourth digit ratio and personality among Indian men." American Journal of Human Biology.)
Conclusion: This study affirmed the link between 2d:4d and domains of Big Five personality factors among Indian men and inverse relationship between 2d:4d and more “female” hands in the domains of disorganization, carelessness, and revenge planning even in men, emphasizing the effect of prenatal testosterone exposure on human personality."
Neonatal testosterone treatment turns female rat brains into male brains, as far as impulse control is concerned
Personal summary:In rats, there is a sex difference where males have less impulse control than females. When just after birth (neonatally) the female rats were treated with testosterone, this sex difference disappeared however, and the impulse control in female rats became like that in male rats. When the female rats were treated with testosterone in puberty or as adults, there was no difference in impulse control. In other words, neonatal testosterone treatment made female rats, for the rest of their lives, behave as male rats as far as impulse control is concerned.
"The current set of experiments aimed to explore mechanisms underlying sex differences in impulsive behavior in adult rats and sex differences in structures involved in impulse control. Preliminary studies demonstrated sex differences in adult impulsive action and prepubertal impulsive choice with males making more impulsive responses than females. In our studies, neither prepubertal nor adult gonadectomy, and subsequently a loss of gonadal hormone exposure, had any effect on a sex difference in impulsive action. Neonatal exposure of gonadal hormones in females led to a masculinization of impulsive responding in adulthood and eliminated an observed sex difference. This result demonstrates neonatal gonadal hormones to be an organizing mediator of an adult sex difference in impulsive action. No sex difference was seen in adult impulsive choice across hormone conditions. Analysis of myelin protein levels within the orbitofrontal cortex (OFC), a region important for inhibiting impulsive behavior, revealed adult females to exhibit greater levels of myelin basic protein (MBP) than males. This adult sex difference was revealed to be mediated by organizing effects of pubertal gonadal hormone exposure. Inactivation of indirect pathway projecting striatal neurons, neurons important for inhibition of motor output, via designer receptors exclusively activated by designer drug (DREADD) technology, led to a decrease in impulsive responding in adult males and females, eliminating an observed sex difference. Collectively, these results demonstrate for the first time periods of gonadal hormone driven organization of brain morphology and behavior with implications for sex differences in decision making and impulse control."(DARLING, Jeffrey Scott. Mechanisms Underlying Sex Differences In Impulsivity. 2019. PhD Thesis. Tulane University School of Science and Engineering.)
Lower 2D:4D ratio associated with higher sociability, greater personal social capital, larger personal social-network size, liking parties and the company of friends, and isolation intolerance
"Elevated prenatal exposure to testosterone as indicated by a low second-to-fourth finger length (2D:4D) ratio relates to more aggressive/hostile behaviour in men, especially in challenging situations. The personality trait sociability describes how much people enjoy interacting with others. Given its role in approach and avoidance behaviour, sociability could also be influenced by prenatal sex hormones, but studies thus far have been inconclusive. Here, we investigated the association between 2D:4D ratio and the personality trait sociability, complemented by personal social capital and personal social-network size, in a population-based cohort of 4998 men. Lower 2D:4D ratios was significantly correlated with higher sociability, greater personal social capital, and larger personal social-network size. These effects were consistent across both hands individually and their mean value. Furthermore, two factors of sociability, (1) liking parties and the company of friends and (2) isolation intolerance, were significantly correlated with this prenatal testosterone marker. An exploratory analysis revealed no link between the 2D:4D ratio and responses to the aggression personality trait or items related to anti-social-personality disorder. Our data suggest that prenatal androgen exposure organizes the brain with lasting effects on social behaviour."(Buchholz, Verena Nadine, Christiane Mühle, Bernd Lenz, Johannes Kornhuber, and Gerhard Gmel. "Lower digit ratio (2D: 4D) indicative of excess prenatal androgen increases sociability in men and is associated with greater social capital." Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience 13 (2019): 246.)
Low digit ratio associated with faster reaction time
"Our results concluded that there is a negative correlation between the digit ratio and the reaction time. Those individuals who had lower digit ratios had faster reaction times than those who had higher digit ratios."(Khan, Muhammad Zirik, Muhammad Hammad Malik, Roshaan Ahmad, Huma Saeed Khan, Shahid Hasan, and Zeeshan Ashraf Chaudhry. "2D: 4D digit ratios in males and females and its correlation with simple reaction time: A cross sectional Study at Combined Military Hospital (CMH), Lahore, Pakistan." JPMA (2019).)
Low digit ratio associated with more risk-taking
"We examine the relationship between digit length ratios (2D:4D and rel2, the length of the second finger relative to the sum of the lengths of all four fingers) and risk-taking behaviors across five domains: financial, social, recreational, ethical, and health. In a subsample of male Caucasians (ethnically homogeneous), lower rel2 was predictive of greater financial, social, and recreational risk-taking, whereas lower 2D:4D was predictive of greater risk-taking in two domains (social and recreational). In the full male sample (ethnically heterogeneous), the only significant correlation was a negative association between 2D:4D and financial risk. A composite measure of risk-taking across all five domains revealed that both rel2 and 2D:4D were negatively correlated with overall risk-taking in both male subsamples. No significant correlations were found in the female subsamples. Finally, men were more risk-seeking than women across all five contexts."(Stenstrom, Eric, Gad Saad, Marcelo V. Nepomuceno, and Zack Mendenhall. "Testosterone and domain-specific risk: Digit ratios (2D: 4D and rel2) as predictors of recreational, financial, and social risk-taking behaviors." Personality and Individual Differences 51, no. 4 (2011): 412-416.)
High salivary testosterone and cortisol implicated in aggression in children
"The aim of this piece of research was to study the existence of clusters based on anger, empathy and cortisol and testosterone measures associated with aggressive behavior in school-aged children. The sample group comprised 139 eight-year-old children (80 boys and 59 girls). Aggressive behavior was measured using the Direct and Indirect Aggression Scale. Both psychological and biological variables were used to determine psychobiological profiles. The psychological variables considered were trait anger, measured using the State-Trait Anger Expression Inventory for Children and Adolescents, and empathy, measured using the Empathy Quotient-Child Version. Testosterone and cortisol concentrations were measured through saliva samples and analyzed using an ELISA (Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay). A Cluster Analysis revealed three clusters which were clearly different as regards their psychological and biological characteristics. The analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed that the cluster characterized by having higher anger levels, lower empathy levels and higher testosterone and cortisol levels was more aggressive than the other two (p < .0001, η2 = .19). The results indicate that studying psychological and biological variables together may help establish differentiated aggression patterns among children."(Pascual-Sagastizabal, Eider, José Ramón Sánchez-Martín, Oscar Vegas, José Manuel Muñoz, Paloma Braza, María Rosario Carreras, Nora del Puerto-Golzarri, and Aitziber Azurmendi. "Aggressive Behavior in School-aged Children: Clusters based on Anger, Empathy and Testosterone and Cortisol Measures." The Spanish Journal of Psychology 22 (2019).)
High 2D:4D ratio associated with higher agreeableness in men
"According to modern views on human bio-sociality, Big Five personality traits have been shaped in the process of human evolution and their expression is an outcome of the complex interaction of prenatal predispositions and cultural environment. Present study investigates the impact of prenatal androgenization and cultural norms on the personality traits in adult men from four ethnic groups living on the territory of Russian Federation. The study was conducted on 263 young men (age range 17-30 years), including Russians, Armenians, Ob-Ugric and Buryats. The results revealed significant population differences in 2D:4D ratios on both hands, with lowest ratios for Asian sample, increasing in populations to the West. Significant ethnic differences were found for Openness to New Experience, Conscientiousness, and Neuroticism. Positive association between 2D:4D ratios on the right hand and Agreeableness in men with no respect to population origin was detected. This relationship becomes stronger, when controlling for aggressiveness."(Victoria, Rostovtseva, Butovskaya Marina, and Mkrtchjan Ruzan. "2d: 4d, Big Fives and Aggression in Young Men of Caucasian, Ural and Asian Origin." Social Evolution & History 18, no. 1 (2019).)
Low 2D:4D ratio associated with initimate partner violence
"Hormonal and neuropsychological impairment in intimate partner violence (IPV) perpetrators could play a role in domestic violence. For characterizing whether there is a specific psychobiological response to stress, participants who had previously been jailed for IPV and controls were compared for testosterone and cortisol levels, tested for 2D:4D ratio (as an indicator of masculinization), and given several trait questionnaires and neuropsychological tests related to executive functions and theory of mind. (...) The 2D:4D ratio was lower in IPV [intimate partner violence] perpetrators than in controls."(Romero‐Martínez, Ángel, et al. "High testosterone levels and sensitivity to acute stress in perpetrators of domestic violence with low cognitive flexibility and impairments in their emotional decoding process: A preliminary study." Aggressive behavior 39.5 (2013): 355-369.)
Possible association between high testosterone and cognitive inflexibility
"It appears as though hormone imbalances could decrease cognitive flexibility. A study published in 2013 discovered that individuals with low levels of cognitive flexibility also had high testosterone. While high testosterone may not have been the direct cause for their poor cognitive flexibility, it could have been a contributing factor.("7 Ways To Increase Your Cognitive Flexibility", Mental Health Daily, 7/2015 - author known as GLOOM has a bachelor's degree in psychology)
Since there are established associations between stress levels and cognitive flexibility, and also symbiotic relationships between stress and hormones, it is possible to consider that levels of certain hormones could alter both stress and/or cognitive flexibility. The elevations in testosterone may contribute to poorer cognitive flexibility indirectly via effects on the noradrenergic system or via some other mechanism. Perhaps the high testosterone is a direct contributing factor to reduced cognitive flexibility in certain (violence-prone) individuals.
It is unknown specifically which hormone(s) and threshold levels are most likely to decrease cognitive flexibility, but it is still a logical possibility to consider that imbalances may have detrimental effects.
Source: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/23677518"
Low 2D:4D individuals less consientious, less scrupulous, and less apt to assume precautionary behavior in unsafe conditions
"In the sample of [34 healthy cavers, aged between 24 and 71 years] analyzed in this study, the 2D:4D ratio appears related both with the propensity of Risk Taking (DRT - Deliberate Risk Taking) and, particularly, with the aptitude to assume a Precautionary Behavior (PB) in unsafe conditions (...). Moreover, only Conscientiousness, a personological factor evaluated by the BFQ-2, was positively correlated with the 2D:4D (...). The relation between 2D:4D ratio and Conscientiousness, that is the disposition to have an organized rather than spontaneous behavior, could be considered as a significant predictor for a possible attitude for paying more attention in taking appropriate precautions during risky situations. Others studies (Nicholson et al., 2005) confirmed that the Emotional Stability, Agreeableness and Conscientiousness are negatively correlated with all domains of risk-taking, although we found a significant correlation only with the latter (Conscientiousness). In fact, the individuals with lower 2D:4D ratios seem to be less conscientious and scrupulous. This outcome is also coherent with the significant correlation between 2D:4D ratio and RTI [Risk Taking Inventory] factors (PB, DRT) (...). In fact, the correlations between 2D:4D and RTI factors are, respectively, positive with PB and negative with DRT, suggesting that there might be an early organizational effect of sex-steroids on some personality aspects reflecting the choice of the caving than other sports. Therefore, cavers with lower 2D:4D ratios seem to be less careful in taking precautions when they decide to take a risk."
(Rinella, Sergio, Andrea Buscemi, Simona Massimino, Vincenzo Perciavalle, Marta Maria Tortorici, Daria Ghiunè Tomaselli, Valentina Perciavalle, Donatella Di Corrado, and Marinella Coco. "Risk-taking behavior, the second-to-fourth digit ratio and psychological features in a sample of cavers." PeerJ 7 (2019): e8029.)
(...)
Item level analysis revealed significant correlations with the items “interacting with people makes me feel like a part of a large community,” “the people I interact with would be good job references for me” and “if I needed an emergency loan, I know someone I can turn to”
Women with lower 2D:4D ratios are more materialistic
"We explore the relationship between digit ratios (2D:4D) and materialism in women. Digit ratio is a sexually dimorphic trait that is indicative of prenatal testosterone and estrogen exposure. Across two studies, we found that masculinized digit ratios (i.e., exposure to a high testosterone‐to‐estrogen ratio) were associated with the happiness dimension of materialism. Furthermore, we show that women with feminized digit ratios (i.e., high estrogen‐to‐testosterone ratio) who were assigned to an intrasexually competitive condition scored higher on the success dimension of materialism. Overall, these findings suggest that prenatal testosterone exposure promotes stronger beliefs that possessions are an important source of happiness, while prenatal estrogen exposure promotes stronger beliefs that possessions are an important means of signaling success. Thus, prenatal hormone exposure not only influences masculinized and feminized behavior but also shapes consumers’ materialistic beliefs."(Nepomuceno, Marcelo V., Cristina M. de Aguiar Pastore, and Eric Stenstrom. "Prenatal hormones (2D: 4D), intrasexual competition, and materialism in women." Psychology & Marketing.)
Low digit ratio and high circulating testosterone associated with less empathic accuracy (independent of sex)
"Empathy is a cornerstone of human sociality. It has important consequences for our interpersonal rela-tionships and for navigating our social world more generally. Although research has identified numerous psychological factors that can influence empathy, evidence suggests that empathy may also be rooted in our biology and, in particular, the gonadal steroid hormone testosterone. To date, much of the research linking testosterone and empathy has focused on the 2D:4D ratio (i.e., the ratio of the lengths of the index and ring fingers), and the results have been mixed. These mixed results, however, may be due to reliance on self-report measures to assess empathy, which can be vulnerable to self-presentation, as well as social-cultural norms about gender/sex differences in empathy. Moreover, although some have argued that digit ratio is an indicator of prenatal androgen exposure, the evidence for this to date is weak. Here, we aimed to follow up on this prior work, using a naturalistic “empathic accuracy” task in which participants dynamically track, in real-time, the emotional state of targets. We show that both lower digit ratio (Study 1; N = 107) and higher circulating testosterone (Study 2; N = 76) are associated with poorer empathic accuracy performance; critically, these effects hold when controlling for sex/gender. In neither study, however, did we find effects on self-reported empathy. Our results highlight the limitations of self-report measures and support the notion that endogenous testosterone levels as well as 2D:4D ratio are related to key social-cognitive competencies like empathic accuracy."(Nitschke, Jonas P., and Jennifer A. Bartz. "Lower digit ratio and higher endogenous testosterone are associated with lower empathic accuracy." Hormones and behavior (2019): 104648.)
Women with low salivary testosterone levels are better at recognizing their own face
"Capacity to recognize one’s own face (hereinafter referred to as self face) is afundamental component of various domains of social cognition such as empathy inhumans. Previous research has demonstrated that a high level of androgen suppressesempathic behavior and social brain function. Taking these into consideration, wehypothesized that people with high androgen level show reduced response to self face.(Doi, Hirokazu, and Kazuyuki Shinohara. "Low Salivary Testosterone Level Is Associated With Efficient Attention Holding by Self Face in Women." Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience (2019).)
(...)
The analyses revealed that self face holds visuospatial attention more effectively in women with low than high salivary testosterone level, but no such trend was observed in men. This pattern of results indicates that low testosterone level is associated with a pronounced response to self face as we hypothesized and raises the possibility that multiple aspects of self-face processing are under the influence of endocrinological function."
'Hot' executive function and agression associated with higher testosterone/cortisol ratios in saliva, but not with 2D:4D ratios
"‘Cool’ executive functions (EF) refer to logical and strategic cognitive processes such as planning and reasoning, whereas ‘hot’ EF include affect-driven cognitive processes, such as risk-taking in decision making. In the present crosssectional study was investigated whether prisoners perform worse than non-prisoners on measures of hot and cool EF. Subsequent objectives were to determine if performance on tasks of executive functioning was related to measures of (reactive and proactive) aggression within the offender group, and whether testosterone and cortisol influenced the latter relationship. Male prisoners (n = 125) and a non offender control group (n = 32) completed frequently applied measures of hot and cool EF (assessed with the Iowa Gambling task and Wisconsin Card Sorting Task respectively). Aggression characteristics in prisoners were assessed through self-report questionnaires, behavioural observations, and conviction histories. Endogenous testosterone and cortisol levels were obtained through saliva samples, while prenatal testosterone exposure was determined using the finger length of the index and ring fingers (the ‘2D:4D ratio’). The results indicated that prisoners performed significantly worse than non-prisoners on cool EF, and to a lesser extent on hot EF, but no meaningful relationship could be proven between measures of EF and aggression in the offender group. Weak to moderate significant correlations were found between testosterone/cortisol ratios (not prenatal testosterone exposure) and hot EF as well as self-reported aggression."(Kuin, N. C., J. de Vries, E. J. A. Scherder, J. van Pelt, and E. D. M. Masthoff. "Cool and hot executive functions in relation to aggression and testosterone/cortisol ratios in male prisoners." Annals of Behavioral Neuroscience 2, no. 1 (2019): 206-222.)
Low 2D:4D in men associated with higher sociability, bigger personal social capital, and larger personal social networksize - but relations may be of worse quality, and more directed at social status
"Here, we investigated the association between 2D:4D and the personality trait sociability complemented by personal social capital and personal social network size, in a population-based cohort of 4998 men. Lower 2D:4D correlated significantly with higher trait sociability, bigger personal social capital, and larger personal social networksize. These effects were consistent across both hands separately and their mean value. Furthermore, both factors of sociability (1) liking party and company of friends and (2) isolation intolerance, correlated significantly with the prenatal testosterone marker. The exploratory analysis revealed no link between 2D:4D and responses to the personality trait aggression items or items of anti-social-personality disorder.(...)
Item level analysis revealed significant correlations with the items “interacting with people makes me feel like a part of a large community,” “the people I interact with would be good job references for me” and “if I needed an emergency loan, I know someone I can turn to”
(...)
Sociability involves the opioid system of the brain (Knowles et al., 1989; Kalin et al., 1995). (...) During social laughter – related to the sociability factor “party and friends” – endogenous opioids are released, and the depletion during social isolation motivates to seek company – related to the sociability factor “isolation intolerance” (Knowles et al., 1989; Kalin et al., 1995). The minor G-allele of the μ-opioid receptor 1 polymorphism rs1799971 is associated with more pleasure experienced in social situations (Troisi et al., 2011), and mice with this variant have increased motivation for non-aggressive social interactions and show less avoidance after social defeat (Briand et al., 2015). Taken together, prenatal androgen exposure may organize cerebral opioid signaling with behavioral effects on sociability. (...)
In our adult cohort, we did not find any significant correlation between 2D:4D and aggression, which might be explained by the low precision due to the employed self-measurement technique and the fact that correlations of aggression and 2D:4D in adults are mainly found in challenging situations (Hönekopp and Watson, 2011) and in other situations are small at the best (Hönekopp and Watson, 2011).
(...)
Although we found that low 2D:4D in men is associated with higher trait sociability and possibly more social bonds to rely on, there is evidence for a more avoidant attachment style (Del Giudice and Angeleri, 2016) and lesser quality of relationships in people with low 2D:4D (Knickmeyer et al., 2005). Furthermore, intimate partner violence is actually higher in low 2D:4D men (Romero-Martínez et al., 2013). Thus, sociability and a bigger social capital in men do not necessarily mean that intimate or close relationships are better on the long term. They might even be worse as subjects are more directed at social status than intimacy."(Buchholz, Verena N., et al. "Lower Digit Ratio (2D: 4D) Indicative of Excess Prenatal Androgen Is Associated With Increased Sociability and Greater Social Capital." Frontiers in Behavioral Neuroscience (2019).)
Personality trait F: GREGARIOUSNESS/ Liveliness
+ keyed Am the life of the party.
Love large parties.
Joke around a lot.
Enjoy being part of a loud crowd.
Amuse my friends.
Act wild and crazy.
– keyed Seldom joke around.
Don't like crowded events.
Am the last to laugh at a joke.
Dislike loud music.
In the study the max. 2D:4D measured was 1,095, the lowest 0.838 (!), with a mean of 0.957.
("A study on correlation between 2D:4D with personality traits among young adult women", Urboshi Barman and Dr. Pintu Sil, International Journal of Physiology, Nutrition and Physical Education 2019; 4(2): 420-423)
High 2D:4D in young adult Indian women associated with more liveliness
"A total of 73 young adult women college students having the age of 21 to 30 years were selected randomly as subjects for the present study. All the subjects were studying in college level. Criterion measure for this study were length of index finger (2D) and ring finger (4D) of right hand and personality traits. Instruments and tools used to collect data in this study were small sliding breadth caliper (Varner’s scale) and the Cattell’s Sixteen Personality Factor Questionnaire (16PF).Notes:
(...)
Conclusions: From the result of the study it was concluded that digit ratio has significant positive correlation with Personality Trait-F i.e. Liveliness among young adult women. Except this factor there was no correlation between digit ratio with other personality traits among young adult women."
Cattell’s Sixteen Personality Factor Questionnaire (16PF)
https://ipip.ori.org/new16PFKey.htmPersonality trait F: GREGARIOUSNESS/ Liveliness
+ keyed Am the life of the party.
Love large parties.
Joke around a lot.
Enjoy being part of a loud crowd.
Amuse my friends.
Act wild and crazy.
– keyed Seldom joke around.
Don't like crowded events.
Am the last to laugh at a joke.
Dislike loud music.
In the study the max. 2D:4D measured was 1,095, the lowest 0.838 (!), with a mean of 0.957.
("A study on correlation between 2D:4D with personality traits among young adult women", Urboshi Barman and Dr. Pintu Sil, International Journal of Physiology, Nutrition and Physical Education 2019; 4(2): 420-423)
Low 2D:4D ratio not associated with more hunting success in Tanzanian Hadza male hunters; Tanzanian Hasza men have higher 2D:4D ratio than men in most Western populations
"The ratio of index- and ring-finger lengths (2D:4D ratio) is thought to be related to prenatal androgen exposure, and in many, though not all, populations, men have a lower average digit ratio than do women. In many studies an inverse relationship has been observed, among both men and women, between 2D:4D ratio and measures of athletic ability. It has been further suggested that, in hunter-gatherer populations, 2D:4D ratio might also be negatively correlated with hunting ability, itself assumed to be contingent on athleticism. This hypothesis has been tested using endurance running performance among runners from a Western, educated, and industrialized population as a proximate measure of hunting ability. However, it has not previously been tested among actual hunter-gatherers using more ecologically valid measures of hunting ability and success. The current study addresses this question among Tanzanian Hadza hunter-gatherers. I employ a novel method of assessing hunting reputation that, unlike previous methods, allows granular distinctions to be made between hunters at all levels of perceived ability. I find no statistically significant relationship between digit ratio and either hunting reputation or two important hunting skills. I confirm that Hadza men have higher mean 2D:4D ratios than men in many Western populations. I discuss the notion that 2D:4D ratio may be the consequence of an allometric scaling relationship between relative and absolute finger lengths. Although it is difficult to draw clear conclusions from these results, the current study provides no support for the theorized relationship between 2D:4D ratio and hunting skill."(Stibbard-Hawkes, Duncan NE. "No Association between 2D: 4D Ratio and Hunting Success among Hadza Hunters." Human Nature (2019): 1-21.)
Children with narrower faces (low testosterone) more likely to go to higher education levels
"We asked whether height, cranial volume and face width (a testosterone-dependent trait), measured in childhood predict later educational attainment independently of each other, family socioeconomic position (SEP) and sex. (...)(Valge, Markus, Richard Meitern, and Peeter Hõrak. "Morphometric traits predict educational attainment independently of socioeconomic background." BMC Public Health 19, no. 1 (2019): 1696.)
[W]ithin each category of SEP (family socioeconomic position), rural vs urban origin and sex, taller children and those with larger heads and relatively narrower faces were more likely to proceed to secondary and/or tertiary education."
High digit ratio associated with more depression
"Participants with high (feminine) digit ratios, were found to be more depressed (84%) in comparison to those with low (masculine) digit ratios(16%). Using the Z test for single proportions, the difference was found to be highly statistically significant (p<0.001)."(Jeevanandam, Saravanakumar, and K. Muthu Prathibha. "Measurement of 2D: 4D ratios in patients with major depressive disorders: A pilot study." (2019).)
In mice, high prenatal androgen levels causes lifelong changes in GnRH neuron regulation
"These results suggest prenatal androgen exposure programs marked changes in GnRH [gonadotropin-releasing hormone] neuron regulation by homeostatic steroid feedback. PNA [prenatal androgenation] lowers GnRH neuron activity in low-steroid states (before puberty, OVX [ovariectomy]), and renders activity in adulthood dependent upon ongoing exposure to elevated ovarian androgens."(Dulka, Eden A., Laura L. Burger, and Suzanne M. Moenter. "Ovarian androgens maintain high GnRH neuron firing rate in adult prenatally androgenized female mice." Endocrinology (2019).)
Low right 2D:4D associated with schizophrenia
"While the left 2D:4D ratio of the patients with schizophrenia was not different from the controls’, the right 2D:4D ratio was significantly lower. The correlation between finger lengths and the SAPS and SANS scores by gender showed a negative correlation of the left and right 2D:4D ratio with the SANS scores in female patients, while the SANS scores were found to be positively correlated with the right 2D:4D ratio in men."(Dusunen Adam The Journal of Psychiatry and Neurological Sciences 2019;32:295-301, "Investigation of second to fourth finger length ratio (2D:4D) in schizophrenia patients", Faruk Kilic, Umit Isik, Arif Demirdas, Fazilet Ayaz)
Muscular mass, not face width-to-height ratio or 2D:4D associated with aggression
"[O]ur results show that the intergroup conflict scenario promotes cooperation within group members and aggression toward outgroup members. Regarding the hormonal underpinnings of this phenomenon, we find that body musculature is positively associated with aggression and cooperation, but only for cooperation when context (inter-group competition) is taken into account. Finally, we did not find evidence that the formidability of the group affected individual rates of aggression or cooperation, controlling for individual characteristics.(Muñoz-Reyes, J. A., P. Polo, N. Valenzuela, P. Pavez, O. Ramírez-Herrera, O. Figueroa, C. Rodriguez-Sickert, D. Díaz, and M. Pita. "The Male Warrior Hypothesis: Testosterone-related Cooperation and Aggression in the Context of Intergroup Conflict." Scientific Reports 10, no. 1 (2020): 1-12.)
We found that muscular mass was a positive predictor of aggression in both contexts [(intergroup and control)]. However, neither the facial width-to-height ratio nor the index 2D:4D were significant predictors of aggression in the PSAP [Point Subtraction Aggression Paradigm], regardless of the context."
Analysts with masculine faces (high facial WHR) take more risks at work and make higher forecasts of their earnings
"We investigate the relation between underlying risk preferences on analysts’ work‐related decisions. Specifically, we examine whether facial width‐to‐height ratio (fWHR), an innate personal characteristic that has been linked to financial risk tolerance, is associated with analysts’ stock coverage decisions and the boldness of their earnings forecasts and stock recommendations. We find that high‐fWHR analysts cover firms with lower earnings predictability, and issue bolder forecasts and recommendations."(Cleary, S., Jona, J., Lee, G., & Shemesh, J. Underlying risk preferences and analyst risk‐taking behavior. Journal of Business Finance & Accounting.)
Low 2D:4D in transmen, high 2D:4D in transwomen
"Here, we investigated if the 2D:4D digit ratio, a biomarker of prenatal T effects, is related to GD. We first report results from a large Iranian sample, comparing 2D:4D in 104 transwomen and 89 transmen against controls of the same natal sex. We found significantly lower (less masculine) 2D:4D in transwomen compared to control men. We then conducted random-effects meta-analyses of relevant studies including our own (k = 6, N = 925 for transwomen and k = 6, N = 757 for transmen). In line with the hypothesized prenatal T effects, transwomen showed significantly feminized 2D:4D (d ≈ 0.24). Conversely, transmen showed masculinized 2D:4D (d ≈ − 0.28); however, large unaccounted heterogeneity across studies emerged, which makes this effect less meaningful. These findings support the idea that high levels of prenatal T in natal females and low levels in natal males play a part in the etiology of GD. As we discuss, this adds to the evidence demonstrating the convergent validity of 2D:4D as a marker of prenatal T effects."(Sadr, M., Khorashad, B. S., Talaei, A., Fazeli, N., & Hönekopp, J. 2D: 4D Suggests a Role of Prenatal Testosterone in Gender Dysphoria. Archives of Sexual Behavior, 1-12.)
Low 2D:4D associated with more overconfidence
"Using data collected from students from a large university in Brazil, we find that testosterone is positively correlated with higher levels of overconfidence. (...) We also find that the marginal effect of prenatal testosterone on overconfidence is higher for left-handed than for right-handed persons. This means that the role of the prenatal testosterone, as measured by the 2D:4D ratio, on overconfidence is more relevant to left-handed persons."(da Silva, Eduardo Borges, Thiago Christiano Silva, Michel Constantino, Diego Raphael Amancio, and Benjamin Miranda Tabak. "Overconfidence and the 2D: 4D ratio." Journal of Behavioral and Experimental Finance (2020): 100278.)
Indivuduals diagnosed with gender dysphoria and assigned female gender at birth have lower right-hand 2D:4D ratio than female control group
"The 2D:4D digit ratio on the right hand of the AFB-GD [Assigned Female gender at Birt, diagnosed with Gender Dysphoria] group was significantly lower (p=0.028) than that of the female controls, but it did not differ significantly as compared to male controls. (...) The 2D:4D digit ratio on the right hand of the AFB-GD group was significantly lower (p=0.028) than that of the female controls, but it did not differ significantly as compared to male controls."(SAĞLAM, Tarık, Hasan BAKAY, Mehmet Enes GÖKLER, and Şenol TURAN. "2D: 4D Finger Length Ratios in Individuals with Gender Dysphoria.")
Lesbians on average have a smaller 2D:4D digit ratio
"On average, the length of the index finger (digit 2) divided by the length of the ring finger (digit 4) on the right hand, is greater in women than in men. Converging evidence makes it clear that prenatal androgens affect the development of digit ratios in humans and so are likely responsible for this sex difference. Thus, differences in 2D:4D between groups within a sex may be due to average differences between those groups in prenatal androgen exposure. There have been many reports that lesbians, on average, have a smaller (more masculine) digit ratio than straight women, which has been confirmed by metaanalysis. These findings indicate that lesbians were, on average, exposed to greater prenatal androgen than straight women, which further indicates that greater levels of prenatal androgen predispose humans to be attracted to women in adulthood. Nevertheless, these results only apply to group differences between straight women and lesbians; digit ratios cannot be used to classify individual women as gay or straight."(Swift-Gallant, A., Johnson, B. A., Di Rita, V., & Breedlove, S. M. (2020). Through a glass, darkly: Human digit ratios reflect prenatal androgens, imperfectly. Hormones and Behavior, 120, 104686.)
The earlier in male adolescence there is exposure to testosterone (puberty), the more the brain will be male-typical
"Experiments in male rodents demonstrate that sensitivity to the organizational effects of steroid hormones decreases across the pubertal window, with earlier androgen exposure leading to greater masculinization of the brain and behavior. Similarly, some research suggests the timing of peripubertal exposure to sex steroids influences aspects of human psychology, including visuospatial cognition. However, prior studies have been limited by small samples and/or imprecise measures of pubertal timing. We conducted 4 studies to clarify whether the timing of peripubertal hormone exposure predicts performance on male-typed tests of spatial cognition in adulthood.(Shirazi, T. N., Self, H., Cantor, J., Dawood, K., Cárdenas, R., Rosenfield, K., ... & Balasubramanian, R. (2020). Timing of peripubertal steroid exposure predicts visuospatial cognition in men: Evidence from three samples. Hormones and Behavior, 121, 104712.)
(...)
Our results suggest that, for some aspects of neural development, sensitivity to gonadal hormones declines across puberty, with earlier pubertal hormone exposure predicting greater sex-typicality in psychological phenotypes in adulthood."
Low digit ratio associated with more severe Obsessive Compulsive Disorder symptoms in men; high digit ratio associated with higher score on "washing" dimension
"In men with OCD (Obsessive Compulsive Disorder), analyses showed a negative association between 2D:4D and OC symptom severity after controlling for depression. Moreover, a positive relationship between 2D:4D and the symptom dimension “washing” and a negative with “checking” was found in men (...)."(Nitsche, K., Moritz, S., & Jelinek, L. (2020). Prenatal sex hormones and finger length: Digit ratio (2D: 4D) as a biological marker of early developmental processes in patients with obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD). Journal of Obsessive-Compulsive and Related Disorders, 100525.)
Low anogenital distance (low prenatal testosterone) associated with more premature ejaculation
"The goal of essay is to investigate the relation of anogenital distance that predicts prenatal testosterone exposure with premature ejaculation.(Sertkaya, Z., Ertaş, K., & Tokuç, E. (2020). The relationship between premature ejaculation and anogenital distance. Andrologia, e13571.)
(...
In the premature ejaculation group, the distances were found lower (77.46 ± 2.31 and 54.78 ± 2.56 mm) than the control group (81.32 ± 3.11 and 58.16 ± 3.48 mm). There were statistical differences between two groups (p < .001). It was concluded that it is likely to have a negative relationship between anogenital distance and premature ejaculation diagnostic tool score."
In boys, high 2D:4D associated with less word space in copying and higher word formation in dictation
"[A] negative association was observed between right 2D:4D ratio with word space in copying (r=-.23, P<.001) as well as a significant positive association between left 2D:4D ratio with word formation (r=.13, P=.04) in dictation in boys."(Ghorbani, S., Yadolahzadeh, A., Shakki, M., & Noohpisheh, S. (2020). Association Between Second to Fourth Digit Ratio with Handwriting Quality and Speed in Primary School Children. International Journal of Pediatrics.)
High 2D:4D ratio associated with more lifetime success for Mount Everest climbers
"The results indicate not only that the 2D:4D ratio positively predicts lifetime mountaineering success but that the more risk averse open-minded and emotionally stable the climbers, the more active and successful compared to their peers."(Savage, D., Chan, H. F., Moy, N., Schaffner, M., & Torgler, B. (2020). Personality and individual characteristics as indicators of lifetime climbing success among Everest mountaineers. Personality and Individual Differences, 162, 110044.)
Financial analysts with higher fWHR (high testosterone) display opportunistic forecasting behavior
"He et al. (2018) find achievement‐striving analysts exert more effort and exhibit better performance. In this study, we also employ the facial width‐to‐height ratio (fWHR) of analysts as a proxy for achievement drive to re‐examine the performance of achievement‐striving analysts. We argue that achievement‐striving analysts’ superior performance can be alternatively explained by their opportunistic forecast issuances. We find analysts with greater fWHR tend to issue downwardly biased last forecasts before firms’ announcement of actual earnings to curry favour with corporate managers. We also find that analysts with greater fWHR issue more optimistic stock recommendations, especially to underwriting clients of their affiliated brokerage firms, and thus exhibit lower stock picking ability. High‐fWHR analysts are also more likely to issue bold positive forecasts but less likely to convey bold negative news. The market shows its concern regarding such opportunistic forecasting behaviour and penalizes analysts with greater fWHR by reacting less to the forecast revisions they issue."(Chan, K. H., Wang, R. R., & Wang, R. The Macbeth Factor: The Dark Side of Achievement‐driving Analysts. Abacus.)
Extreme digit ratios (highest and lowest) associated with more generosity in non-normative Dictator Game variant
"It is unclear whether DG [Dictator Game] generosity expresses pure altruism or compliance with social norms. Socialization and biological factors may have diverse effects on these two different motivations. In the present study, we aimed at contributing to this discussion. We randomly assigned participants to two independent conditions. In the prescriptiv e norm condition, participants were incentivized to accurately estimate others ́ opinion about the most socially appropriate option in the DG (i.e., the prescriptive norm), and then made their decisions as dictators. Participants in the control conditions made their decisions as dictators without any prior estimation. We found that the normative exercise increased generosity (relative to the control condition) in women but not in men. In a sub-sample, we also measured participants ́ 2D:4D digit ratios as a proxy of a socialization-free sex-dimorphic hormonal influence on behavior. We found no evidence that the normative effect of the estimation exercise was modulated by participants ́ digit ratios. In contrast, generosity in the control condition was higher, the more extreme (highest and lowest) the digit ratios were."
(Senci, C. M., Breccia, F., & Freidin, E. (2020). Attention to Prescriptive Norms Increases Dictator Game Generosity in Women but not Men: Using the 2D: 4D Digit Ratio to Test the Role of Biology. Journal of Psychology, 7, 21.)
Fathers’ facial morphology does not correspond to their parental nurturing qualities
"The Nurturant Fathering Scale ratings did not correspond to any of the facial masculinity measures."
(Saxton, T., Lefevre, C., Newman, A. V., McCarty, K., & Hönekopp, J. (2020). Fathers’ facial morphology does not correspond to their parental nurturing qualities. (preprint))
Androgens and the developing hippocampus
"The hippocampus is central to spatial learning and stress responsiveness, both of which differ in form and function in males versus females, yet precisely how the hippocampus contributes to these sex differences is largely unknown. In reproductively mature individuals, sex differences in the steroid hormone milieu undergirds many sex differences in hippocampal-related endpoints. However, there is also evidence for developmental programming of adult hippocampal function, with a central role for androgens as well as their aromatized byproduct, estrogens. These include sex differences in cell genesis, synapse formation, dendritic arborization, and excitatory/inhibitory balance. Enduring effects of steroid hormone modulation occur during two developmental epochs, the first being the classic perinatal critical period of sexual differentiation of the brain and the other being adolescence and the associated hormonal changes of puberty. The cellular mechanisms by which steroid hormones enduringly modify hippocampal form and function are poorly understood, but we here review what is known and highlight where attention should be focused."
(Androgens and the developing hippocampus, KE Kight, MM McCarthy - Biology of Sex Differences, 2020)
Male-to-female transgenders have higher mean 2D:4D (self-measured)
"Transgendered belief—the conviction that one is the opposite gender to one’s natal gender—may be influenced by prenatal sex steroids. We consider this possibility by examining the relationship between digit ratio (2D:4D—a suggested correlate of fetal testosterone and estrogen), natal gender, felt gender, and transsexual drug therapy in a large online survey (the BBC Internet Study). There were 209,317 participants who reported their gender, their felt gender, and whether they were taking/had taken transsexual drug therapy (male-to-female (MtF) or female-to-male (FtM)). Participants included natal males who felt male (M→M, n = 104,939) and those who felt female (M→F, n = 4760) and natal females who felt female (F→F, n = 84,904) and those who felt male (F→M, n = 4705). Transsexual drug therapy (MtF and FtM) was reported by 830 and 223 participants, respectively. Digit length was determined by direct self-measurement. Mean 2D:4D of M→F and MtF individuals was higher (more “feminized”) than for M→M and natal males, respectively. These effects were found in the total sample, the most numerous ethnic group (Whites) and the two largest national White samples (the UK and the USA). The mean 2D:4D of F→M and FtM participants did not differ from that of F→F and natal females, respectively. We conclude that M→F and MtF individuals may have experienced lower prenatal testosterone and higher estrogen than M→M and natal males, respectively. There was no evidence for an effect of prenatal sex steroids on transgendered belief or transsexualism in F→M and FtM individuals."
(Manning, J. T., Trivers, R., & Fink, B. Digit Ratio (2D: 4D),
Transgendered Belief, and Transsexual Drug Therapy in the BBC Internet
Study. Evolutionary Psychological Science, 1-9.)
No association between 2D:4D digit ratio and criminal behavior in female twins
"[W]e analyze a sample of female dizygotic twin pairs drawn from the National Longitudinal Study of Adolescent to Adult Health and employ a proxy measure of prenatal testosterone based off of the twin testosterone transfer (TTT) hypothesis. The analyses revealed that prenatal testosterone is not associated with nonviolent criminal involvement, violent criminal involvement, psychopathic personality traits, being arrested, and being incarcerated."
(Joyner, B., & Beaver, K. M. Evaluating the Potential Association between Prenatal Exposure to Testosterone and Criminal Involvement and Criminogenic Traits.)
Androgen Deprivation Therapy has long-term effects on cognitive function, depression and quality of life
"Testosterone concentration was positively associated with visuospatial performance across and within the test groups. Patients with long‐term ADT (Androgen Deprivation Therapy) showed an overall decline in cognitive performance. Compared to untreated patients, ADT was also associated with a reduced intergroup bias during socio‐economic decision‐making, which was in line with previous observations in young men suggesting that testosterone may promote ingroup favoritism. Finally, depression scores were increased in ADT, while quality of life was negatively associated with the treatment."
(Sarah Katharina Charlotte, H., Sophie, K., Janna, P., Jasmin, C., Burkhard, B., Thorsten, S., & Esther Kristina, D. The impact of long‐term androgen deprivation therapy on cognitive function and socio‐economic decision‐making in prostate cancer patients. Psycho‐Oncology.)
Males with bipolar disorder have higher 2D:4D ratio
"Patients with bipolar disorder had considerably higher right-hand 2D:4D ratios compared to controls. Both the right and left 2D:4D ratios of male patients were significantly greater than those of males in the control group. Female patients showed no differences in right or left 2D:4D ratio compared to healthy controls.
Conclusion:
These findings suggest that a high 2D:4D digit ratio of right hand is associated with the presence of bipolar disorder in males."
(Faruk, K., Ümit, I., Arif, D., & Hüseyin, E. İ. Investigation of Second to Fourth Finger Length Ratio (2D: 4D) in Patients With Bipolar Disorder. Revista brasileira de psiquiatria (Sao Paulo, Brazil: 1999), S1516-44462020005018202.)
Patients with schizophrenia have greater 2D:4D
"In this study, we enrolled 843 patients with schizophrenia (387 men and 456 women), all of whom met the diagnostic criteria of the Diagnostic and Statistical Manual of Mental Disorders, fourth edition (DSM-IV), and 1050 normal healthy controls (477 men and 573 women). The digit lengths of both hands were measured in all subjects and the 2D:4D ratio was analyzed.
Results
In the healthy controls, the 2D:4D ratio was sexually dimorphic, with a larger value in women than in men. In addition, the 2D:4D ratio in the schizophrenia patients was significantly larger than in the healthy controls. The 2D:4D ratio of the right hand was more sexually dimorphic than the left hand. Furthermore, the difference in 2D:4D ratios between the male patients and male controls was significantly larger than in their female counterparts."
(Han, Y., Deng, W., Lei, W., Lin, Y., Li, Y., Li, M., & Li, T. (2020). Association between the 2D: 4D ratio and schizophrenia. Journal of International Medical Research, 48(6), 0300060520929148.)
Systematic review: fetal testosterone plays plausible role in autistic symptoms
"FT (fetal testosterone) plays a plausible role in driving social and non-social ASD-related cognition (Autism Spectrum Disorder) as well as ASD symptoms across the sexes. FT accounts for gender differences on eye contact frequency and value-laden proposition use and mediates the narrowing of interest toward systems and exerts sex-specific effects on numerical and language abilities, though these studies require independent replication. The role of FT on the differentiation of play is consistently non-significant. Where an effect exists, it is largely dwarfed by the effect of sex and hence it is equivocal that second trimester FT affects play."
(Xiong, H., & Scott, S. (2020). Amniotic testosterone and psychological sex differences: A systematic review of the extreme male brain theory. Developmental Review, 57, 100922.)
Anabolic androgenic steroids associated with impaired Theory of Mind
"Anabolic androgenic steroids are used to improve physical performance or increase lean muscle mass. About one-third of users develop a dependency syndrome, which is characterized by elevated rates of psychopathology, cognitive impairments, and aggressive and antisocial behaviors. The mechanisms behind these intra- and interpersonal problems are not known. (...)Male and female weightlifters who were dependent on anabolic androgenic steroids had impaired ToM (Theory of Mind). Their reduced social cognition may be one contributing factor to the elevated rates of antisocial behavior reported in this population."
(Vaskinn, A., Hauger, L. E., & Bjørnebekk, A. (2020). Theory of mind in users of anabolic androgenic steroids. Psychopharmacology, 1-9.)
2D:4D not a relevant predictor of depression
"The aim of the present study is to test the suggested associations between depression, neuroticism and the 2D:4D ratio in a large, representative sample of over 3,000 German individuals. It was hypothesized that a higher 2D:4D (supposedly representing a more “feminine” prenatal hormone exposure) would positively predict (1) one’s history of depression as well as (2) neuroticism rates and (3) acute depressive symptom scores. Controlling for biological sex, we only found suggestive evidence for linear associations with neuroticism in the case of left hand 2D:4D ratios and the mean 2D:4D of both hands. However, additional analyses indicated that these results may have been spurious due to confounding. Our findings suggest that the 2D:4D ratio is not a relevant predictor of depression, while there was mixed evidence in the case of neuroticism."
(Lautenbacher, L. M., & Neyse, L. (2020). Depression, neuroticism and 2D: 4D ratio: evidence from a large, representative sample. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1-10.)
Exogenous testosterone increases audience effect in healthy males
"Several studies have implicated testosterone in the modulation of altruistic behaviours instrumental to advancing social status. Independent studies have also shown that people tend to behave more altruistically when being watched (i.e. audience effect). To date, little is known about whether testosterone could modulate the audience effect. In the current study, we tested the effect of testosterone on altruistic behaviour using a donation task, wherein participants were asked to either accept or reject a monetary transfer to a charity organization accompanying a personal cost either in the presence or absence of an observer. We administered testosterone gel or placebo to healthy young men (n = 140) in a double-blind, placebo-controlled, mixed design. Our results showed that participants were more likely to accept the monetary transfer to the charity when being observed compared to when they completed the task alone. More importantly, this audience effect was amplified among people receiving testosterone versus placebo. Our findings suggest that testosterone administration increases the audience effect and further buttress the social status hypothesis, according to which testosterone promotes status-seeking behaviour in a context-dependent manner."
(Wu, Y., Zhang, Y., Ou, J., Hu, Y., & Zilioli, S. (2020). Exogenous testosterone increases the audience effect in healthy males: evidence for the social status hypothesis. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 287(1931), 20200976.)
Low digit ratio associated with higher accuracy in soccer passing
"It was observed that the mean score in soccer passing accuracy performance, i.e., LSPT Total performance (TP) of the lower digit ratio, group was a significantly better performer than that of the high digit ratio group. A higher level of fetal testosterone, characterized by lower values of the digit finger ratio (2D:4D), may be associated with a higher performance of soccer passing accuracy in multifaceted aspects including passing, dribbling, controlling, turning, decision-making, and cognition."
(Islam, M. S., & Kundu, B. (2020). Soccer Passing Accuracy Differentiates Between High and Low Digit Ratio (2D: 4D) Soccer Players. American Journal of Sports Science, 8(3), 49-55, doi: 10.11648/j.ajss.20200803.11 )
Mini-review: testosterone increases risk-taking and financial market instability, cortisol has the opposite effect
"As stated, power poses and winning in competitive situations increase testosterone levels and increase risk-taking, and the normal levels of this hormone in the body of people have a positive relationship with level of risk-taking and ambition and change the assessment of risk. Experimental studies of financial markets have shown that increasing the level of this hormone increases the risk of traders, the size and time of retention of price bubbles and, consequently, the instability of markets. Concerning the physiological effects of testosterone on the brain, it has been shown that the activity of some parts of the brain such as OFC and Nucleus Accumbens, which affect risky behaviours, increases under the influence of testosterone, thus increases people risk. Concerning the change of attitudes and behaviours related to risk-taking, testosterone increases people’s level of effort to achieve a higher social status and reduce financial generosity.(...)In general, increasing cortisol reduces people risk-taking, so any factor that increases cortisol levels indirectly reduces people’s risk-taking and changes the market stability. These factors include exposure to Power Poses and exposure to competitive and stress situations. In this regard, stress in both cross-sectional and long-term states has significant effects on increasing cortisol levels and reducing risk. This effect is more in males than females. Gender is a factor that changes the effect of cortisol on people behaviour.Many studies have investigated the combined effects of testosterone and cortisol on risk-taking and it has been found that cortisol plays an important mediating role in the relationship between testosterone and risk-taking. Another important point is that cross-sectional and long-term exposure to cortisol yields different results, so that cross-sectional increase of steroid hormones such as cortisol improves function, while long-term high levels of these hormones cause irrational behaviours in risk-taking area. Concerning the effect of cortisol on the brain, we can also refer to a study that links the level of this hormone with ventral-striatal, a part of the brain that is related to the reward system.Research studies conducted on the effects of hormones on changing the financial behavior have had much strength (...)."
(Beytollahi, A. Chemistry of financial behaviors: a mini review of hormones effect on financial behaviors (2020.)
Meta-review: low 2D:4D associated with ASD, ADHD, and addictions; high 2D:4D with schizophrenia
"We finally included 43 case-control studies which compared the 2D:4D ratio of patients with ASD (16), schizophrenia (8), gender non-conformity (7), addictions (5), ADHD (4), mood disorders (2), and intellectual disability (1) to non-clinical controls. Meta-analyses showed that, overall, psychiatric patients had lower 2D:4D than healthy controls (n = 43, overall sample = 9484, MD = -0.0056, 95% CI from -0.0093 to -0.002, I2 = 74%), with more pronounced differences in the right hand, males, and children. Considering psychiatric disorders individually, significant differences were found in the ASD, ADHD, and addictions groups, in which 2D:4D was significantly lower than healthy controls. Conversely, the right hand of males with schizophrenia showed higher 2D:4D than healthy controls. No other significant differences were detected."
(Fusar-Poli, L., Rodolico, A., Sturiale, S., Carotenuto, B., Natale, A., Arillotta, D., ... & Aguglia, E. Second-to-fourth digit ratio (2D: 4D) in psychiatric disorders: A systematic review of case-control studies., Published online: July 26, 2020)
Oxytocin receptor gene polymorphism (rs53576) and digit ratio associates with aggression: comparison in seven ethnic groups
"The data were collected in Russia and Tanzania and included seven ethnic groups of European, Asian, and African origin. The total sample included 1705 adults (837 males, 868 females). (...)The ethnic group factor was the most significant predictor of ratings on BPAQ [Buss-Perry Aggression Questionnaire] (...).Our data suggest that both oxytocin (OXTR gene polymorphism) and fetal testosterone (2D:4D) may significantly affect emotional (anger) and cognitive (hostility) aggression in humans (...)."
(Butovskaya, M., Rostovtseva, V., Butovskaya, P., Burkova, V., Dronova, D., Filatova, V., ... & Lazebny, O. (2020). Oxytocin receptor gene polymorphism (rs53576) and digit ratio associates with aggression: comparison in seven ethnic groups. Journal of Physiological Anthropology, 39(1), 1-15.)
Aggressive and violent behavior may be associated with life-course exposure to testosterone
"Using indications of testosterone exposure, such as 2D:4D, anogenital distance, muscularity and physical strength, and masculine-feminine appearances and mannerisms, this study tested the hypothesis that life-course exposure to testosterone promotes offending behavior. An online sample of 324 research participants was asked nine questions regarding testosterone-promoted traits. When correlations were performed for the sample as a whole, strong support was found for the hypothesis that exposure to testosterone promotes offending behavior, at least regarding aggressive and violent offenses. Results were weakened when the correlations were performed for males and females separately, especially regarding the two prenatal testosterone exposure variables (i.e., 2D:4D and anogenital distance). However, substantial support for the hypothesis remained for general testosterone-promoted traits (especially muscularity and physical strength for males, and masculine mannerisms for females). Overall, this study supports recent theories that brain exposure to testosterone could be contributing to variations in criminality, especially when violence is involved. The study also suggests that self-reported indicators or testosterone exposure may provide more reliable evidence for testosterone's influence on aggressive and violent behavior than do direct measures of testosterone in the blood or saliva following puberty."
(Hoskin, A. W., & Ellis, L. Androgens and offending behavior: Evidence based on multiple self-reported measures of prenatal and general testosterone exposure. Personality and Individual Differences, 168, 110282.)
Increased facial masculinity associated with increased severity of neurodevelopmental disorders (in men and women)
"Emerging research indicates a strong association between facial morphology and NDDs [ Neurodevelopmental disorders], with evidence suggesting facial masculinity may better capture latent risk factors related to mental disorders. The goal of this study is to compare the capacity of digit ratio and automated facial landmarking to predict NDD diagnosis and genetic risk in a sex-independent manner. (...)Surprisingly, increasing facial masculinity was significantly associated with increasing severity symptoms of NDD (p=0.03 for female and p=0.01 for male). Digit ratio was not associated with NDD severity. On the other hand, genetic analysis showed that increasing masculinity, based on digit ratio and facial landmarks, was associated with increasing polygenic estimates for educational attainment and social dissatisfaction. In addition, the facial masculinity measure specifically associated with polygenic risk for mental disorders while the masculinity measure from digit ratio associated with polygenic estimates for sex hormone traits."
(Huang, Y. Estimating masculinity in neurodevelopment disorders (Doctoral dissertation, University of Iowa).
Increased facial masculinity associated with corporate illegality
"We find a positive relationship between male entrepreneurs’ facial masculinity and new venture corporate illegality. Moreover, we explore the moderating role of individual differences (personal accountability) and social factors (social instability). These factors decrease the likelihood of male entrepreneurs with more facial masculinity to engage in new ventures corporate illegality. Although the facial masculinity of firm leaders may benefit firms by improving firm performance, our results show that there is a need to consider this stably biological trait when predicting unethical behaviors among new ventures."
(Gong, M., Zhang, Z., & Jia, M. (2020). Face Tells the Truth: How Male Entrepreneur's Facial Masculinity Predicts New Venture Corporate Illegality. IEEE Transactions on Engineering Management.)
Overconfidence in men associated with low prenatal testosterone (high 2D4D ratio)
"This paper examines whether foetal testosterone exposure predicts the extent of confidence and over-confidence in own absolute ability in adulthood. To study this question, we elicited incentive-compatible measures of confidence and over-confidence in the lab and correlate them with measures of right hand 2D:4D, used as as a marker for the strength of prenatal testosterone exposure. We provide evidence that men with higher prenatal testosterone exposure (i.e., low 2D:4D ratio) are less likely to set unrealistically high expectations about their own performance. This in turn helps them to gain higher monetary rewards. Men exposed to low prenatal testosterone levels, instead, set unrealistically high expectations which results in self-defeating behavior.(...)To measure confidence and overconfidence, we implemented an incentive-compatible scheme. We introduced participants to an unfamiliar task, and we asked them to report the number of tasks they expected to solve during the experiment. Their total final earnings depended on the precision of their estimate, so subjects had incentives to truthfully report their expected performance (...)."
(Dalton, P. S., & Ghosal, S. (2014). Self-confidence, overconfidence and prenatal testosterone exposure: evidence from the lab.)
No association between serum levels of sex hormones and handedness in humans
"In the largest study of the phenomenon to date (n = 9708), I find that, contrary to the prediction of current theories, the [serum] testosterone and oestradiol levels of left- and mixed-handed individuals are no different to those of right-handers."
(Richardson, T. (2020). No association between sex steroids and handedness in humans.)
Tramadol (an opioid) dependence associated with lower 2D:4D
"Patients with tramadol dependence had lower 2D:4D ratios of their right and left hands when compared with those without tramadol use disorder."
(Khalifa, F. N., Shaheen, S. H., Magdi, M. M., & Basyoni, H. A. (2020). Relationship Between Second-to-Fourth Digit Ratio (as a Biomarker) and Tramadol Dependence. Addictive Disorders & Their Treatment.)
Higher 2D:4D ratio in Male-to-Female transgender compared with male control group
"In our study providing new original data, we found a significantly higher (i.e. feminized) left-hand 2D:4D in the male-to-female transgender (MtF) identity [mean age: 32.3 (18; 61)] than in the male control group [mean age: 34.5 (18; 65)] with a Cohen’s d = 0.271. Concordantly, the meta-analytic results suggest a significant difference in 2D:4D among MtF individuals compared to male controls [g = 0.153; 95% CI (0.063; 0.243)], which was even more pronounced when individuals had been diagnosed by a clinician instead of self-identified as transgender [g = 0.193; 95% CI (0.086; 0.300)].
(...)
In both studies, no significant results were revealed for female-to-male transgender individuals [mean age: 26.1 (18; 53)] versus female controls [mean age: 27.2 (18; 55)]."
(Siegmann, E. M., Müller, T., Dziadeck, I., Mühle, C., Lenz, B., & Kornhuber, J. (2020). Digit ratio (2D: 4D) and transgender identity: new original data and a meta-analysis. Scientific Reports, 10(1), 1-11.)
Girls with increased testosterone production display more male-typical and less female-typical play behavior
"We report findings from two studies investigating possible relations of prenatal androgen exposure to a broad measure of children's gender-typed behavior, as well as specifically to children's toy and playmate preferences. Study 1 investigated these outcomes for 43 girls and 38 boys, aged 4 to 11 years, with congenital adrenal hyperplasia (CAH, a genetic condition causing increased adrenal androgen production beginning prenatally) compared to similarly-aged, unaffected relatives (41 girls, 31 boys). The predicted sex differences were found for all of the outcome measures. Furthermore, girls with CAH showed increased male-typical and decreased female-typical behavior and toy and playmate preferences compared to unaffected girls. Study 2 investigated the relationship of amniotic fluid testosterone to gender-typed behavior and toy and playmate preferences in typically developing children (48 girls, 44 boys) aged 3 to 5 years. Although the predicted sex differences were found for all of the outcome measures, amniotic fluid testosterone was not a significant correlate, in the predicted direction, of any outcome measure for either sex. The results of study 1 provide additional support for an influence of prenatal androgen exposure on children's gender-typed behavior, including toy and playmate preferences. The results of study 2 do not, but amniotic fluid testosterone may be an insufficiently sensitive measure of early androgen exposure. A more sensitive and reliable measure of prenatal androgen exposure may be needed to consistently detect relations to later gender typed behavior in non-clinical populations."
(Spencer, D., Pasterski, V., Neufeld, S. A., Glover, V., O'Connor, T. G., Hindmarsh, P. C., ... & Hines, M. (2020). Prenatal androgen exposure and children's gender-typed behavior and toy and playmate preferences. Hormones and Behavior, 127, 104889.)
Girls that shared the womb with twin boys have lower scores on the Reading the Mind in the Eyes Test (Twin Testosterone Transfer hypothesis)
"This study researched the Twin Testosterone Transfer hypothesis, which predicts that “Female fetuses developing between two males [in the womb] tend to show masculinized ...traits as adults ... due to the transfer of testosterone from male fetuses” (1). This study aimed to de-termine whether opposite-sex twin females had lower socio-cognitive ability as compared to single-ton females through the “Reading the Eyes Through the Mind Test” (RMET) test, which measures a form of social cognition known as “Theory of Mind”. Thus, the study tested the question, “Does the exposure to elevated levels of prenatal testosterone for opposite-sex twin females result in lower Theory of Mind ability?” Ultimately, the results showed that opposite-sex twin females have lower RMET scores, and therefore lower socio-cognitive ability than singleton females, thus validating the Twin Testosterone Transfer hypothesis."
(Kota, R. Teory of Mind Ability in Opposite-Sex Twin Females: The TTT Hypothesis.)
Digit ratio inversely correlates with Systemizing Quotient
"SummaryAbstract
- Digit ratio in both gender reversely correlated with higher score in SQ.There was no correlation between empathizing quotient and digit ratio.
- Cognitive empathy in women correlated with higher digit ratio.
- Digit ratio as a biomarker of prenatal testosterone exposure predict cognitive style.
Digit ratio (2D:4D) is a biomarker for prenatal hormonal exposure. Some studies suggest that prenatal hormonal exposure might influence our cognitive styles characterized by systemizing and empathizing tendencies while other studies do not support these findings. By assessing 156 university students of engineering or mathematics (science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) (female: 63 and male 93) we concluded that digit ratio may support the hypothesis on sexual differences in cognitive styles."
(Rajab, A., Shafizadeh, M., Nakhjavani, M., Vahabie, A. H., Salehi, M., Zarei, S., ... & Mirfazeli, F. S. Digit ratio (2D: 4D) a possible biomarker for cognitive style: A study on Iranian engineering and mathematics university students. Personality and Individual Differences, 172, 110575.)
No association between sex hormone levels at birth or 2D:4D, and economic preferences later in life (n=533)
"Economic preferences may be shaped by exposure to sex hormones around birth. Prior studies of economic preferences and numerous other phenotypic characteristics use digit ratios (2D : 4D), a purported proxy for prenatal testosterone exposure, whose validity has recently been questioned. We use direct measures of neonatal sex hormones (testosterone and oestrogen), measured from umbilical cord blood (n= 200) to investigate their association with later-life economic preferences (risk preferences, competitiveness, time preferences and social preferences) in an Australian cohort (Raine Study Gen2). We find no significant associations between testosterone at birth and preferences,except for competitiveness, where the effect runs opposite to the expected direction. (...) We similarly find no significant associations between 2D : 4D and preferences (n= 533 ...). (...) Our results suggest a reinterpretation of prior findings relating 2D : 4D to economic preferences, and highlight the importance of future large-sample studies that permit detection of small effects.(...)[P]reviously detected small effects come from low-powered studies, which could lead to overestimation of effect sizes (type-M errors). It is important to note that many studies also report null effects. Parslow et al. [22] survey the literature on 2D : 4D and risk attitudes and find that based on 18 papers, 93 out of 109 reported tests are nonsignificant. Studies with larger samples will have more power to make more definitive claims. It is also interesting to establish relevant moderators for the effects of hormones on outcome measures (...). For example, one moderator could be levels of adult sex hormones."
(van Leeuwen, B., Smeets, P., Bovet, J., Nave, G., Stieglitz, J., & Whitehouse, A. (2020). Do sex hormones at birth predict later-life economic preferences? Evidence from a pregnancy birth cohort study. Proceedings of the Royal Society B, 287(1941), 20201756.)
Longitudinal pregnance cohort study finds no evidence that early childhood digit ratio was associated with child sex, anogenital distance or gender-typical play behavior
"[W]e measured right-hand digit ratio in 4-year-old children participating in The Infant Development and the Environment Study, a multicenter longitudinal cohort study that has been following mother–child dyads since the first trimester of pregnancy (n = 321). We assessed sex differences in digit ratio and fit multivariable linear regression models to examine digit ratio in relation to: (1) child sex; (2) maternal sex steroid hormone concentrations in early pregnancy; (3) newborn anogenital distance, another proposed measure of sensitivity to prenatal androgens; and (4) gender-typical play behavior as measured by the Preschool Activities Inventory (PSAI) at age 4. We observed no sex difference in digit ratio; the mean 2D:4D was 0.97 ± 0.05 mm in both sexes. Furthermore, digit ratio was not associated with maternal sex steroid concentrations in early pregnancy, anogenital distance in either sex, or PSAI scores in either sex in covariate-adjusted models. In conclusion, we observed no evidence that early childhood digit ratio was associated with child sex or hormone-sensitive measures in this cohort."
(Barrett, E., Thurston, S. W., Harrington, D., Bush, N. R., Sathyanarayana, S., Nguyen, R., ... & Swan, S. (2020). Digit ratio, a proposed marker of the prenatal hormone environment, is not associated with prenatal sex steroids, anogenital distance, or gender-typed play behavior in preschool age children. Journal of Developmental Origins of Health and Disease, 1-10.)
Unclear association between prenatal sex hormones (measured in amniotic fluid) and hand preference
"We examine correlations betweentestosterone and estradiol measured from second trimester amniotic fluid and hand preference (Dutch language version of the Edinburgh Handedness Inventory) and hand skill asymmetry (pegboard task) measuredat 15 years of age.Prenatal sex hormoneexposurewasnot associated with the direction of hand preferencein either males or females.However, in females, high levels of prenatal testosterone were associated with weaker lateralisation of hand skill, and high levels of prenatal estradiol were associatedwith weaker hand preference. In addition, high levels of prenatal testosterone were associated with increasedtask duration (i.e.,slow hand speed) for therightand lefthandsofmales.Thepattern of results observed here is not entirely consistent with any of the main theories linking sex hormones with handedness, suggesting that an association between these variables may be more complex than initially thought."
(Richards, G., Beking, T., Kreukels, B. P., Geuze, R. H., Beaton, A. A., & Groothuis, T. An examination of the influence of prenatal sex hormones on handedness: Literature review and amniotic fluid data.)
Association between low 2D:4D, intrasexual competitiveness, and conspicuous consumption
"In Study 1, we find that masculinized digit ratios (an indicator of high prenatal testosterone exposure) are only related to greater conspicuous consumption preferences for men that score high on an intrasexual competitiveness trait measure. In Study 2, we find that masculinized digit ratios are associated with greater conspicuous consumption preferences, but only among men who are primed with an intrasexual competition recall task. Finally, the purpose of Study 3 was to test if similar effects held when measuring circulating testosterone. We show that baseline levels of circulating testosterone are associated with greater conspicuous consumption preferences, but only after men are primed with intrasexual competition. Overall, we identify intrasexual competition as a crucial precondition for relationships between testosterone (prenatal and circulating) and conspicuous consumption to emerge. We argue that men with masculinized digit ratios and men with high circulating testosterone may be more likely to choose conspicuous products as a status‐signaling strategy in the mating market if they are inherently intrasexually competitive or when they encounter an intrasexually competitive situation."
(Nepomuceno, M. V., & Stenstrom, E. Consumption on steroids: The effect of testosterone on preferences for conspicuous consumption and the moderating role of intrasexual competition. Journal of Behavioral Decision Making.)
No significant association between 2D:4D and self-employment in large study
"In this preregistered study, we replicate the 2D:4D results on a sample of more than 2100 adults from the German Socioeconomic Panel- Innovation Sample (SOEP- IS). We find no statistically significant associations between 2D:4D and self- employment."
(Fossen, F. M., Neyse, L., Johannesson, M., & Dreber, A. 2D: 4D and Self-Employment: A Preregistered Replication Study in a Large General Population Sample. Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice, 1042258720985478.)
Estrogens have a significant influence on brain and behavior
"Estrogens are not only crucial in sexual maturation and reproduction but are also highly involved in a wide range of brain functions, such as cognition, memory, neurodevelopment, and neuroplasticity. To add more, the recent findings of its neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory effects have grown interested in investigating its potential therapeutic use to psychiatric disorders."
(Hwang, W. J., Lee, T. Y., Kim, N. S., & Kwon, J. S. (2021). The Role of Estrogen Receptors and Their Signaling across Psychiatric Disorders. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 22(1), 373.)
More masculine voices associated with avoidant attachment
"We explored the association between sexually dimorphic vocal properties [voice pitch, measured by fundamental frequency (F0) and F0 variation, the within-subject SD in F0 across the utterance (F0-SD)], attachment styles, and communication patterns among Chinese heterosexuals in romantic relationships. Men’s F0-SD positively correlates with constructive communication pattern and negatively correlates with avoidant attachment style. No significant correlations are found for women. These findings suggest that men with masculine voices are more avoidantly attached, using avoidant communications."
(Zhang, J., & Zheng, L. (2020). Masculine Voices Predict Attachment Style and Relationship Communication Patterns in Romantic Relationships. Journal of Sex & Marital Therapy, 1-8.)
Modest Exercise-Induced Increases in Testosterone Concentration Are Not Associated with Mating Strategy Change in Healthy Young Men
"Research has demonstrated that increases in testosterone (T) concentration can affect the expression of behaviours and preferences that are typical of high mating effort. However, little research has considered whether such T increases affect mating strategy more generally and whether this is achievable using a physical intervention. In this pilot study, we examined whether exercise-induced changes in T covary with, or predict, changes in male mating strategy. Healthy young men (N = 94) completed a measure of short- and long-term relationship preference, before and after a series of short cycling sprints. Salivary T was measured pre- and post-exercise, along with salivary cortisol (C), which is known to moderate some behavioural effects of T. A significant group-level increase in T was observed, though this was smaller than anticipated (~ 10%, d = 0.27) with substantial intragroup variation. No group-level change in C or mating preferences emerged. Testosterone change did not significantly predict a change in short- or long-term mating preference from baseline, even with inclusion of C change as a moderator. The current findings suggest that modest exercise-induced increases in T concentration have little impact on male mating strategies. Pharmaceutical interventions, which produce larger and more consistent T increases, may be required to observe mating strategy change."
(Thomas, A. G., Kowal, M., Sorokowski, P., Żelaźniewicz, A., Nowak, J., Orzechowski, S., & Crewther, B. T. Modest Exercise-Induced Increases in Testosterone Concentration Are Not Associated with Mating Strategy Change in Healthy Young Men. Evolutionary Psychological Science, 1-6.)
Hungry consumers with low (vs. high) digit ratios make more masculine food choices.
"Highlights
- Hungry consumers with low (vs. high) digit ratios make more masculine food choices.
- This association applies to both men and women.
- Digit ratios do not predict the gender image of satiated consumers’ food choices.
This study investigated the link between individuals’ 2D:4D digit ratio (a biomarker associated with prenatal testosterone exposure) and their inclination to make masculine food choices. Furthermore, the study investigated whether this potential association would be moderated by consumers’ levels of hunger (vs. satiation). Participants (N = 216; 50% female) made a set of binary food choices between items pretested to be perceived as masculine (vs. feminine) and indicated the lengths of their second (2D) and fourth (4D) digits (i.e., index and ring fingers), which were used to calculate their 2D:4D digit ratios. Additionally, they self-reported their self-perceived gender identity and their subjective sense of hunger (vs. satiation). The results revealed that low, masculine digit ratios had no overall impact on masculine food choices. However, among both men and women and irrespective of their self-perceived gender identity, hungry (vs. satiated) participants with masculine digit ratios made more masculine food choices. Thus, although digit ratios did not act as an antecedent of participants’ general tendency of making masculine food choices, the specific visceral state of hunger interacted with participants’ digit ratios to predict choices of masculine foods. Taken together, these findings expand the knowledge on when and how prenatal exposure to sex hormones may affect consumers’ food preferences and in which specific way a particular visceral state may moderate the link between biologically based factors and consumer choice."
(Otterbring, T., Elbæk, C. T., & Lu, C. (2020). Masculine (Low) Digit Ratios Predict Masculine Food Choices in Hungry Consumers. Food Quality and Preference, 104168.)
Children of high income parents have low 2D:4D, and vice versa
"This study examined the association of income inequality (operationalized as relative parental income) and children’s 2D:4D. Participants self-measured finger lengths (2D=index finger, and 4D=ring finger) in a large online survey conducted in July 2005 (the BBC Internet Study) and reported their parents’ income. Children of parents of above-average income had low 2D:4D (high prenatal testosterone, low prenatal oestrogen) while the children of parents of below-average income had high 2D:4D (low prenatal testosterone, high prenatal oestrogen). The effects were significant in the total sample, present among Whites (the largest group in the sample), in the two largest national samples (UK and USA) and were greater for males than females."
(Manning, J. T., Fink, B., Mason, L., & Trivers, R. (2021). Parental income inequality and children’s digit ratio (2D: 4D): a ‘Trivers-Willard’effect on prenatal androgenization?. Journal of Biosocial Science, 1-9.)
"Unusual" 2D:4D (high in boys and low in girls) associated with body dissatisfaction in adolescents
"We found that the 2D:4D was positively related to appearance dissatisfaction in boys with first spermatorrhea, which means that low prenatal androgen exposure may increase boys' dissatisfaction with their appearance. In girls with breast development being lower than Tanner stage II, their 2D:4D was negatively related to their body shape dissatisfaction, which means that high prenatal androgen exposure may increase girls' dissatisfaction with their body shape."
(Yuan, Y., Hu, J., Sun, L., Zhang, Y., Wang, B., Yao, R., ... & Fu, L. (2021). An association between body image dissatisfaction and digit ratio among Chinese children and adolescents. Scientific reports, 11(1), 1-8.)
High 2D:4D in women associated with emotional stability and impulse control
"We found a positive association between 2D:4D and emotional stability, as well as with its subdimensions emotion control and impulse control. This association could be quadratic and nonlinear. However, no association was found with the other four dimensions. We also measured anxiety, depression and global life satisfaction, variables related to neuroticism. We observed that emotional stability is positively associated to social desirability and global life satisfaction, and negatively related to anxiety and depression. On the other hand, we did not find any association between 2D:4D and anxiety, depression, and global life satisfaction."
(Rodríguez-Ramos, Á., Moriana, J. A., García-Torres, F., & Ruiz-Rubio, M. (2021). Emotional stability is related to 2D: 4D and social desirability in women: Possible implications on subjective well-being and psychopathology. Plos one, 16(3), e0248368.)
In female nonhuman primates, 2D:4D is associated with mating system

Fig. 5: Association between intersexual dominance patterns and female primate
mean 2D:4D (group mean ± standard deviation). Number of species (S) and
number of individuals (I) included in each category are given below the
intersexual dominance pattern.

Fig. 4: Relationship between female primate mean 2D:4D ratio (group mean ±
standard deviation) and mating system subcategory. Number of species (S)
and number of individuals (I) included in each category are given below
the mating system subcategory.
(Howlett, C., & Wheeler, B. C. (2021). Prenatal Androgen Effects as a Proximate Mechanism Underpinning Variation in Social Behavior Among Female Nonhuman Primates. International Journal of Primatology, 1-29.)
Higher 2D:4D correlates with greater gender nonconformity among gay men, and with higher "bottoms" tendency (compared to "tops")
"First, we replicated the finding that gay men with a receptive ASR (Anal Sex Role) preference (bottoms) report greater gender nonconformity (GNC) compared to gay men with an insertive ASR preference (tops). We then found that Tops have a lower (male-typical) average right-hand digit ratio than Bottoms, and that among all gay men the right-hand 2D:4D correlated with GNC, indicating that a higher (female-typical) 2D:4D is associated with increased GNC."
(Swift-Gallant, A., Di Rita, V., Major, C. A., Breedlove, C. J., Jordan, C. L., & Breedlove, S. M. (2021). Differences in digit ratios between gay men who prefer receptive versus insertive sex roles indicate a role for prenatal androgen. Scientific Reports, 11(1), 1-8.)
Male combat athletes have lower 2D:4D than controls; judo, wrestling and kick-boxing have slightly lower 2D:4D than karate and taekwondo
"The 2D:4D ratio of combat athletes was significantly lower than that of the controls. Moreover, a lower 2D:4D ratio was found among wrestlers, judo athletes and kickboxers than in the control group, and a higher 2D:4D ratio was found, but with borderline significance, among karate and taekwondo athletes. Moreover, multivariate analysis adjusted for age showed that judo, Olympic wrestling and kick-boxing athletes combined had 2D:4D ratios significantly lower (by 0.035 on average) than those of the rest of the subjects and that karate and taekwondo athletes together had 2D:4D ratios significantly higher (by 0.014 on average) than those of the rest of the subjects."
(Adamczyk, J. G., Safranow, K., Gajewski, A. K., Boguszewski, D., Sozański, H., Sołtyszewski, I., ... & Żekanowski, C. (2021). The Second-to-Fourth Digit (2D: 4D) Ratio of Male Combat Athletes is Associated with the Choice of Sport. Journal of Human Kinetics, 78.)
No difference in 2D:4D ratio between persons with Autism Spectrum Disorder and neurotypicals
"Here, we present a cross-sectional study of 2D:4D in boys (N = 91, mean age 7.63) and adults (N = 36 mean age 22.8) with ASD as well as neurotypical students, 506 participants in total. Digit ratio was assessed by taking measurements from digital scans, compared between groups and correlated with the autism quotient. (...) No significant differences were found in digit ratios between neurotypical subjects and those with ASD nor was there a relationship with the reported autistic traits, which leads us to question the reliability of 2D:4D and its relation to ASD."
(Kyselicová, K., Belica, I., Vidošovičová, M., Janšáková, K., Neščáková, E., Špajdel, M., ... & Ostatníková, D. (2021). Autism spectrum disorder and new perspectives on the reliability of second to fourth digit ratio. Developmental Psychobiology.)
Does testosterone influence success? Not much, research suggests
"Similar to previous studies the research found that men with higher testosterone had higher household income, lived in less deprived areas, and were more likely to have a university degree and a skilled job. In women, higher testosterone was linked to lower socioeconomic position, including lower household income, living in a more deprived area, and lower chance of having a university degree. Consistent with previous evidence, higher testosterone was associated with better health for men and poorer health for women, and greater risk-taking behaviour for men.
In contrast, there was little evidence that [...] testosterone-linked genetic variants were associated with any outcome for men or women. The research team concluded that there is little evidence that testosterone meaningfully affected socioeconomic position, health, or risk-taking in men or women. The study suggests that -- despite the mythology surrounding testosterone -- it might be much less important than previously claimed.[...] There is evidence from experiments that testosterone can make a person more assertive or more likely to take risks -- traits which can be rewarded in the labour market, for instance during wage negotiations. But there are other explanations. For example, a link between higher testosterone and success might simply reflect an influence of good health on both. Alternatively, socioeconomic circumstances could affect testosterone levels. A person's perception of their own success could influence testosterone: in studies of sports matches, testosterone has been found to rise in the winner compared to the loser."
(University of Bristol. "Does testosterone influence success? Not much, research suggests." ScienceDaily. ScienceDaily, 28 July 2021.)
Marginally significant negative correlation between 2D:4D digit ratio and overclaiming
"[W]e asked individuals to rate their confidence in solving a set of different math problems and their familiarity with a set of math concepts. Some of these concepts were nonexistent, thereby allowing participants to overclaim knowledge.
[...] To test who tends to overclaim knowledge, we examined whether overclaiming was related to any of the potential antecedents [...]. The positive influence of height, b = 0.02, SE = 0.01, t(163) = 1.94, p = .054, and the negative influence of digit ratio, b = −1.65, SE = 0.98, t(163) = −1.68, p = .095, were marginally significant."
(Keller, L., Bieleke, M., Koppe, K. M., & Gollwitzer, P. M. (2021). Overclaiming is not related to dark triad personality traits or stated and revealed risk preferences. Plos one, 16(8), e0255207.)
Note to self: http://bernhardfink.com/?page_id=382 -> start at Millet 2006





